Language development
advertisement

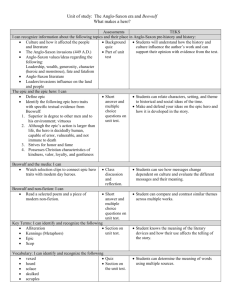
British Literature Exam Review Kirk How to study for the Semester Exam (Oh! Mrs. Kirk is soooo nice!) -Glance over/re-read all works that we have read -Look at all notes and handouts -add info on review sheet to help remember and better understand -study with a partner (he/she may remember something you do not/ vice versa) -Think about how literature reflects time period (culture, values, beliefs, etc.) ________________________________________________________________________ Language development Celtics Romans- as early as 55 BC Germanic Tribes: 450 AD (Angles, Saxons, and Jutes (Frisians) *English is largely a Germanic language Vikings or Danes French influence 1066: William the Conqueror and feudalism Alfred the Great: Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, Exeter Book, and Translations (aid of monks) ________________________________________________________________________ Periods of study Anglo-Saxon Period 449-1066 Beowulf Epic translated by monks who added Christian elements to pagan tale Partially explains Beowulf’s characteristics- boastful (not modest) Self-importance and desire for fame partly due to brevity of life Valhalla and Warrior Code Riddles Scops were professional orators, story-tellers, etc. Oral literature Elements of Anglo-Saxon poetry? Caesura Kennings Alliteration Rhythmic/musical No definite end rhyme Common themes: Elegiac Heroic or Fame * People did appreciate beauty as supported through the artifacts of Sutton Hoo. Climate was harsh, affecting life expectancy. Through the literature of the period, what else can we tell about the Anglo-Saxons? Entertainment important?-Mead Halls (setting of Beowulf). Riddles show much of what was emphasized as well: (remember riddle contest in class) Agrarian: plow (farming elements), images related to the sea (anchor and iceberg), cup of mead. British Literature Exam Review Kirk Medieval Period (1066-1485) Geoffrey Chaucer is the Father of English Literature- Why? (look at p.86) The Canterbury Tales offering best cross-section of 14th century England Satire- Targets? By what means? light humor, sarcasm, and irony Irony: Situational, Dramatic, and Verbal To what degree? Subtle, Harsh, and Biting Devices used? Satire of Estates, Physiognomy, Heroic Couplet form Frame Story- set up within the prologue Remember: April, 29 pilgrims, supposedly leaving on Pilgrimage to see the shrine of Thomas BecketWhy? Host’s role in the plan to tell the tales Each tale is another opportunity for satire Condescension towards women Questions the validity of marriage Questions the credibility of the Church Mock Epic (trivial matters on a heroic scale) Which characters did Chaucer admire? Ballads (look at p. 164-177) A narrative song told of common folk-legend and folklore “Barbara Allen” “Lord Randall” “Get Up and Bar the Door” Refrain, repetition, quatrains Romances and Arthurian Legends Sir Gawain and the Green Knight The Knight and Code of Chivalry ( look at p. 140) Romantic hero compared and contrasted to Anglo-Saxon warrior Adventurous tales of courage and loyalty, honor king and women Devout and mannerly Hundred Year’ War, the Black Death, and the Peasants’ Revolt British Literature Exam Review Kirk The Renaissance 1485-1660 Drama, sonnets, and the King James Translation of the Bible (1611) overshadow this period. Time of Shakespeare, Spenser, and Sir Philip Sydney! 17th century poetry! > John Donne and Metaphysical poetry, the Cavalier writers, and John Milton What is a tragedy? (look at Macbeth handout) tragic flaw, learns a lesson about self, climax is in Act III, etc. Macbeth: themes? literary devices: hyperbole, dramatic irony, microcosm Hamlet: introspective- “To be or not to be …” Compare/Contrast Shakespeare’s Hamlet and Macbeth What are the two sonnet types and how can we tell the difference? English/Shakespeare: Three quatrains (four line stanzas) with a rhyming couplet ababcdcdefefgg Italian/Petrarchian: Octave- poses problem or question (abba abba- varies) Sestet- resolution or answer (cde cde or cdccdc) Sonnet Cycle or Sequence: several sonnets on same theme/topic (Book of sonnets) Spenser’s Amoretti “little love poems” (p.206) Sydney’s Astrophel and Stella Common theme of man’s desire for a beautiful woman Apostrophe? Addressing an object “O Moon” and “Come, Sleep…” Pastoral poetry? shepherds and rustic life are idealized Companion poems: showing two attitudes toward life and love Christopher Marlowe’s “The Passionate Shepherd” Sir Walter Raleigh’s “The Nymph’s Reply” 23rd Psalm- “The Lord is my shepherd…”Extended Metaphor (look at p. 246) Prodigal Son Parable- moral message or lesson (look at p. 248) Ben Johnson’s elegies (p.404) and the “Tribe of Ben” or “Sons of Ben”= Cavalier poets Cavalier poets: Richard Lovelace (Stone walls do not a prison make/Nor iron bars a cage) Robert Herrick “To the Virgins, to Make Much of Time” John Donne (p.390)- The Metaphysical Poet- “No man is an island; every man is a piece of the continent, a part of the main.” “Ask not for whom the bell tolls; it tolls for thee.” “Death, thou shalt die.” Holy sonnets and meditations Andrew Marvell’s “To His Coy Mistress”-heavy carpe diem poem AND metaphysical John Milton- Puritan writer- sonnets and Paradise Lost (epic), blindness and purpose for writing “To justify…” Remember his famous quotes: “Better to reign in Hell, than serve in Heaven,” and “The mind is its own place, and in itself can make a Heaven of Hell, a Hell of Heaven.” British Literature Exam Review Kirk Vocabulary : Define and/or list examples. Example: microcosm: philosophical term used to explain the relationship between man and the universe; “small world” representing “larger world.” For instance, Shakespeare employs a microcosm of depicting the state of the entire nation by portraying the lords from all parts of Scotland leaving the banquet hall in a disorderly fashion in Macbeth. alliteration apostrophe: Ex: “Come, Sleep!” … “Death be not proud!” Define? ballad caesura carpe diem chivalry dramatic irony elegiac: resembling or characteristic of a poetic elegy (praising the dead) in form or content. Ex:? epic epic hero hyperbole: extreme exaggeration Ex:? juxtaposing kenning metaphor motif: Ex: Macbeth- blood, sleeplessness, clothing, babies, fate, gender. Define? oxymoron parable: conveys a moral message or lesson. Ex:? paradox: personification physiognomy satire similie sonnet: English VS Italian. Define? tragedy British Literature Exam Review Kirk warrior code