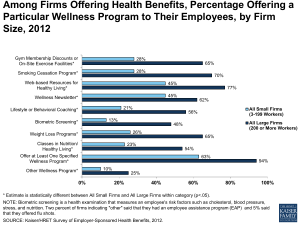
Industry Structure
advertisement
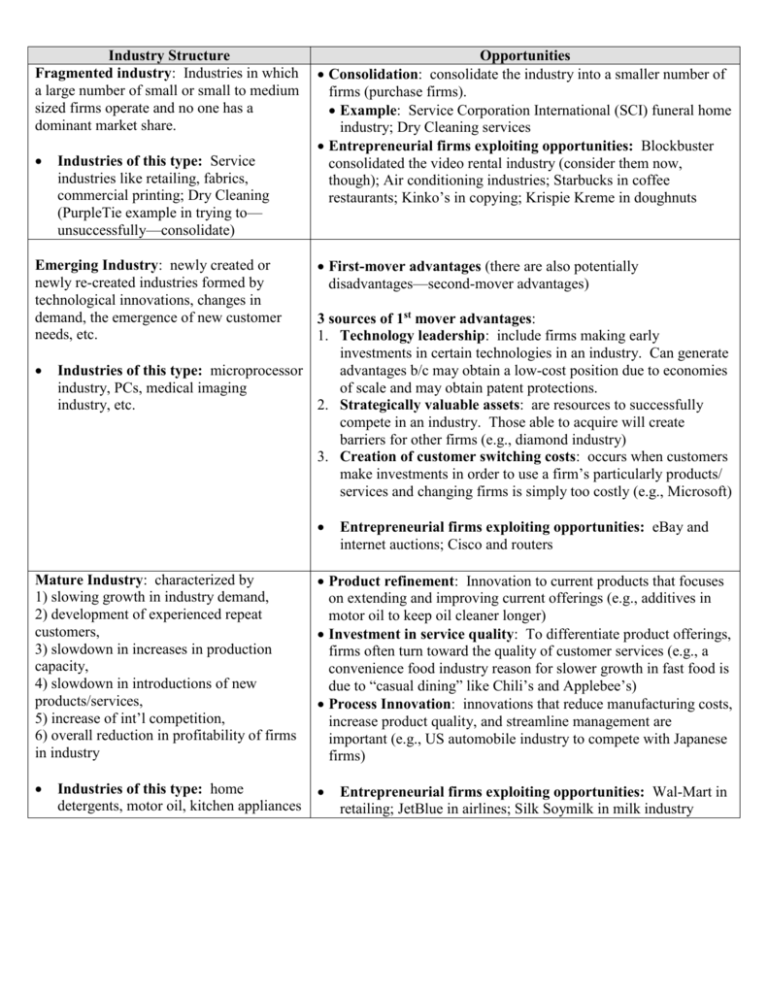
Industry Structure Fragmented industry: Industries in which a large number of small or small to medium sized firms operate and no one has a dominant market share. Industries of this type: Service industries like retailing, fabrics, commercial printing; Dry Cleaning (PurpleTie example in trying to— unsuccessfully—consolidate) Emerging Industry: newly created or newly re-created industries formed by technological innovations, changes in demand, the emergence of new customer needs, etc. Opportunities Consolidation: consolidate the industry into a smaller number of firms (purchase firms). Example: Service Corporation International (SCI) funeral home industry; Dry Cleaning services Entrepreneurial firms exploiting opportunities: Blockbuster consolidated the video rental industry (consider them now, though); Air conditioning industries; Starbucks in coffee restaurants; Kinko’s in copying; Krispie Kreme in doughnuts First-mover advantages (there are also potentially disadvantages—second-mover advantages) 3 sources of 1st mover advantages: 1. Technology leadership: include firms making early investments in certain technologies in an industry. Can generate Industries of this type: microprocessor advantages b/c may obtain a low-cost position due to economies industry, PCs, medical imaging of scale and may obtain patent protections. industry, etc. 2. Strategically valuable assets: are resources to successfully compete in an industry. Those able to acquire will create barriers for other firms (e.g., diamond industry) 3. Creation of customer switching costs: occurs when customers make investments in order to use a firm’s particularly products/ services and changing firms is simply too costly (e.g., Microsoft) Entrepreneurial firms exploiting opportunities: eBay and internet auctions; Cisco and routers Mature Industry: characterized by 1) slowing growth in industry demand, 2) development of experienced repeat customers, 3) slowdown in increases in production capacity, 4) slowdown in introductions of new products/services, 5) increase of int’l competition, 6) overall reduction in profitability of firms in industry Product refinement: Innovation to current products that focuses on extending and improving current offerings (e.g., additives in motor oil to keep oil cleaner longer) Investment in service quality: To differentiate product offerings, firms often turn toward the quality of customer services (e.g., a convenience food industry reason for slower growth in fast food is due to “casual dining” like Chili’s and Applebee’s) Process Innovation: innovations that reduce manufacturing costs, increase product quality, and streamline management are important (e.g., US automobile industry to compete with Japanese firms) Industries of this type: home detergents, motor oil, kitchen appliances Entrepreneurial firms exploiting opportunities: Wal-Mart in retailing; JetBlue in airlines; Silk Soymilk in milk industry Industry Structure Opportunities Declining Industry: An industry that has Market Leadership: Wait out shakeout period and enjoy a more experienced an absolute decline in unit sales benign environment—should try to gain majority of market share over a sustained period of time (e.g., Defense industry) Niche: narrow scope of operations and focus on a narrow segment Industries of this type: Defense of the declining industry industry—even in accounting for Gulf Harvest: Engage in a long, systematic withdrawal from the and Iraq Wars; video rental industry industry, extracting as much value as possible during withdrawal period. Divestment: Like a harvest strategy, but happens very quickly Global Industry: An industry that is experiencing significant international sales o Entrepreneurial firms exploiting opportunities: Nucor in steel—exploiting the steel in the minimill industry—smaller and produce a narrower range of products…they are energy efficient and high-quality. o o Can pursue a multidomestic or global strategy Multidomestic strategy: compete for market share on a country-by-country basis and vary their product or service offerings to meet demands of the local market (e.g., Fast Food Industry) Global Strategy: Use the same basic approach in all foreign markets (e.g., Athletic Shoes industry) Industries of this type: Athletic shoes; Fast food o