Lecture 1 Introduction to biological membranes: membrane lipids
advertisement

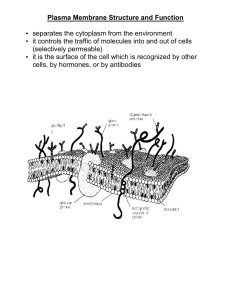
IBBT622D: Special Topics in Membrane Biology Cell Membranes, Membrane Proteins, Membrane-­‐Mediated Biological Processes, & Membrane Biotechnology Lecture 1.1. Tales of Two Molecules: Membrane Lipids & Membrane Proteins Cells are Rich in Membranes EM images of plasma cells High S/V ratio Assuming the cell is a sphere of 10 µm radius Total [lipid] in PM ≈ Total [lipid] ≈ Protein crowding Membranes in eukaryoIc cells. Cell membranes: Early Models Cell membranes: Fluid Mosaic Model Singer & Nicholson (1972) Science 175:720-731 • The lipid bilayer as a permeability barrier and host for membrane proteins • Membrane proteins: free homogeneity), but no (Brownian, lateral Cell membranes: Present Models Engelman, Nature (2005), 438, 578; Kusumi et al., Ann Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct (2005), 34, 351 Jacobson et al, Nature Cell Biol (2007), 9, 7 Updated version: lipid-protein composite i) Membrane proteins: ii) Thickness: iii) Transbilayer iv) Lateral v) Curvature: P/L = (w/w) for erythrocyte plasma membrane for mitochondria for myelin Heterogeneity in cell membranes Curvatures in cell membranes McMahon & Gallop, Nature (2005), 438, 590 Tales of Two Molecules: Membrane Proteins & Lipids Membrane Proteins 1) % x 25,000 2) % of current drug targets (GPCRs & channels) 3) Diverse functions: receptors, channels, transporters, & etc 4) An active area of structural biology What about lipids? “Nucleic acids and proteins are informational macromolecules…On the other hand, polysaccharides and lipids do not have information-carrying function” Lehninger, A. L. Biochemistry: the molecular basis of cell structure and function (1975). 1) Serve as permeability barriers and provide ( ) 2) Solubilize 3) Then, why there are so many lipids? 4) 5) Lecture 1.2. Structures & ProperIes of Membrane Lipids Major Lipids of Cell Membranes Glycerophospholipids Sphingophospholipids sn-1 sn-2 SAPC Sterols SM Glyco(sphingo)lipids Cholesterol GM1 ganglioside Lipid Headgroup & Hydrophobic Tails in the Bilayer 30Å Hydrocarbon region (core) O OO O O P O O O O NH3 + OO O O P O O 15Å Interfacial region O NH3 + 15Å (Glycero)Phospholipid Structures: Headgroup Two neutral PLs: PC vs. PE PC PE O O O O O O OO O P O O O O P O O O N + + NH3 (Glycero)Phospholipid Structures: Acyl chains Saturated vs. Unsaturated FA ω-­‐3 vs. ω-­‐6 PUFA Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) arachidonic acid (AA) Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) 1-­‐Stearoyl-­‐2-­‐docosahexaenoyl-­‐sn-­‐glycero-­‐3-­‐phospho-­‐ L-­‐serine (SDPS) (Brain) 1-­‐Stearoyl-­‐2-­‐arachidonoyl-­‐sn-­‐glycero-­‐3-­‐ [phosphoinositol-­‐4,5-­‐bisphosphate] (PIP2) Structure of sphingolipids Sphingomyelin SOPC Structures of sterols cholesterols Cholesterol esters Oxyterols Phase TransiIon of Lipids Lβ Pβ Lα or Ld Lipids FA composiIon Tm (oC) PalmiJc acid 16:0 63.1 Oleic acid 18:1 13.4 Arachidonic acid 20:4 -­‐49.5 POPC 16:0 18:1 -­‐2 DMPC 14:0 23 DPPC 16:0 41 Effect of Cholesterol on Membrane Structure SL-Chol & SL-SL Association: Lipid Rafts? PC SM Cholesterol Polymorphic phases of phospholipids: Polymorphism The molecular shape hypothesis of amphiphiles Molecular Shape O O OO O O OO O O P O O O O O P O O N + PC Cylinder + NH3 PE Cone O OH O O P O O N + LysoPC Inverted Cone Physical States Micelles bilayer Lamellar Inverted (reverse) micelles HII HI Membrane Curvature Molecular Shape O O O O OO O O P O O O O O P O O Curvature OO N + + NH3 O OH O O P O O N + Differential Effects of Lipids on Membrane Curvature Membrane Curvature & Membrane Remodeling Fusion Fission