Grade 9 Biology Unit 3 – (Organization and Maintenance of
advertisement

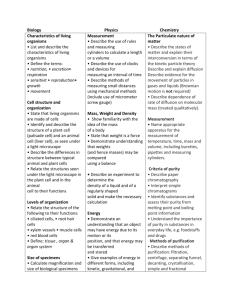
Grade 9 Biology Unit 3 – (Organization and Maintenance of Organisms) Structure and Function of Components of Animal Cell Levels of Organization Structure and Function of Components of Plant Cells Function of Plasma Membrane in Detail including the process of Diffusion, Active Transport and Osmosis Standards and Benchmarks: STANDARD 1: Learners understand the nature of scientific knowledge and inquiry Make and use tables, charts, graphs, and scale drawings to justify scientific arguments and claims in oral and written presentations. Participate in group discussions on scientific topics by restating or summarizing accurately what others have said, asking for clarification or elaboration, and expressing alternative positions. STANDARD 4: Learners understand the interrelationship between structure and function Explain the structures and functions of the basic molecules of living organisms and the chemical reactions necessary for life. Describe the cell as the fundamental unit of living organisms capable of receiving and integrating messages and responding to changes in the environment. Analyze the organization, development and basic processes of the human body. By the end of this unit, students will be able to: State that living organisms are made of cells Identify and describe the structure of a plant cell (palisade cell) and an animal cell (liver cell), as seen under a light microscope Describe the differences in structure between typical animal and plant cells Relate the structures seen under the light microscope in the plant cell and in the animal cell to their functions Relate the structure of the following to their functions: ciliated cells – in respiratory tract root hair cells – absorption xylem vessels – conduction and support muscle cells – contraction red blood cells – transport Identify and label the cuticle, cellular and tissue structure of a dicotyledonous leaf, as seen in cross-section under the light microscope, and describe the significance of these features in terms of functions, to include: distribution of chloroplasts – photosynthesis stomata and mesophyll cells – gas exchange vascular bundles (xylem and phloem) – transport and support Define: tissue as a group of cells with similar structures, working together to perform a shared function organ as a structure made up of a group of tissues, working together to perform specific functions organ system as a group of organs with related functions, working together to perform body functions Diffusion: Define diffusion as the net movement of molecules from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration down a concentration gradient, as a result of their random movement Describe the importance of diffusion of gases and solutes and of water as a solvent Active Transport: Define active transport as movement of ions in or out of a cell through the cell membrane, from a region of their lower concentration to a region of their higher concentration against a concentration gradient, using energy released during respiration Discuss the importance of active transport as an energy-consuming process by which substances are transported against a concentration gradient, e.g. ion uptake by root hairs and uptake of glucose by epithelial cells of villi Osmosis: Define osmosis as the diffusion of water molecules from a region of their higher concentration (dilute solution) to a region of their lower concentration (concentrated solution), through a partially permeable membrane Describe the importance of osmosis in the uptake of water by plants, and its effects on plant and animal tissues Describe and explain the importance of a water potential gradient in the uptake of water by plants Schedule for Unit 3: Date / Day Activity Oct. 6 Day 3 Unit 2 Test ; Start Unit 3 – PP 1 Homework Animal and Plant Cell On a poster paper – draw and label parts of an Animal and Plant Cell (work in pairs) – in class and at home if needed - Due Oct. 10- you will get some class time on Oct. 10 as well ; For the poster: See Rubric Poster due next class Oct. 10 Day 7 Lab: 1 - Poster Continue with Animal Plant Cells PP 2 – continue to build poster in class include Leaf Structure Finish Posters and hand & Answer questions on WS – Due next in (45 minutes) ; Class & Do WS (p6-9) Lab activity 2: Look at prepared slides of Animal Cell and Plant Cells / Make slides – Cheek cells & Elodea Cells (Activity 2.1- 2.2 WS Oct. 21 Day 1 Review WS & Lab answers ; Oct. 8 Day 5 Oct. 23 Day 3 Quiz next class on Structure and Function of animal and plant cells Quiz 1 ; PP 3 – Diffusion Answer the questions for Activity 3.1 ; and 3.2 Lab 2: Diffusion Demo 1 and 2 (Activity 3.1/3.2) Oct. 27 Day 5 Oct. 29 Day 7 Oct. 31 Day 1 Nov. 4 Day 3 Nov. 6 Day 5 Go over questions & Quiz ; Do Osmosis PP 4; Lab 3: Osmosis (activity 3.3) Go over questions ; PP 5 Active Transport ; Start in class WS p. 1018 Answer Question of Activity 3.3 Go over WS; Lab 4: Different Solutions in Plants Quiz 2; Study for Test next class. **I will try to grade your quiz in class and go over it in class as well. Test on Unit 3 Quiz next class on Diffusion ; Osmosis and Active Transport Rubric for Cells Poster: Items 4 Points assessed Work compatibility with partner Poster itself Diagram Information Total : Student worked diligently on project ; proactive and communicating with partner ; no time wasted ; Teacher did not have to remind student to be on task Entire poster was used ; visually appealing and colorful A diagram of plant and animal cell was drawn with all the required components in proportion; this includes structure of the leaf ; each structure was labeled Every structure had detailed description of function using scientific language associated with the structure Finish WS for HW Test next class on Unit 3 3 Points 2 Points Student worked with partner ; was proactive most of the time ; very little time was wasted ; Teacher had to mention to stay on task Student worked with partner ; was some of the time proactive ; wasted time ; Teacher had to repeat to remain on task Some of the poster space was used ; was somewhat appealing and colorful Diagrams were partial with only some of the components drawn and or labeled Very little of the poster space was used ; was not very appealing visually Descriptions were partial ; limited use of scientific language Many details missing ; limited work Many elements missing from the diagram ; partial on too many items