Science 9 Chapter 9 Electrostatics: PRE
advertisement

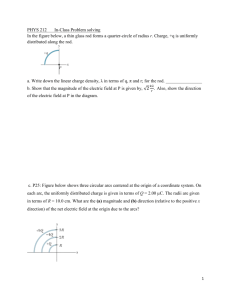
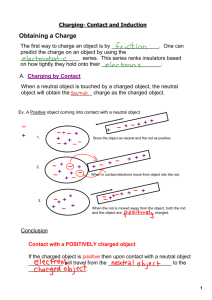
Science 9 Chapter 9 Electrostatics: PRE-TEST Page 1 of 2 Part I. Mulitple Choice. (1 point each) You may want to refer to the table of the Electrostatic Series on the last page. 1. When a plastic comb is rubbed with a piece of animal fur and is brought close to a fine stream of water from a tap, the stream of water will be (a) attracted to the comb. (b) repelled by the comb. (c) unaffected by the comb. (d) first attracted, then repelled. 2. Hypothesize (pretend) that you and a partner each have an inflated balloon attached to a string. If you each rubbed your balloon against your hair and then, holding them by their strings, brought them close together, they would: (a) move toward each other. (b) move away from each other. (c) bob rapidly back and forth. (d) be unaffected by each other. 3. When a negative ion is formed, an atom must (a) lose an electron. (b) lose a proton. (c) gain an electron. 4. (d) gain a proton. The nucleus of an atom contains (a) positive electrons and neutral neutrons. (b) positive protons and neutral neutrons. (d) negative electrons and negative neutrons. (c) negative electrons and neutral neutrons. 5. To reduce the problem of "fly-away" hair on entering a building from outside on a winter day, your neck scarf should be made of (a) acrylic (plastic). (b) wool. (c) cotton. (d) silk. 6. To protect against a fire, copper used for wiring in a house would best be covered with (a) aluminum. (b) glass. (c) rubber. (d) nickel. 7. When a positive rod is used to induce a charge on a neutral object, there is a movement of: (a) -ve charge from the rod into the object. (b) +ve charge from the rod into the object. (c) -ve charge in the object toward the rod. (d) +ve charge in the object toward the rod. 8. When a negative rod is used to induce a charge on a neutral object, there is a movement of: (a) -ve charge from the rod into the object. (b) +ve charge from the rod into the object. (c) -ve charge in the object toward the rod. (d) -ve charge in the object away from the rod. Part II. Shorter Answer. (1 point each) Answer each of the following in complete sentences or paragraphs. Please notice there is a table of the Electrostatic Series on the last page. Do any 8 of questions 1 - 11. Choose only 8. Only do 8 – your choice of 8. 1. Explain why it is easier to conduct a test to determine and know for sure that two objects have like charges than it is to determine and know for sure that they have opposite charges. 2. Beatnik was working at a cash register with rubber soled shoes. He noticed his feet got sore standing on the hard tile floor of the store, so he brought a cloth mat from home, made of cotton. It was softer to stand on and made his feet less tired, but he noticed he often got a shock when touching articles made of metal, and even shocked the customers sometimes when reaching for their money or credit card. He noticed Prissy working at the cash register next to him wore the very same shoes, and was also standing on a mat, but she had no trouble with static building up. (a) What material must her mat have been made of? (b) Explain the difference why Beatnik was getting static buildup, while Prissy wasn’t. 3. If you wanted to polish a glass mirror and you wanted to reduce the chances of building up a static charge on the mirror that would attract dust, should you use a cloth made of cotton, silk, or wool? Explain/justify your answer. 4. To neutralize a charged pith-ball electroscope, all you have to do is hold it gently with your fingertips for a very short time. Explain what happens (i.e. discuss what is charged, oppositely charged, and/or neutral, and what happens to the charge(s) when you neutralize by touch). 5. Using the electrostatic series as a reference (see last page of test), predict the relative strength of static electric charges transferred to polyethylene (plastic) when rubbed by a cloth made of wool compared with a cloth made of cotton. Justify your prediction. 6. Briefly explain why you might receive an electric shock after sliding across a plastic or vinyl seat cover in a car, but you do not receive a shock if lightning strikes the outside of your car when the windows are closed. 7. Cat's fur will lose electrons to copper more readily than it will lose electrons to ebonite. Since this is true, explain why you cannot use fur to build up a static electric charge on a copper rod held in your hand but you can use the fur to build up a static electric charge on an ebonite rod held in your hand. 8. Explain why a static discharging wick on an aircraft must end in a point and not a blunt end. 9. Would static electric charges tend to build up more quickly on an airplane flying below the clouds or on one flying above the clouds? Explain your answer. 10. Suppose that you had to conduct a series of demonstrations to successfully show the effects of static electricity to obtain credit for your science course. If you could schedule the demonstrations at any time in the school year, what time of year would you choose to have the best chances of success? Explain your choice. 11. A worker at a gas station complains of having to clean up gasoline spills from the asphalt around the pumps. The employee thinks it would be much easier to keep the area clean if the asphalt and the area around the gas pumps were both painted with a heavy coating of plastic. The worker approaches you as the manager of the station with the idea. Explain to the employee why the suggestion is unacceptable. Science 9 Chapter 9 Electrostatics: PRE-TEST Page 2 of 2 Part III. Longer Answer. (3 points each). Answer in complete sentences/paragraphs, or draw as instructed. 1. (a) List the materials needed to create a negatively charged rod by friction. (b) Explain how to use the negatively charged object from part a to charge the pith-balls negatively. (c) Explain in detail how to confirm the pith-balls are negatively charged, and not positively charged or neutral. 2. (a) If a wool cloth were rubbed on a plastic rod, draw a diagram to show what charges are located where – draw the wool cloth and plastic rod, showing the location of the charge buildups. (b) Draw a “before and after” diagram to show how a negatively charged balloon is beside a neutral wall, and then ends up being attracted to the wall. (c) Draw 2 diagrams – one showing a negative rod held near a small stream of water coming out of a tap, and the other showing a positive rod held near a small stream of water coming out of a tap. 3. Suppose you were painting a room while wearing wool socks. (a) What would happen if you shuffled your feet back and forth over a cotton drop-cloth and then reached for a metal doorknob? (b) Explain whether any charge you build up on yourself would be positive or negative (hint: electrostatic series). (c) Would using a polyethylene (plastic) drop cloth instead of a cotton one, while you were wearing wool socks, improve the situation described or make it worse? Explain. 4. (a) Copy and complete the following “before and after” diagrams by drawing charged particles to show why a neutral dust particle is attracted to the screen of an operating television set, which emits small negative charges. (The “a” diagram is neutral dust particle approaching screen; the “b” diagram is after it has approached.) (b) Draw a charged object touching what started out as a neutral object, showing the location of charges properly. (c) From part b, after the charged object was touched to the neutral object for a while, it was pulled away and then brought back toward the object. Draw what would happen, showing the charges. 5. Draw and label diagrams to show the distribution of charges in (a) an uncharged metal-leaf electroscope. (b) a positively charged metal-leaf electroscope. (c) a negatively charged metal-leaf electroscope. 6. Predict and explain what will happen to a negatively charged metal-leaf electroscope when it is approached by (a) a neutral object. (b) a positively charged object. (c) a negatively charged object. 7. There is a lightning (and thunder) storm occurring, but it hasn’t started to rain yet. Some kids are outside playing. Jilpoke is rubbing a balloon (made of rubber) against her hair. Buster is rubbing his dog with a silk scarf. (a) List the 4 items “balloon”, “Jilpoke’s hair”, “dog”, “scarf”, and beside each item indicate +, -, or neutral. (b) List the 4 items in the order of which is most likely to be hit by lightning (most likely first, least likely last). (c) In fact, the lightning did strike but it hit a tall metal tower nearly a kilometre away. At the time of the strike, what charge would have been on the metal tower? Explain your answer. Material acetate glass wool cat's fur, human hair calcium, magnesium, lead silk aluminum, zinc cotton paraffin wax ebonite polyethylene (plastic) carbon, copper, nickel rubber sulphur platinum, gold ELECTROSTATIC SERIES Hold on Electrons weak Increasing tendency to gain electrons Strong