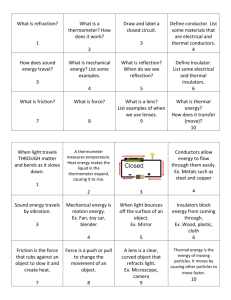
Specific heat capacity - Physikalisch
advertisement

Temperature Measurements According to the International Temperature Scale of 1990 and Associated Uncertainties PB Steffen Rudtsch 7.42 230th PTB Seminar Conductivity and Salinity Content Thermodynamic temperatures and temperature scales Definition of the unit kelvin ITS-90 and fixed points Resistance thermometry Error sources and uncertainty budget Steffen Rudtsch Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Definition of a Temperature Scale Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Problem: Temperature is an intensive thermodynamic property (value does not depend on the amount of the substance). How can we define a universal temperature scale whose properties does not depend on specific substances or thermometers? W. Thomson (later Lord Kelvin, 1848) Absolute zero and a second fixed point Efficiency of reversible Carnot-cycle T1=T2(1-η) Measurement of Thermodynamic Temperatures Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Gas thermometer: equation of state of an ideal gas T pV k = 1,38065·10-23 J/K p V = N k T bzw. = Ttpw ptpwVtpw (Boltzmann constant) V=const., p→0 N: Number of atoms Dielectric constant gas thermometer (DCGT) N ε = ε0+α0 V ε − ε0 p= kT α0 α0- atomic polarisibility T p ε tpw − ε 0 = ⋅ Ttpw ptpw ε − ε 0 Measurement of the change in capacitance of a gas-filled capacitor after evacuation Thermodynamic Temperatures Basis: Fundamental Physical Laws Gas Properties: - Equation of state of an ideal gas - Dielectric constant - Speed of sound - Spectral-line Doppler broadening Electron Gas: - Thermal noise Photons: - Total radiation of a blackbody - Spectral emission of a blackbody Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt International Temperature Scale of 1990 Definition of the unit kelvin Fixed points of the ITS-90 Interpolation instruments Interpolation equations Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Definition of the Kelvin and Triple Point of Water Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt The kelvin, unit of thermodynamic temperature, is the fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water. 13. CGPM (1967): Metrologia, 4 (1968), 147 Ttpw = 273,16 K (Definition) ptpw = 611,66 Pa Fixed Points of the ITS-90 T90 ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← ← Cu (fp) Au (fp) Ag (fp) Al (fp) Zn (fp) Sn (fp) In (fp) Ga (mp) H2O (tp) Hg (tp) Ar (tp) O2 (tp) Ne (tp) e-H2 (vp) e-H2 (vp) e-H2 (tp) 4 He (vp) 1084,62 °C 1064,62 °C 961,78 °C 660,323 °C 419,527 °C 231,928 °C 156,5985 °C 29,7646 °C 273,16 K 234,3156 K 83,8058 K 54,3584 K 24,5561 K ≈ 20,3 K ≈ 17,0 K 13,8033 K 4,2221 K ∆ Tth.dyn /mK ∆ TITS-90 /mK 60 50 40 25 13 5 3 1 0 1,5 1,5 1 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,5 0,3 15 10 3 2 1 1 1 0,25 0,1 0,25 0,3 0,4 0,4 0,4 0,4 0,4 0,1 Fixed-Point Measurement Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt ITS-90: Interpolation Instruments and Equations 0,65 K to 5,0 K: Vapour pressure 3He und 4He 3,0 K to 24,5561 K: Gasthermometer (He) T90 / K = A0 + 9 ∑ i= 1 Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt ln( p ) / Pa - B Ai C i a + bp + cp 2 T90 = 1 + Bx ( T90 ) N / V T90 / K - 754,15 13,8033 K bis 961,78 °C: Wr ( T90 ) = C0 + ∑ Ci 481 Standard Platinum Resistance Thermometer i = 1 9 above 961,78 °C: Radiation Thermometer ( ) Lλ ( T90 ) exp c2 [ λ T90 ( X ) ] − 1 = −1 Lλ [T90 ( X ) ] exp c2 [ λ T90 ] − 1 −1 ( ) X: Ag, Au, Cu; c2=0,014388 m·K i Standard Platinum Resistance Thermometer Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Platinum wire of highest purity Induction free winding, Free of mechanical stress Specific gas filling in order to control oxidation Special heat treatment.... Resistance Thermometers IPRT Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt SPRT Reference Function for Resistance Thermometers Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt [ Callendar-van Dusen: R( t ) = R (0 ° C) ⋅ 1 + At + Bt 2 + C (t − 100)t 3 ITS-90 (SPRT calibration) Determination of resistance ratio W is required. - extrapolated to I = 0 mA Reference Function 0 °C to 961.78 °C: ] RSPRT ( Fixed Point ) R W = = RSPRT (TPW) R0 T90 / K - 754,15 Wr ( T90 ) = C0 + ∑ Ci 481 i= 1 9 i Wr (T90 ) − 2,64 T90 / K = 273,15 + D0 + ∑ Di 1,64 i=1 9 i Calibration of Platinum Resistance Thermometers Purity of the Platinum: Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt W(29,7646 °C) ≥ 1,1807 W(-38,8344 °C) ≤ 0,844235 Calibration Certificate for SPRTs: Deviation Function (deviation from reference function) W (T90 ) − Wr (T90 ) = a (W − 1) + b(W − 1) + 2 5 ∑ c [ ln(W )] i= 1 i 2+ i SPRT-Calibration: Uncertainty Budget Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Quantity u(TGa) mK u(TIn) mK u(TSn) mK u(TZn) mK u(TAl) mK u(TAg) mK Impurities 0,06 0,25 0,31 0,40 0,65 Hydrost. Pressure 0,01 0,02 0,02 0,54 0,54 0,02 0,02 0,08 Gas Pressure 0,01 0,10 0,08 0,12 0,30 0,30 Standard Resistor 0,01 0,01 0,01 0,01 0,01 0,01 Bridge 0,02 0,11 0,12 0,16 0,20 0,25 TPW 0,08 0,09 0,11 0,15 0,20 0,28 Self-heating 0,05 0,15 0,20 0,20 0,20 0,20 Immersion 0,01 0,20 0,10 0,10 0,10 0,10 Fixed Point Value 0,03 0,06 0,06 0,06 0,20 0,20 Type B (combined) 0,12 0,40 0,43 0,64 0,65 0,87 Type A 0,05 0,20 0,15 0,15 0,30 0,30 Standard Uncertainty 0,13 0,45 0,45 0,66 0,66 0,71 0,92 PTB-Budget Resistance Measurement Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Resistance Thermometer typically between 25 Ω and 10 kΩ 1. Digital Multimeter (8 ½ digits) U(T) ≈5 mK Problems: - Stability reference resistor - Self-heating - Offset thermovoltages 2. Potentiometric Method U(T) < 1 mK High-precision standard resistor RS including its temperature control different currents are used d RS < 2 ⋅ 10 − 7 a − 1 d t rel I ≈ 1 mA RS RT Resistance Measurement RT Highest level with < 2 ⋅ 10 − 8 U commercial equipment RS Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt U(T) < 5 µK AC-Bridges Inductive voltage divider (ratio transformer) typically 25 Hz or 30 Hz Manufacturer: Automatic Systems Laboratories (ASL) “DC”-Bridges Current comparator (current reversal necessary) Manufacturer: Measurement International, Guildline Measurement Errors and Corrections 1. Self Heating of the Resistance Thermometer Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Typical Measurement Errors Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt 1. Stability of the Thermometer - resistance might be changed by mechanical shock or oxidation (SPRT, IPRT) - Drift even after careful heat treatment (Thermistors) 6. Hysteresis up to ∆T = 500 mK at IPRTs (not at SPRTs) - depend on thermal “history” of the IPRT - caused by thermal expansion of the ceramic substrate / powder Thermal Measurement Errors Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt A contact thermometer measures only its own temperature. 4. Change of the temperature of the investigated object - heat conduction - heat storage/capacity 5. Heat dissipation and thermal coupling i.e. thermometer and object have different temperatures 6. Dynamic behavior and thermal lag 7. Radiation errors Heat Dissipation and Thermal Coupling TFurnace TEnvironment Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Dynamic Behavior and Thermal Lag Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt T2 T1 The dynamic behavior depend on the construction of the thermometer and the thermal coupling between object and thermometer. Example of an Uncertainty Budget Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Calibration of a resistance thermometer in a liquid bath (more details in DKD-R 5-1) tx = tN + δtKal + δtDrift + cRδRR + δtBr + δtWaN + δtWAP + δtEWN + δtHom + δtStab tx: ITS-90 temperature of the resistance thermometer to be calibrated tN: Mean of the temperature of the SPRT (reference) δtKal: Correction based on the SPRT calibration δtDrift: Correction based on the drift of the SPRT cRδRR: Correction based on the calibration of the standard resistor c R: Sensitivity of the bridge δtBr: Correction based on the bridge calibration δtWaN: Correction based on heat conduction of the SPRT δtEWN: Correction based on self-heating of the SPRT δtWAP: Correction based on heat conduction of the resistance thermometer δtHom: Correction based on the in-homogeneity of the bath Example of an Uncertainty Budget Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Calibration of a resistance thermometer in a liquid bath (more details in DKD-R 5-1) Quantity Estimate Standard uncertainty Probability distribution Sensitivity coefficient Uncertainty contribution tN Temperature SPRT 180.234 °C 1.2 mK Normal 1 1.2 mK δtKal Calibration SPRT 0K 7.5 mK Normal 1 7.5 mK δtDrift Drift SPRTRef 0K 3.5 mK Rectang. 1 3.5 mK δRR Standard Resistor 0Ω 0.07 mΩ Normal 10 K/Ω 0.7 mK δtBr Bridge 0K 1.5 mK Normal 1 1.5 mK δtWaN Heat cond. SPRT 0K 1.2 mK Rectang. 1 1.2 mK δtHom Homogeneity bath 0K 4.6 mK Rectang. 1 4.6 mK δtStab Stability bath 0K 3.5 mK Rectang. 1 3.5 mK tx Temperature 180,234 °C 10 mK Summary Definition of the unit kelvin International Temperature Scale of 1990 Sensors and instruments Sources of uncertainty Uncertainty budget Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt