Lesson Plan
advertisement

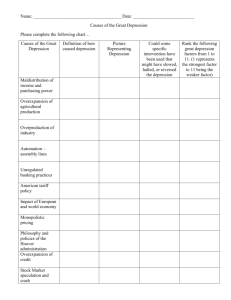
SOCIAL STUDIES LESSON PLAN RESOURCES SOCIAL STUDIES CLASS Economics TOPIC Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy LESSON 2 The Great Depression OBJECTIVES By the end of this lesson, the student will be able to: Explain how the diagram The Business Cycle represents the economy. Identify the causes of the Great Depression. Describe the policies that President Hoover enacted to solve the problems of the Great Depression. Describe the policies that President Roosevelt enacted to solve the problems of the Great Depression. Evaluate the effectiveness of President Roosevelt’s New Deal legislation in solving the problems of the Great Depression. CLASSROOM SUPPLIES NEEDED Depending on what content and which activities are provided, some to all of the items below will be needed. Whiteboard and dry erase markers or flipchart paper and markers LESSON RESOURCES Depending on what content and which activities are provided, some to all of the items below will be needed. Pre-Work For Students To Read Before Class Handout 1 - What Are The Causes of the Great Depression? Handout 2 - What Caused the Depression in 1929? Pre-Work for Students to View Before Class n/a Handout to Provide Students In Class Handout 3 - Why Was the Fair Labor Standards Act Created? Handout 4 – Pros and Cons of New Deal Legislation Online Videos Students Will Watch In Class n/a Economics > Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy > The Great Depression Page 1 SOCIAL STUDIES LESSON PLAN RESOURCES SOCIAL STUDIES CLASS Economics TOPIC Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy LESSON 2 The Great Depression KEY VOCABULARY AND IMPORTANT CONCEPTS Business Cycle Peak Depression Expansion Recession Great Depression Contraction Trough Laissez-faire Economics STUDENT PRE-WORK FOR THIS LESSON Directions 1. Students are to read two articles. Resource Handout 1 - What Are The Causes of the Great Depression? Handout 2 - What Caused the Depression in 1929? Class Preparation Students will use information presented in the handouts to prepare a group assignment in class. ANTICIPATORY SET FOR THE LESSON (5 MINUTES) Mode Topic Teacher Question Class Discussion Teacher asks students “How does an understanding of the Business Cycle help you make better decisions about your current and future plans?” Students’ answers should reflect their knowledge of the relationship between the Business Cycle and the economy. The phases of the Business Cycle provide information on whether or not the economy is growing. When individuals understand the current state of the economy, they can make better decisions about their current and future plans. During the Great Recession, many college students decided to continue in school because the job outlook was poor. Individuals in the workforce postponed looking for other employment opportunities. Many seniors postponed retirement for a few years because of their financial concerns. Economics > Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy > The Great Depression Page 2 SOCIAL STUDIES LESSON PLAN RESOURCES SOCIAL STUDIES CLASS Economics TOPIC Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy LESSON 2 The Great Depression LESSON CONTENT AND ACTIVITIES: THE PHASES OF THE BUSINESS CYCLE (5 MINUTES) Mode Topic Teacher Lecture Class Discussion The Phases of The Business Cycle Teacher shows the graph of the Business Cycle and identifies each phase. Teacher tells students to look at the names given to the various phases of the Business Cycle. Teacher asks students to speculate on the kind of economic activity that occurs at each phase. The discussion should include the following information: Peak -The peak phase represents the highest level of economic growth. The unemployment rate declines to its lowest level. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increases to its highest level. A peak is followed by a decline in economic growth. Contraction - During the contraction phase economic growth begins to decline. Businesses are producing less goods and services. This is reflected in decreasing GDP numbers. The unemployment rate increases as businesses begin to lay off workers. Trough - The trough is the lowest point of the business cycle. It is a very deep recession. The unemployment rate is high. The GDP numbers decline as the demand for goods and services declines significantly. Expansion- When the economy begins to grow, economists look for signs that the trough has come to an end. The demand and supply of goods and services increase. GDP numbers increase. Businesses begin to hire employees. The unemployment rate decreases. Economics > Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy > The Great Depression Page 3 SOCIAL STUDIES LESSON PLAN RESOURCES SOCIAL STUDIES CLASS Economics TOPIC Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy LESSON 2 The Great Depression LESSON CONTENT AND ACTIVITIES: THE CAUSES OF THE GREAT DEPRESSION (30 MINUTES) Mode Topic Teacher Lecture The Great Depression Teacher Reviews Graphic Organizer The teacher defines the Great Depression. The Causes of the Great Depression Teacher will review the causes of the Great Depression as indicated by the graphic organizer. Teacher Provides Instructions Teacher tells students that these causes were identified in the articles that they read for pre-work. They will use the information to prepare a group assignment. Causes of The Great Depression Teacher organizes students into groups of four. Teacher assigns each group a cause of the Great Depression as depicted in graphic organizer in the Power-Point. a. Group 1-Stock Speculation and Stock Market Crash b. Group-2-Credit and Debt c. Group 3-Supply/Demand and Agricultural Issues d. Group 4-International Problems and World War I Teacher instructs students to review information from both articles. a. Handout 1-What Are The Causes of the Great Depression? b. Handout 2- What Caused the Depression in 1929? Teacher instructs students to use both articles to gather information about the “cause” they have been assigned. Teacher tells students that they may include additional information that they have read or researched. Teacher instructs students to work together to identify the information that they want to present to the class. Teacher instructs students to use the whiteboard and dry erase markers to Economics > Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy > The Great Depression Page 4 SOCIAL STUDIES LESSON PLAN RESOURCES SOCIAL STUDIES CLASS Economics TOPIC Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy LESSON 2 The Great Depression LESSON CONTENT AND ACTIVITIES: THE CAUSES OF THE GREAT DEPRESSION (30 MINUTES) Mode Topic develop their presentations. Teacher tells students that the whole group may present the information, or they may choose a spokesperson to present for the group. Each group has three minutes to present their information. Student Activity Students’ presentations should include the following information: Stock Speculation and Stock Market Crash Wealthy Americans invested their money in the Stock Market. Stock prices rose dramatically, until the summer of 1929. As prices declined, investors began to sell their stocks. Eventually, no one bought stocks, and when the market crashed, investors were left with stocks that they had purchased at inflated prices. Credit and Debt Americans purchased goods and services on credit in the 1920s. Because wages for workers only rose 8 percent, many of them created a lot of debt. Many workers decreased their spending habits before the Stock Market crashed. After the crash, people lost jobs and could not pay their debts. Supply/Demand and Agricultural Issues During World War I, American farmers grew crops for European nations. After the war, European nations produced their own crops, which decreased the demand for American crops. American farmers had to cut their supply, and lay off employees. Many farmers lost their farms and livelihood due to the Dust Bowl, or the severe drought that plagued the United States in the 1930s. International Problems and World War I When the Stock Market crashed, America could not continue to loan money to European nations to help them rebuild their post-World War I economies. The United States also levied a protectionist tariff on imported goods. When European products did not sell in the United States, European nations could not pay back money owed to the United States. Economics > Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy > The Great Depression Page 5 SOCIAL STUDIES LESSON PLAN RESOURCES SOCIAL STUDIES CLASS Economics TOPIC Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy LESSON 2 The Great Depression LESSON CONTENT AND ACTIVITIES: THE CAUSES OF THE GREAT DEPRESSION (30 MINUTES) Mode Topic LESSON CONTENT AND ACTIVITIES: LIFE DURING THE GREAT DEPRESSION (5 MINUTES) Mode Topic Teacher Lecture Class Discussion Life During The Great Depression: Decline Teacher Lecture Class Discussion Life During The Great Depression: Prosperity Teacher and students discuss the economic impact of the Great Depression. The discussion includes the rise in unemployment, the failure of the banks, the development of “Hoovervilles”, the development of gangs and homelessness. Teacher and students discuss the businesses that prospered during the Great Depression. The following businesses are included: Kellogg’s Cereal, R J Reynolds, Chevrolet, and movie houses. LESSON CONTENT AND ACTIVITIES: PRESIDENT HOOVER’S ADMINISTRATION (10 Minutes) Mode Topic Teacher Lecture Class Discussion President Hoover and The Great Depression Teacher Lecture Class Discussion Teacher describes the initial steps that President Hoover took to solve the problems that occurred during the Great Depression. President Hoover and The Great Depression The teacher continues to describe the legislation that President Hoover and the Congress passed to solve the problems that occurred during the Great Depression. The discussion includes appropriations for public works projects, the provisions of the Smoot Hawley Tariff Act, the Revenue Act, and the function of the Reconstruction Finance Corporation. Teacher discusses the reasons for President Hoover’s defeat in the 1932 election. LESSON AND CONTENT ACTIVITIES: PRESIDENT ROOSEVELT’S ADMINISTRATION (30 MINUTES) Mode Topic Teacher Lecture Economic Conditions In 1933 Economics > Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy > The Great Depression Page 6 SOCIAL STUDIES LESSON PLAN RESOURCES SOCIAL STUDIES CLASS Economics TOPIC Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy LESSON 2 The Great Depression Class Discussion Teacher and students discuss the economic conditions that President Roosevelt faced when he took office in 1933. Included in discussion are the high unemployment rate, farm foreclosures, and bank failures. Teacher Lecture Class Discussion President Roosevelt’s New Deal Administration 1933 Teacher and students discuss the initial steps that President Roosevelt took to solve the problems that occurred during the Great Depression. The discussion includes the provisions of the Emergency Banking Act, the function of the Tennessee Valley Authority, and the function of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). Teacher Lecture Class Discussion President Roosevelt’s New Deal Administration 1934 Teacher and students continue to discuss legislation passed by President Roosevelt and the Congress, to address the problems that occurred during the Great Depression. The discussion includes the creation of the Securities and Exchange Commission and its purpose, the function of the Federal Housing Administration, and the provisions of the Reciprocal Tariff Act. Teacher Lecture Class Discussion President Roosevelt’s New Deal Administration 1935 Teacher and students continue to discuss the legislation passed by President Roosevelt and the Congress to address the problems that occurred during the Great Depression. The discussion includes the provisions of the Social Security Act, the function of the Work Progress Administration, and the provisions of the Wagner Act. Teacher Lecture Class Discussion President Roosevelt’s New Deal Administration 1937 Teacher and students continue to discuss the legislation passed by President Roosevelt and the Congress to address the problems that occurred during the Great Depression. The discussion includes the provisions of the Fair Labor Standards Act, and the function of the United States Housing Authority. Pros and Cons of New Deal Legislation Teacher directs students to choose one or more of the laws enacted by Congress under President Roosevelt, and develop an argument that either supports the policy or opposes the policy. Economics > Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy > The Great Depression Page 7 SOCIAL STUDIES LESSON PLAN RESOURCES SOCIAL STUDIES CLASS Economics Student Activity TOPIC Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy LESSON 2 The Great Depression Students may use Handout 3- Why Was the Fair Labor Standards Act Created?, to develop their arguments. Students may research additional information on the policy. Students may use information from the lecture notes, and any readings that the teacher has provided. Students’ arguments should include a summary of the legislation, and the problems that it attempted to solve. Students will use Handout 4- Pros and Cons of New Deal to list information that they need to make their arguments to the class. Students should include the following information in their arguments: The purpose of The Fair Labor Standards Act was to provide for better working conditions, and a better salary for employees. The law established a 40 hour work week, a minimum wage of $.40 per hour, and time-and-a half overtime pay. The bill also restricted child labor. Students who support the legislation, could use the same arguments that those who supported the bill in the 1930s used. Supporters argued that a shorter workday led to increased employment, because it was cheaper to pay the hourly rate to more employees, than pay the over-time rate to fewer employees. Students could also argue that the bill eliminates some of the dangerous working conditions, and eliminated child labor, which were positive results. Students who oppose the legislation, could cite the fact that the Supreme Court had already ruled laws providing for a minimum wage, unconstitutional. Students could argue that employers were providing much needed jobs for displaced farmers and immigrants. Students could argue that the jobs that employers provided, kept the unemployment rate at a low level of 3.3 percent from 1923-1929. Students could also argue that the minimum wage requirement would decrease profits, and prevent employers from hiring additional workers. President Roosevelt’s New Deal Administration 1935-1940 Teacher describes economic conditions as measured by the unemployment rate, the national debt, and GNP. LESSON ASSESSMENT AND STUDENT LEARNING EVALUATION (15 MINUTES) Economics > Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy > The Great Depression Page 8 SOCIAL STUDIES LESSON PLAN RESOURCES SOCIAL STUDIES CLASS Economics TOPIC Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy Mode Topic Student Activity Assessment/Evaluation LESSON 2 The Great Depression Write a short answer response that describes the degree of effectiveness of Roosevelt’s policies in solving the economic crisis of the Great Depression. Use information from the lecture, class discussions, and the articles that have been provided, to support the main ideas of your argument. President Roosevelt’s policies helped to alleviate some of the problems caused by the Great Depression. When President Roosevelt took office in 1933, the economic outlook was dismal. Twenty-five percent (25%) of Americans were unemployed. Farmers lost half of their farms to bank foreclosures. Forty percent (40%) of the banks failed. The national debt was forty percent (40%) of GNP. President Roosevelt took several steps to provide relief to persons who lost the jobs, to help the economy recover, and to reform the systems that led to the Great Depression. Programs like the Tennessee Valley Authority, and the Works Progress Administration, employed large numbers of people for public works projects. Laws such as the Reciprocal Tariff Act allowed President Roosevelt to negotiate tariffs with foreign nations, and increase trade. The Emergency Banking Act stabilized the banks so that only a few banks failed after 1933. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insured deposits up to $2500.00, which provided some protection for savings. The Social Security Act set up a pension system for the elderly, which was funded by workers, and guaranteed by the federal government. The economy improved under the leadership of President Roosevelt. Industrial production was fifty-five (55%) higher in 1935, than it was in 1933. The unemployment rate declined from nineteen percent (19%) in 1938, to 17.2 % in 1939, and 14.6% in 1940. The Gross National Product was fifty eight (58%) higher in 1940 than it was in 1932. Despite these improvements, the policies enacted by President Roosevelt under the New Deal, did not end the Great Depression. World War II, which led to increased industrial output of military equipment, finally ended the Great Depression. Economics > Key Economic Events That Have Shaped American Government and Policy > The Great Depression Page 9