Naming Acids and Bases Worksheet/Notes Name: Chemistry 2
advertisement

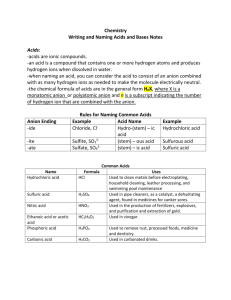
Naming Acids and Bases Worksheet/Notes Chemistry 2 points Name: ________________________ Date: _____________ Hour: _______ According to Arrhenius’s definition, all acids produce H+ ions when dissolved in water. Because of this, the formulas of most acids contain hydrogen. In fact, most acid formulas start with hydrogen. How can you tell just by looking at a chemical’s formula that it is an acid? __________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ There are two types of acids: binary acids and oxyacids. Binary acids contain only two elements, hydrogen and a nonmetal. Another way to think about it is that the anion of a binary acid contains a nonmetal. Oxyacids contain more than two elements, and two of the elements are hydrogen and oxygen. Another way to think about oxyacids is that they contain hydrogen and a polyatomic anion. What is a binary acid? ____________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Below are the formulas of several acids. Circle the binary acids. Put a square around the oxyacids. HCl H2S HMnO4 NaOH HC2H3O2 HF Sr(OH)2 H2SO4 H3N Binary acids have a very simple naming system. Every binary acid’s name starts with hydroand ends with -ic acid. The rest of the name is taken from the anion’s name. For example, HBr’s anion is Br- or bromide. The -ide is dropped, so just the brom- part is used. The name of HBr is then hydrobromic acid. Fill in the following chart about naming binary acids (may need ion chart): Formula Anion Name of Anion Name of Acid ex> HBr Br- bromide hydrobromic acid HF H3N HI How can the formula of a binary acid be written from just the name? Remember that all charges in a compound must add to zero. If you know the charge of the anion, you can add enough positive hydrogen ions to the beginning of the compound’s formula to cancel out the negatives. For example, in hydrobromic acid, I know the bromide ion is present. Bromide has a 1- charge. I would need one hydrogen ion to cancel out the bromide, so the formula for hydrobromic acid is HBr. What would the formulas of the following acids be (may need ion chart)? (a) hydrochloric acid: __________________ (c) hydroselenic acid: _______________ (b) hydrophosphoric acid: _______________ (d) hydrosulfuric acid: ______________ Oxyacids are slightly more difficult to name. Their names are still based on the anion present, though. If an anion starts with per- and ends in -ate, the acid will be per-______-ic acid. If the anion just ends in -ate (and DOESN’T start with per-), the acid will be ______-ic acid. If the anion starts with hypo- and ends in -ite, the acid will be hypo-______-ous acid. If the anion ends in -ite and DOESN’T start with hypo-, the acid will be ______-ous acid. For example, the acid HMnO4 contains the MnO4- (permanganate) ion. It is called permanganic acid; the -ate part of the ion’s name is dropped (just like the -ide part was dropped with binary acids). Some students find putting these naming rules in a chart form helpful: Name of ion Name of acid per_____ate per_____ic acid _____ate _____ic acid _____ite _____ous acid hypo_____ite hypo_____ous acid _____ide hydro_____ic acid Fill in the following chart about naming oxyacids (using your ion chart): Formula Anion Name of Anion Name of Acid ex> HMnO4 MnO4- permanganate permanganic acid HNO3 H2SO3 HClO HIO4 Writing the formula of an oxyacid from its name is very similar to the process with binary acids. In the name, look for any prefixes and suffixes. If you see per-, you know the anion will start with per-; if you see -ic acid and no per-, you know the anion will end in -ate. Go to the ion chart and find the anion. Add enough hydrogens to the front of the formula to cancel out the negative charge. For example, the formula for chromic acid would be H2CrO4. How did I do that? I saw -ic acid on the end and knew the ion would end in -ate. I looked on my ion chart for something with chromium in it that ended in -ate and found chromate, CrO42-. Since it had a 2- charge, I added 2 H+ ions to the front, making H2CrO4. Write the formula of the following acids (using your ion chart): (a) carbonic acid _______________ (d) oxalic acid _______________ (b) nitrous acid _______________ (e) acetic acid _______________ (f) phosphoric acid _______________ (c) hypochlorous acid _______________