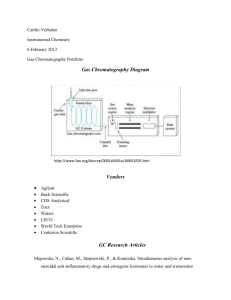
Unit I - Chromatography-I Lectures - 20
advertisement

KHANDESH COLLEGE EDUCATION SOCIETY’S MOOLJI JAITHA COLLEGE, JALGAON NAAC Accredited “A” Grade (2004 to 2009) reaccredidation process is in progress UGC Honored “College with Potential for Excellence” ISO 9001:2008 Certified Certificate Course In Analytical Chemistry SYLLABUS Department of Chemistry Moolji Jaitha College, Jalgaon. 2010-2011 CERTIFICATE COURSE IN ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY PAPER – I FUNDAMENTALS OF ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY 6 Credits Unit – I: Basic Tools and Operations of Analytical Chemistry Lectures - 20 The Laboratory Notebook, Laboratory Materials and Reagents, The Analytical Balance, Volumetric Glassware, Preparation of Standard Base Solutions, Preparation of Standard Acid Solutions, Other Apparatus- Handling and Treating Samples, Igniting Precipitates Gravimetric Analysis, Laboratory Safety. Unit – II: Data Handling and Spreadsheets in Analytical Chemistry Lectures - 10 Accuracy and precision, Determinate Errors, Indeterminate Errors, Significant Figures, Rounding off, Ways of Expressing Accuracy, Standard Deviation, Use of Spreadsheets in Analytical Chemistry. Unit – III: Calculations Used in Analytical Chemistry Lectures-20 Some Important Units of Measurements- SI Units, Distinction between Mass and Weight, The Mole, The Millimole, Calculating the Amount of Substance in Moles and Millimoles, Solutions and their Concentrations- Concentraton of Solutions, Density and Specific Gravity of Solutions, Chemical Stoichiometry- Empirical and Molecular Formulas, Stoichiometric Calculations. Unit – IV: Aqueous Solutions and Chemical Equilibria Lectures-15 The Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solutions – Classifying Solutions of Electrolytes, Acids and Bases, Amphiprotic Species, Autopyrolysis, Strengths of Acids and Bases, Chemical Equilibrium – The Equilibrium State, Equilibrium Constant Expressions, Types of Equilibrium Constants, Applying Solubility Product Constants, Applying Acid Base Dissociation Constants, Buffer Solutions – Calculation of pH of Buffer Solutions, Properties of Buffer Solutions. Unit – V: Effect of Electrolytes on Chemical Equilibria Lectures-15 The Effects of Electrolytes on Chemical Equilibria – The Effect of Ionic Charges on Equilibria, The Effect of Ionic Strength, the Salt Effect, Activity Coefficients – Properties of Activity Coefficients, The Debye-Huckel Equation, Equilibrium Calculations Using Activity Coefficients, Omitting Activity Coefficients in Equilibrium Calculations Unit – VI: Solvent Extraction Lectures-10 Introduction, Principles of Solvent Extraction, Sequence of Extraction Process, Extraction Techniques, Applications References: 1. Analytical Chemistry, Fifth edition by G. D. Christian, John Wiley and Sons. 2. Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, Eighth edition by Skoog. West, Holler and Crouch, Published by Thomson, Brooks / Cole. 3. Instrumental methods of Chemical Analysis, by Chatwal and Anand, Himalaya Publishing House CERTIFICATE COURSE IN ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY PAPER – II INSTRUMENTAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS 6 Credits Unit I - Chromatography-I Lectures - 20 Introduction to Chromatography, Classification of Chromatography, Paper Chromatography, Types of Paper Chromatography, Experimental Details for Qualitative Analysis, Experimental Details for Quantitative Analysis, Applications. Thin Layer Chromatography - History and Origin, superiority of TLC over other Chromatographic Techniques, Experimental Techniques, Applications of TLC, Limitations, Scope. Column Chromatography - Introduction, Principle, Experimental Details, Theory of Development, Factors Affecting Column Chromatography, Applications of Column Chromatography. Unit II - Chromatography-II Lectures - 20 Ion Exchange Chromatography - Introduction, Definition, Cation Exchangers, Anion Exchangers, Regeneration, Ion Exchange Column Used in Chromatographic Separations, Selection of Suitable Systems, Applications of Ion Exchangers Gas Chromatography - Introduction,Principles of Gas Chromatographic Separations, Instrumentations, Evaluations, Retention Volume, Resolution,Applications Unit III: Conductometric Measurements Lectures-15 Introduction, Some Important Laws, Definitions and Relations, Effect of Dilution, Conductance Measurement, Applications of Conductance Measurement, Types of Conductometric Titrations, Disadvances of Conductometirc Titrations Unit IV: Potentiometry Lectures-20 Electrodes of First Kind, Electrodes of Second Kind, Redox electrodes, Cells Without Liquid Junction, Cells with Liquid Junction, Reference Electrodes- Saturated Calomel Electrodes, Measurement of Potential, Determination of Concentration From Potential Measurements, Residual Liquid Junction Potential, Accuracy of Direct Potentiometric Measurements, The Glass pH Electrode, Standard Buffers, Accuracy pH Measurements, Measurements with pH Meter Unit V: Introduction to Spectrochemical Methods Lectures-15 Properties of electromagnetic radiations, Interaction of Radiation and Matter, Radiation Absorption- The Absorption Process, Absorption Spectra, Limits to Beer’s Law. References 1. Analytical Chemistry, Fifth edition by G. D. Christian, John Wiley and Sons. 2. Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, Eighth edition by Skoog. West, Holler and Crouch, Published by Thomson, Brooks / Cole. 3. Instrumental methods of Chemical Analysis, by Chatwal and Anand, Himalaya Publishing House CERTIFICATE COURSE IN ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY PRACTICAL COURSE 8 Credits Determination of chloride contents in a given water sample by Mohr’s method. Estimation of calcium from the drug sample. Estimation of phosphorus from the fertilizer. Determination of pH of the soil sample using universal indicator. Determination of Rf values of the components of binary mixture by TLC. Analysis of Aspirin by conductometric titration. Determination of pH of Hair shampoos / tooth pastes. Determination of the amount of Cu2+ by titration with EDTA spectro photometrically using liquor ammonia. 9. Determination of pKa valueof given organic acid by pH metric titration. 10. Determination of solubility of a sparingly soluble salt coductometrically. 11. Conductometric titration of strong acid, weak acid and salt with NaOH. 12. Determination of nitrate in the given water sample spectrophotometrically. 13. Determination of hardness of the given water sample titrimetrically. 14. Determine amount of chloride, bromide and iodide present in their mixture by potentiometric titration. 15. Gravimetric estimation of Ni(II) as Ni-DMG. 16. Estimation of Manganese volumetrically by Volhard’s method. 17. Determination of sulphate in given water sample spectrophotometrically. 18. To determine the amount of Na/K in given water sample using flame photometer. 19. Determination of organic carbon of given soil sample. 20. Determination of calcium in calcium carbonate using oxidation reduction titration. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. References 1. A text book of quantitative inorganic analysis by A.I.Vogel. 3rd edition. 2. Systematic practical chemistry by P.C. Kamboj. Vishal Publishing Co. 3. Methods in Environmental Analysis-Wateer,soil and air. By P.K.Gupta,Agrobios (India)