Key words in Essay Questions
advertisement

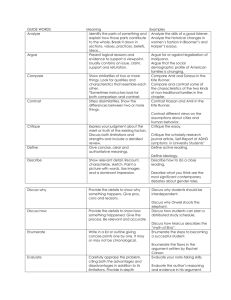
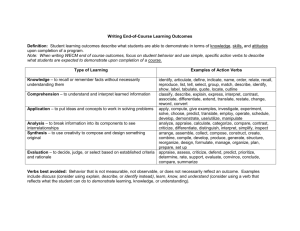
Key Words and Terms in Essay Questions Analyze Assess Cause/Effect Chronological Clarify Compare Contrast Criticize Define Diagram Describe Discuss Enumerate Evaluate Explain Fact Infer Interpret Illustrate Use Break into separate parts and discuss, examine or interpret each part. To what degree? measure: evaluate or estimate the nature, quality, ability, extent, or significance of The beginning / the result Events put in order they happened To make clear Bring out points of similarity and points of difference. Show how things are alike. Example: Compare the legislative branches of the state government and the national government. Bring out points of difference. Show how things are different. Example: Contrast the novels of Jane Austen and William Makepeace Thackery. State your opinion of the correctness or merits of an item or issue; criticism may approve or disapprove. Criticism often includes analysis. Example: Criticize the increasing use of executive agreement in international negotiations. Give the meaning of a word or concept, place it in the class to which it belongs, and set it off from other items in the same class. These are usually short. Example: Define the term “archetype” To label the parts of a process Give an account of; tell about; give a word picture of. List characteristics, qualities and parts. Tell how something looks or how it happened. Example: Describe the Pyramids of Giza. Talk over; consider from various points of views; present the different sides of. Often includes compare & contrast. Tell about the main points and important details. Example: Discuss the use of pesticides in controlling mosquitoes. Name over, one after another; list in concise form. To make a list. Example: Enumerate the great Dutch painters of the seventeenth century. Give the good points and the bad ones; appraise; give an opinion of what is important; regard the value of; talk over the advantages and limitations or strengths and weaknesses. Include evidence to support the evaluation. Example: Evaluate the contributions of teaching machines. Make clear; interpret; make plain; tell “how” to do; tell the meaning of. Give reasons for an event. To give facts that clarify a point. Example: Explain how man can, at times, trigger a full-scale rainstorm. Something that can be proven to be true. To make a conclusion based on fact. Make plain; give the meaning of; give your thinking about; translate. To offer an explaination. Example: Interpret the poetic line. “The sound of a cobweb snapping is the noise of my life.” A word picture; a diagram; a hart; or concrete example to clarify a point. To give examples. Justify Opinion Outline Predict Prove Question Reflect Refute Relate Sequence State Summarize To what extent Trace Example: Illustrate the use of catapults in amphibious warfare of Alexander. Show good reason for; give your evidence; present facts to support your position. Example: Justify the American entry into World War II. Belief based on what a person thinks or feels Describe main ideas; characteristics or events. Does not necessarily mean, write Roman numeral letter outline. To make a guess about the future Establish the truth of something by giving factual evidence or logical reasons. Especially use facts brought out in class. Example: Prove that in a full-employment economy, a society can get more of one product only by giving up another product. To ask. To think about To prove a given position to be false Show connections between events or ideas; provide a larger context. To show how things are alike or connected. To put in correct order Explain concisely. Sum up; give the main points briefly. Include conclusions; avoid unnecessary details. Example: Summarize the ways in which man preserves food. The measurement of an action Follow the course of; follow the trail of; give a description of progress. To tell about the progress or growth. Example: Trace the development of television in school instruction.