Hooke`s Law and Simple Harmonic Motion
advertisement

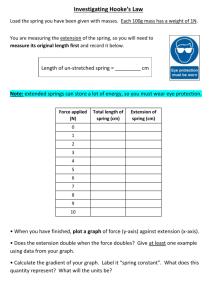
Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Aims To study the oscillations of a mass suspended at the end of a spring. To study Hooke's law in the extension of a spiral spring. To analyse experimental data by graphical methods. In this experimental tutorial you will first undertake a tutorial question to predict the motion of and force on a mass oscillating on the end of the spring, and then perform an experiment to measure these quantities. Part 1: Tutorial Question (15 mins) A mass is attached to the lower end of a spiral spring and oscillated vertically with simple harmonic motion such that its displacement relative to is mean position, x , is given by 2 x A sin T t [1] where A is the maximum displacement and T is the period. 1.1 Sketch the motion, clearly marking A and T . The force, F , due to the extension of the spring from its mean position is given by Hooke's Law: F kx [2] where k is the spring constant. 1.2 Hence, add a graph of force to your sketch. The time period of the oscillations is given by T 2 m k [3] 1.3 If the period is 0.5 s and the mass is 2 kg, what is the value of the spring constant? 1 Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Part 2: Taking data (10 mins) In this experiment the position of a mass suspended on the end of a fixed spring is monitored used data logging software on a PC. An ultrasound sensor1 monitors the position. A force sensor monitors the force. Force sensor Spring To start data taking: Mass Click on EasySense software icon. Select EasyLog from New Experiment menu. Ultrasound Check that the software has detected the force sensor and motion sensors – look for corresponding Figure 1: Experimental set-up boxes in top left of screen. Start the mass bouncing. Keep the motion as vertical as possible – avoid swinging. Wait until the motion has become regular, and then click on "Start". Record data for approximately 20 seconds and then click on "Stop". Part 3: Calculating period of oscillation and spring constant (5 mins) From the Display option on top toolbar select Show Table – this reveals the columns of data of time, force and distance. Clicking on a row of the data brings up a marker on the graph. Using the up and down arrow keys, move the marker until it is on a maximum of one of the sine waves. Note down the corresponding time for this maximum. Now move along 10 maxima, and note the corresponding time. 3.1 Calculate the average period. 3.2 Hence calculate the spring constant. Part 4: Calculating the spring constant from Hooke's Law (20 mins) In this part you will analyse your data using Excel. In EasyLog, click on File – Transfer to Excel. This opens Excel with your data clearly labelled in three columns. 4.1 Use Excel to plot (i) the force due to extension of the spring and (ii) distance about mean position against time on a single graph. Hints: (a) To calculate the average of a column of data in Excel, use the AVERAGE function. 1 This sends out a signal that is reflected from the base of the suspended mass. The reflected signal is then detected. The time between emission and detection allows the distance between mass and detector to be calculated. 2 Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion (b) When referencing a single, specific cell in an Excel equation, use $ signs, e.g. $E$2. (c) Plot the distance in centimetres so that the scale is similar to that of the force on your graph. 4.2 Compare this plot with the graph you sketched in Part 1. 4.3 From your data for force and distance, use Hooke's Law to calculate values for the spring constant. Hint: (d) Consider your columns of data – discard any rogue points. 4.4 From your values, calculate a single, average value for k and compare this with your value from Part 3. Remember to save your work to disk and to add your spreadsheet to your lab book. Part 5: Calculating velocity (Optional) Shut down the Easy Sense software, and then reopen it, this time selecting New Experiment – Graph. When prompted de-select the force sensor as we are only interested in distance this time. Set the data acquisition to run for 2 s, taking points every 20 ms. This will give you 100 data points. 5.1 Plot this scaled velocity and distance on the same graph. What is the phase difference between these two plots? 5.2 How can you explain this in terms of the motion and equation [1]? Hints: (a) As in Part 2 set the mass bouncing vertically again and let the motion settle. Then start the data taking. This time you do not need to stop it yourself. (b) Transfer the data into Excel as before. (c) Correct the distance data as before. x x2 (d) Calculate velocity using 1 where x1 , x2 are the corrected t1 t 2 distances for consecutive data points and t1,t 2 their times. (e) Scale the velocity so that its maximum value is similar to that of the distance. Further work The following questions are related to the topic covered by this experimental tutorial. Exercise book questions D41 – D50. 3 Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Mastering Physics question m.padgett@physics.gla.ac.uk details 4 will be sent by Miles Padgett Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Demonstrators' Answers, Hints, Marking Scheme and Equipment List. Marking Scheme Section 1.1 1.2 1.3 3.1 3.2 4.1 4.3 4.4 Discretionary mark TOTAL Mark 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 10 Answers Part 1: 1.1 See the graph for Part 4 1.2 See the graph for Part 4 1.3 316 Nm-1 Part 3 3.1 Period ~0.585 s 3.2 Spring constant ~115 Nm-1 Part 4 4.1 See accompanying graph and data sheet 4.3 See Part 3. Can plot force against distance – should give a straight line, but very fuzzy. Can be useful to spot outlying points which can significantly skew the average. Part 5 5.1 See graph. Can also do acceleration, but curve will not be smooth. 5 Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Typical data and graph for Part 4 Time s Force N Distance m Distance cm 0 0.03 0.06 0.09 0.15 0.18 0.21 0.24 0.27 0.3 0.33 0.36 0.39 0.45 0.48 0.51 0.54 0.57 0.6 0.63 0.66 0.69 0.75 0.78 0.81 0.84 33.8 33.7 34.2 34.7 35.9 36.6 36.9 37.2 37.2 37.1 36.9 36.5 35.8 34.6 34.1 33.7 33.6 33.5 33.7 33.9 34.5 35.1 36.2 36.8 36.9 37.3 0.233 0.232 0.23 0.224 0.213 0.21 0.205 0.203 0.201 0.201 0.204 0.207 0.213 0.224 0.227 0.232 0.234 0.235 0.234 0.231 0.228 0.222 0.211 0.208 0.203 0.201 23.3 23.2 23 22.4 21.3 21 20.5 20.3 20.1 20.1 20.4 20.7 21.3 22.4 22.7 23.2 23.4 23.5 23.4 23.1 22.8 22.2 21.1 20.8 20.3 20.1 Ave F 35.38154 Ave D 21.77538 Corrected F Corrected D k(N/cm) k(N/m) -1.5815392 -1.6815376 -1.1815376 -0.6815376 0.51846313 1.21846008 1.51846313 1.81846237 1.81846237 1.71846008 1.51846313 1.11846161 0.41846085 -0.7815399 -1.2815399 -1.6815376 -1.7815399 -1.8815384 -1.6815376 -1.4815369 -0.8815384 -0.2815399 0.81846237 1.41846085 1.51846313 1.91846085 1.52461492 1.42461472 1.2246158 0.62461608 -0.4753847 -0.7753853 -1.2753848 -1.4753852 -1.6753841 -1.6753841 -1.375385 -1.0753844 -0.4753847 0.62461608 0.9246152 1.42461472 1.62461512 1.72461533 1.62461512 1.32461601 1.0246154 0.42461567 -0.6753851 -0.9753842 -1.4753852 -1.6753841 1.037337 1.180346 0.964823 1.09113 1.090618 1.571425 1.190592 1.232534 1.0854 1.025711 1.104028 1.040058 0.880257 1.251232 1.386025 1.180346 1.096592 1.09099 1.035038 1.118465 0.86036 0.663046 1.211846 1.454259 1.029198 1.145087 103.7337 118.0346 96.48231 109.113 109.0618 157.1425 119.0592 123.2534 108.54 102.5711 110.4028 104.0058 88.02574 125.1232 138.6025 118.0346 109.6592 109.099 103.5038 111.8465 86.03603 66.30465 121.1846 145.4259 102.9198 114.5087 6 Average k (N/m) 120.9554591 Calculated k 115.3581 Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion 0.87 0.9 0.93 0.96 0.99 1.02 1.05 1.08 1.11 1.14 1.17 1.2 1.23 1.26 1.29 1.32 1.35 1.38 1.41 1.44 1.47 1.5 1.53 1.56 1.59 1.62 1.65 1.68 1.71 1.74 1.77 1.8 37.2 36.9 36.5 36.1 35.5 34.9 34.3 33.9 33.6 33.5 33.5 33.9 34.2 34.8 35.3 36.1 36.5 37 37.2 37.3 37.1 36.9 36.3 35.8 35.2 34.6 34 33.8 33.5 33.6 33.6 34.1 0.201 0.202 0.206 0.209 0.215 0.219 0.226 0.229 0.233 0.234 0.234 0.233 0.228 0.225 0.218 0.215 0.208 0.205 0.201 0.2 0.202 0.203 0.208 0.211 0.219 0.222 0.229 0.231 0.234 0.235 0.233 0.232 20.1 20.2 20.6 20.9 21.5 21.9 22.6 22.9 23.3 23.4 23.4 23.3 22.8 22.5 21.8 21.5 20.8 20.5 20.1 20 20.2 20.3 20.8 21.1 21.9 22.2 22.9 23.1 23.4 23.5 23.3 23.2 1.81846237 1.51846313 1.11846161 0.71846008 0.11846161 -0.4815369 -1.0815392 -1.4815369 -1.7815399 -1.8815384 -1.8815384 -1.4815369 -1.1815376 -0.5815392 -0.0815392 0.71846008 1.11846161 1.61846161 1.81846237 1.91846085 1.71846008 1.51846313 0.91846085 0.41846085 -0.1815376 -0.7815399 -1.3815384 -1.5815392 -1.8815384 -1.7815399 -1.7815399 -1.2815399 -1.6753841 -1.5753839 -1.1753846 -0.875384 -0.2753843 0.12461506 0.82461499 1.1246156 1.52461492 1.62461512 1.62461512 1.52461492 1.0246154 0.72461479 0.02461486 -0.2753843 -0.9753842 -1.2753848 -1.6753841 -1.7753843 -1.5753839 -1.4753852 -0.9753842 -0.6753851 0.12461506 0.42461567 1.1246156 1.32461601 1.62461512 1.72461533 1.52461492 1.42461472 7 1.0854 0.963869 0.951571 0.820737 0.430168 3.864195 1.311569 1.317372 1.168518 1.158144 1.158144 0.971745 1.153152 0.802549 3.312599 2.608937 1.146688 1.268999 1.0854 1.080589 1.09082 1.029198 0.94164 0.619589 1.456787 1.840582 1.228454 1.19396 1.158144 1.033007 1.168518 0.899569 108.54 96.38686 95.15708 82.07371 43.01684 386.4195 131.1569 131.7372 116.8518 115.8144 115.8144 97.1745 115.3152 80.25494 331.2599 260.8937 114.6688 126.8999 108.54 108.0589 109.082 102.9198 94.16401 61.95885 145.6787 184.0582 122.8454 119.396 115.8144 103.3007 116.8518 89.95695 Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion 1.83 1.86 1.89 1.92 1.95 1.98 2.01 34.5 35.2 35.7 36.3 36.7 37.1 37.2 0.226 0.223 0.216 0.212 0.206 0.204 0.201 22.6 22.3 21.6 21.2 20.6 20.4 20.1 -0.8815384 -0.1815376 0.31846237 0.91846085 1.31846237 1.71846008 1.81846237 0.82461499 0.52461587 -0.1753841 -0.5753849 -1.1753846 -1.375385 -1.6753841 8 1.06903 0.346039 1.8158 1.596255 1.121728 1.249439 1.0854 106.903 34.60391 181.58 159.6255 112.1728 124.9439 108.54 Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Typical data and graph for Part 5 Corrected D Velocity Velocity/10 0.168 0.172 0.177 0.183 0.188 0.194 0.199 0.204 0.208 0.211 0.213 0.213 -0.01981 -0.01581 -0.01081 -0.00481 0.00018999 0.00619001 0.01119 0.01619 0.02019 0.02319 0.02519 0.02519 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.25 0.300001 0.25 0.25 0.2 0.15 0.1 0 0 0.26 0.213 0.02519 -0.1 0.28 0.3 0.211 0.208 0.02319 0.02019 -0.15 -0.2 0.32 0.204 0.01619 -0.2 0.34 0.2 0.01219 -0.25 0.36 0.38 0.4 0.195 0.189 0.183 0.00718999 0.00119 -0.00481 -0.3 -0.3 -0.25 0.42 0.178 -0.00981 -0.25 0.44 0.46 0.173 0.168 -0.01481 -0.01981 -0.25 -0.15 0.48 0.165 -0.02281 -0.15 0.5 0.52 0.54 0.56 0.58 0.6 0.62 0.64 0.66 0.68 0.7 0.72 0.74 0.76 0.78 0.8 0.82 0.162 0.161 0.161 0.161 0.163 0.167 0.171 0.176 0.181 0.187 0.192 0.198 0.203 0.207 0.21 0.212 0.213 -0.02581 -0.02681 -0.02681 -0.02681 -0.02481 -0.02081 -0.01681 -0.01181 -0.00681 -0.00081 0.00419 0.01019 0.01518999 0.01919 0.02218999 0.02419 0.02519 -0.05 0 0 0.1 0.199999 0.200001 0.25 0.249999 0.300001 0.25 0.299999 0.25 0.200001 0.15 0.1 0.05 -0.05 0.020000041 0.024999977 0.029999987 0.024999972 0.030000067 0.024999972 0.024999981 0.02000003 0.014999959 0.010000022 0 0 0.010000015 0.014999948 -0.02000006 0.019999955 0.025000037 0.030000015 -0.02999997 -0.025 0.025000037 0.024999963 -0.01499997 0.015000022 0.005000015 0 0 0.01000003 0.019999925 0.02000006 0.025 0.024999925 0.030000089 0.025 0.029999925 0.025 0.02000006 0.01499997 0.01 0.005000015 - Time s Distance m 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.1 0.12 0.14 0.16 0.18 0.2 0.22 0.24 Ave distance 0.18781 9 Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion 0.84 0.212 0.02419 -0.05 0.86 0.88 0.211 0.209 0.02319 0.02119001 -0.1 -0.2 0.9 0.205 0.01719 -0.25 0.92 0.94 0.2 0.195 0.01219 0.00718999 -0.25 -0.25 0.96 0.98 0.19 0.184 0.00219 -0.00381 -0.3 -0.25 1 1.02 0.179 0.174 -0.00881 -0.01381 -0.25 -0.25 1.04 0.169 -0.01881 -0.15 1.06 1.08 1.1 1.12 1.14 1.16 1.18 1.2 1.22 1.24 1.26 1.28 1.3 1.32 1.34 1.36 1.38 1.4 0.166 0.163 0.161 0.161 0.162 0.164 0.167 0.171 0.175 0.181 0.186 0.192 0.197 0.202 0.206 0.21 0.212 0.213 -0.02181 -0.02481 -0.02681 -0.02681 -0.02581 -0.02381 -0.02081 -0.01681 -0.01281 -0.00681 -0.00181 0.00419 0.00919 0.01419001 0.01819 0.02218999 0.02419 0.02519 -0.15 -0.1 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.199999 0.2 0.3 0.250001 0.3 0.25 0.249999 0.2 0.2 0.1 0.05 0 1.42 1.44 0.213 0.212 0.02519 0.02419 -0.05 -0.15 1.46 1.48 0.209 0.206 0.02119001 0.01819 -0.15 -0.25 1.5 1.52 0.201 0.196 0.01319001 0.00819 -0.25 -0.25 1.54 0.191 0.00319 -0.3 1.56 0.185 -0.00281 -0.25 1.58 1.6 1.62 1.64 1.66 1.68 0.18 0.175 0.17 0.166 0.163 0.161 -0.00781 -0.01281 -0.01781 -0.02181 -0.02481 -0.02681 -0.25 -0.25 -0.2 -0.15 -0.1 0 10 0.005000015 -0.005 0.009999955 -0.02000006 0.024999925 0.025000075 -0.025 0.029999925 -0.025 0.025000075 -0.025 0.015000045 0.014999881 -0.01000003 0 0.005000015 0.01000003 0.01499997 0.01999994 0.019999985 0.030000015 0.025000075 0.030000015 0.025 0.024999925 0.019999985 0.019999985 0.01000003 0.005000015 0 0.004999985 -0.01499997 0.015000045 -0.025 0.025000075 -0.025 0.030000015 0.024999851 0.025000075 -0.025 -0.02000006 -0.01499997 -0.01000003 0 Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion 1.7 1.72 1.74 1.76 1.78 1.8 1.82 1.84 1.86 1.88 1.9 1.92 1.94 1.96 1.98 2 0.161 0.161 0.163 0.166 0.169 0.174 0.179 0.185 0.19 0.196 0.201 0.205 0.208 0.211 0.212 0.213 -0.02681 -0.02681 -0.02481 -0.02181 -0.01881 -0.01381 -0.00881 -0.00281 0.00219 0.00819 0.01319001 0.01719 0.02019 0.02319 0.02419 0.02519 11 0 0.1 0.15 0.15 0.25 0.249999 0.3 0.25 0.3 0.250001 0.2 0.15 0.15 0.05 0.05 0.012595 0 0.01000003 0.01499997 0.015000045 0.025 0.024999925 0.030000015 0.025 0.030000015 0.025000075 0.019999985 0.014999955 0.01499997 0.005000015 0.005000015 0.0012595 Physics 1 – Hooke's Law and Simple Harmonic Motion Equipment List 1 meter stand Boss head Force sensor with cable Ultrasound sensor with cable Spring Mass hanger with weights up to 1kg Computer with EasySense software 12