Photosynthesis Lab: Elodea & Bromthymol Blue Worksheet
advertisement

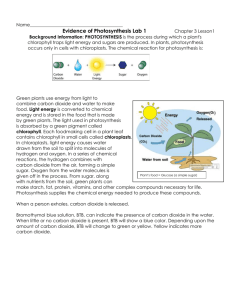
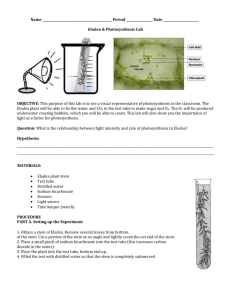
Name: ______________________________________________________ Period: ____ Photosynthesis Lab - Elodea and Bromthymol Blue Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplast, an organelle in plant cells that contains the molecule chlorophyll. Chlorophyll absorbs the energy of sunlight. That light energy is converted to chemical energy through the steps of photosynthesis. The reactions of photosynthesis can be divided into two major types: light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions. The light-dependent reactions convert energy from the sun into a form that the chloroplast can then use to make sugar from carbon dioxide; in the process producing oxygen as a waste product. The light-independent reactions use that energy to make glucose from carbon dioxide. In this lab, you will use bromothymol blue as an indicator to show how much CO 2 is left in test tubes containing plants and exposed to lights. A small piece of elodea will be introduced to a solution containing bromothymol blue and CO2. The point is to determine whether the elodea will have an effect on CO2 levels. Write out the equation for photosynthesis: Write out the equation for cellular respiration: Hypothesis: Write a hypothesis about what will happen to CO2 levels in a solution if an aquatic plant is photosynthesizing. If _____________________________________________________, then _____________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Material Preparation: If concentrated bromthymol blue (BTB liquid) is available, dilute with water (distilled works best) and test the concentration by adding 10 ml of your BTB solution to 15 ml water and bubbling one lung full of air through a straw into the water. It should turn greenish. (If it stays blue, the BTB is too concentrated; if it turns yellow, the BTB is too diluted.) Adjust your solution as necessary and place in dropper bottles for lab teams to use. Photosynthesis Lab - Elodea and Bromthymol Blue 1 Procedures: 1. Combine 15 ml of water (distilled works best) with 10 ml of BTB solution and GENTLY bubble one lungful of air through the straw. The liquid should turn a greenish color. 2. Label four test tubes: "Control," "1.25 cm Elodea" and "4 cm Elodea." And "4 cm dark" The test tube marked "control" will be sealed with masking tape and no plant will be added. 3. The test tube marked "Control" is sealed with masking tape. To the other test tubes, add the designated length of elodea, gently pushing each down into the solution with the straw. 4. Wrap the "4 cm dark" test tube in aluminum foil, so that no light gets in. 5. Place test tubes in rack and take the rack outside and set it in sunlight. 6. View the colors of the test tubes after a half hour (or even overnight). You should notice differences. Results: Record your results in the table below. Sample Control 1.25 cm Elodea 4 cm Elodea 4 cm dark Color Conclusions: Write 2 to 3 sentences based on your results. __________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ Questions: Answer on a separate page in complete sentences and staple paper to this lab. 1. Did the plants alter the level or CO2 in the test tubes? What is the relationship between the size of the plant and the difference in C02 levels? 2. Why did you initially blow into the solution to turn in green? 3. What is the purpose of the control? 4. Compare the 4cm dark to the 4cm in the light test tube. How do you account for any differences in color? 5. In the tubes in which photosynthesis can occur, what gas would eventually replace all of the carbon dioxide in the solution? 6. Can the plants placed in the “dark” test tube perform light independent reactions if it has never been exposed to light? What if it was exposed to light for an hour before being wrapped in aluminum foil? Photosynthesis Lab - Elodea and Bromthymol Blue 2