Physical Science Test #1 – Review Guide Properties of Matter

Properties of Matter
Physical Science Test #1 – Review Guide
1.
A characteristic of matter that can be measured or observed is a _________________________ of that matter.
2.
_______________________________ properties describe the object, while _______________________________ properties describe the material the object is made of.
3.
Decide if each property below is extensive (E) or intensive (I) a.
_____ A rock has a mass of 45 grams. b.
_____ The rock has a volume of 12.3 mL. c.
_____ The rock has a density of 3.66 g/mL. d.
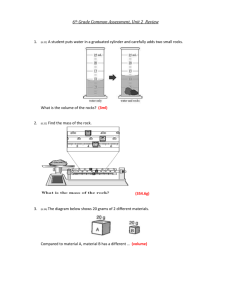
_____ The rock is not flammable. e.
_____ The rock is shaped like a peanut. f.
_____ The rock reacts with acid, creating bubbles.
4.
Properties that describe how matter interacts with other matter are __________________________ properties.
5.
Decide if each property below is a physical (P) or chemical (C) property. a.
_____ The rock is easily crushed with a hammer. b.
_____ The rock has a mass of 45 grams. c.
_____ The rock reacts with acid, creating bubbles. d.
_____ The rock is not flammable. e.
_____ The rock has a density of 3.66 g/mL f.
_____ The rock sinks in water. g.
_____ The rock is a solid. h.
_____ The rock is pink. i.
_____ The rock tastes salty (hint: you really can’t tell this unless you let it “react” with your tastebuds).
Measuring Properties – Mass, Volume, Density
6.
A measure of the amount of matter in an object is the ______________________ of the object.
7.
A measure of the amount of space occupied by that object is the ______________________ of the object.
8.
A calculated property that uses both of the last two properties is ______________________ and describes how close together or far apart the atoms in that object are.
9.
What unit did you measure mass in for your lab?
10.
Name an object with a mass of about 1 gram.
11.
What unit did you measure volume in for your lab?
12.
Describe in detail, how you could measure the volume of your hand by water displacement.
(Remember to name all the equipment you used, and describe the steps you would take to use it.)
13.
How would you measure and calculate the volume of a box of tissues?
14.
What two things do you need to know to calculate density?
15.
If 45 mL of a liquid has a mass of 40 grams, what would its density be?
16.
Would that liquid sink in or float on water? How do you know?
Classification of Matter
17.
Matter is anything that has ___________________ and has ____________________.
18.
A ____________________________________ is made up of one kind of atom or molecule (like elements and compounds).
19.
A __________________________ is made up of more than one kind of atom or molecule in the same place at the same time (but those atoms or molecules are NOT bonded together).
20.
________________________________ are made up of one kind of atom; for example: carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, sodium, or chlorine.
21.
________________________________ are made up of atoms of more than one kind that are BONDED together; for example: water, carbon dioxide, sodium chloride, glucose.
22.
Decide if each formula below is for an Element (E) or Compound (C) a.
______ K b.
______ KCl c.
______ MnO
2
d.
______ N
2 e.
______ SiO
2 f.
______ Xe g.
______ Co h.
______ CO
23.
Name the 5 types of mixtures that we talked about in class, and list an example of each type.
Type of Mixture Example
Dalton’s Atomic Theory and Parts of an Atom
24.
List the 5 ideas that make up Dalton’s Atomic Theory
25.
Fill in the blanks in the chart below about the parts of an Atom
Particle Name Location Mass
Proton In the nucleus
Neutron 1 amu
Charge
−
Answers:
1.
Property
2.
Extensive, Intensive
3.
a.E b.E c.I d.I e.E f.I
4.
chemical
5.
a.P b.P c.C d.C e.P f.P g.P h.P i.C
6.
mass
7.
volume
8.
density
9.
grams (g)
10.
(a plain M&M, a large paper clip, etc.)
11.
Milliliters (mL)
12.
Fill an overflow can with water and let it set until it stops dripping. Hold a graduated cylinder under the spout. Slowly sink your hand into the water in the can, catching the water in the graduated cylinder as it flows out of the spout. Measure the water displaced in the cylinder.
13.
Use a ruler to measure the length and width and height of the box. Multiply these three numbers to get the volume of the box.
14.
Mass and volume
15.
D=m÷V D = 40g÷45mL D= 0.89 g/mL
16.
It would float in water because its density is less than 1 g/mL.
17.
Mass, volume
18.
Pure substance
19.
Mixture
20.
Elements
21.
Compounds
22.
a.E b.C c.C d.E e.C f.E g.E h.C (one capital letter=element, more than one capital letter=compound)
23.
suspensions(muddy water), colloids(smoke,milk,fog), solutions(salt water, Kool-Aid), alloys(steel, brass), emulsions(oil and vinegar salad dressing, greasy dishwater)
24.
all matter is made of atoms, atoms of the same element are alike, atoms of different elements are different, atoms combine (bond) to make compounds, atoms cannot be created or destroyed by chemical or physical reactions
25.
(only the blanks, from left to right, top to bottom) 1amu, +, In the nucleus, none(neutral), Electron, Around the nucleus, 0 amu