Magnets and electromagnets - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
advertisement

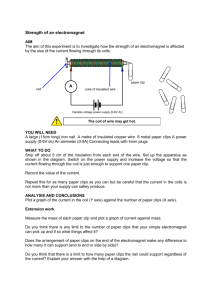
Technicians’ lists of equipment Downloaded from www.catalystscience.co.uk Catalyst 2, Unit J: Magnets and electromagnets Lesson J1: Magnetic fields Main activities J1a What do magnets do? For each group: 2 bar magnets small pieces of iron, nickel, copper and aluminium a compass J1b Magnetic forces For each group: Core, Help: selection of magnets labelled A, B, C and D (A and B should both be ‘strong’ magnets; C and D should be weaker than A and B.) Extension: four similar rods, labelled W, X, Y and Z, made of iron, brass, wood and a magnet bar magnet Plenary activities Looking ahead two bar magnets OHP iron filings acetate sheet (to prevent iron filings touching the magnets) Lesson J2: Magnets Starter activities Capture interest (2) magnet, clamp stand (to hold magnet vertically) thread blu tack paper clip various materials to test, e.g. iron, paper, aluminium, glass This list is in Microsoft Word, so it can be customised to fit each school’s requirements. 1 Technicians’ lists of equipment Downloaded from www.catalystscience.co.uk Catalyst 2, Unit J: Magnets and electromagnets Main activities J2a Plotting magnetic fields For each group: bar magnet (two for each Extension group) plotting compass A4 sheet of plain paper sharp, soft pencil J2b Using a compass to navigate For each group: map showing location of buried treasure and planned route chalk, tape or small object to indicate the starting point orienteering compass trundle wheel or measuring tape stick (or similar) with group name to mark position of treasure Lesson J3: Making magnets Starter activities Capture interest (1) test-tube two-thirds full of iron filings fitted with a tight stopper strong bar magnet small nails or pins to test that a magnet has been made Main activities J3a Making magnets For each group: steel strip bar magnet (possibly different strengths for different groups) paper clips access to a demagnetising coil carrying alternating current Help: test-tube of iron filings with a tight-fitting bung (pupils do not remove the bung) strong bar magnet plotting compass (to test for magnetism) This list is in Microsoft Word, so it can be customised to fit each school’s requirements. 2 Technicians’ lists of equipment Downloaded from www.catalystscience.co.uk Catalyst 2, Unit J: Magnets and electromagnets J3b Making a compass For each group: bar magnet blunt needle or straightened paper clip length of thread filter paper trough of water (large enough to float a needle or straightened paper clip) compass Plenary activities Looking ahead long iron nail (or similar) length of insulated wire wound around nail with turns touching and covering most of its length and with a minimum of 10 cm free at either end, two crocodile clips (to attach to ends of insulated wire), two connecting leads, low-voltage high-current power supply (e.g. Westminster type), small pins, paper clips or nails (to show that the nail is magnetised) Lesson J4: Electromagnets Main activities J4a Making an electromagnet Core: about 1 metre of plastic coated wire stripped at both ends two crocodile clips wooden cylinder (to form a coil of wire) low-voltage dc power supply two connecting leads heat-resistant mat plotting compass blu tack A4 sheet of plain paper Extension: about 1 metre of plastic coated wire stripped at both ends two crocodile clips low-voltage dc power supply two connecting leads clamp stand, or similar, to support wire in a vertical position plotting compass piece of card (about 15 cm square) with central hole This list is in Microsoft Word, so it can be customised to fit each school’s requirements. 3 Technicians’ lists of equipment Downloaded from www.catalystscience.co.uk Catalyst 2, Unit J: Magnets and electromagnets J4b Adding a core to an electromagnet For each group: about 1 metre of plastic coated wire stripped at both ends two crocodile clips wooden cylinder (to form a coil of wire) low-voltage dc power supply two connecting leads heat-resistant mat rods of various materials, as decided by the teacher paper clips or iron nails (to test the strength of the electromagnet) access to a demagnetising coil carrying alternating current Lesson J5: Variables Starter activities Bridging to the unit iron cylindrical core low-voltage, high-current power supply and variable resistor or variable power supply two crocodile clips very tiny magnetic objects, e.g. a few iron filings or tiny steel washers a large magnetic object, e.g. large iron weight or large toy car Lesson J5 Investigate: How to make an electromagnet stronger Main activities J5 Investigate: How to make an electromagnet stronger Core: about 1 metre of plastic coated wire stripped at both ends two crocodile clips wooden cylinder (to form a coil of wire) variable power supply ammeter connecting leads heat-resistant mat iron rod paper clips or iron nails (to test the strength of the electromagnet) access to a demagnetising coil carrying alternating current This list is in Microsoft Word, so it can be customised to fit each school’s requirements. 4 Technicians’ lists of equipment Downloaded from www.catalystscience.co.uk Catalyst 2, Unit J: Magnets and electromagnets Help: about 1 metre of plastic coated wire stripped at both ends connecting leads heat-resistant mat two crocodile clips iron rod wooden cylinder (to form a coil of wire) paper clips or iron nails (to test the strength of the electromagnet) low-voltage dc power supply This list is in Microsoft Word, so it can be customised to fit each school’s requirements. 5