Review W.S. & Answer Key for Rock & Mineral Test (includes half
advertisement
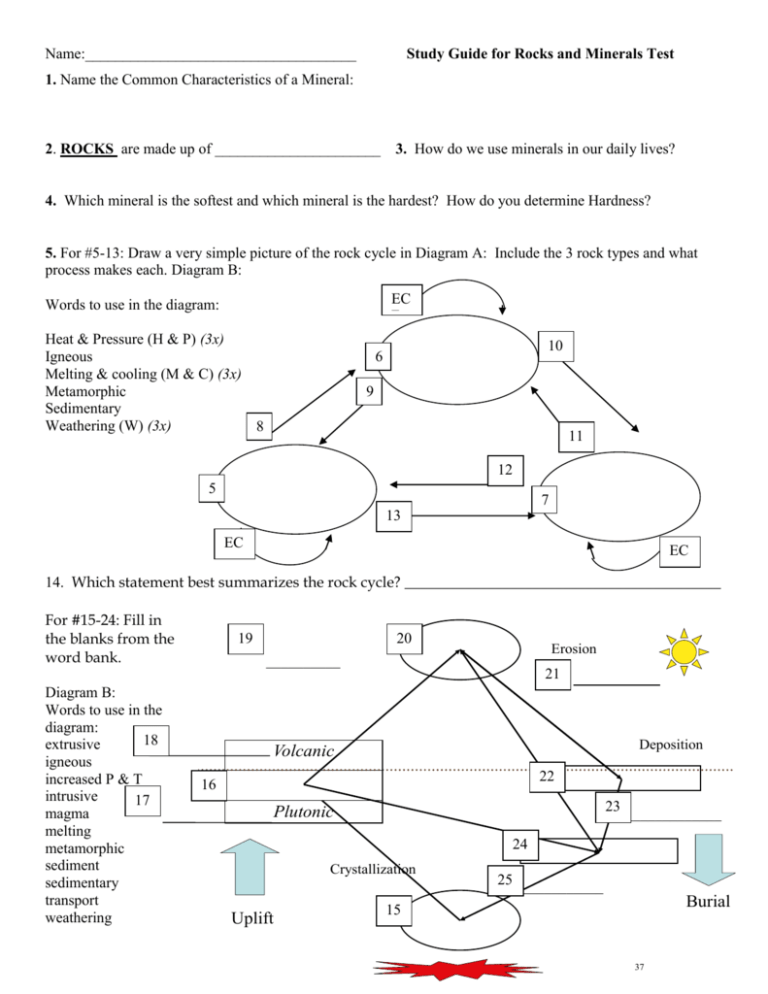
Name:____________________________________ Study Guide for Rocks and Minerals Test 1. Name the Common Characteristics of a Mineral: 2. ROCKS are made up of ______________________ 3. How do we use minerals in our daily lives? 4. Which mineral is the softest and which mineral is the hardest? How do you determine Hardness? 5. For #5-13: Draw a very simple picture of the rock cycle in Diagram A: Include the 3 rock types and what process makes each. Diagram B: EC F Words to use in the diagram: Heat & Pressure (H & P) (3x) Igneous Melting & cooling (M & C) (3x) Metamorphic Sedimentary Weathering (W) (3x) 8 10 6 9 11 12 5 7 13 EC F EC F 14. Which statement best summarizes the rock cycle? __________________________________________ For #15-24: Fill in the blanks from the word bank. Diagram B: Words to use in the diagram: 18 extrusive igneous increased P & T intrusive 17 magma melting metamorphic sediment sedimentary transport weathering 19 20 Erosion __________ 21 Deposition Volcanic 22 16 23 _____________ Plutonic 24 Crystallization Uplift 25 ____________ Burial 15 37 26. What role does gravity play in the rock cycle? What’s the difference between Mechanical and Chemical Weathering? 27. Mechanical Weathering: 28. Chemical Weathering: What’s the difference between Soil and Fossil Formation. 29. Soil Formation: 30 Fossil Formation: What are the characteristics for a rock that is metamorphic, igneous or sedimentary. 31. Metamorphic Rock: 32. Igneous Rock: 33. Sedimentary Rock: Name: _______________________________ Match each Rock Cycle Word with a Definition 1. Crystalization: ____ A. Ice, wind, snow, rain, etc. alter the rock. 2. Intrusive: ____ B. Sediments get placed in one spot. 3. Extrusive: ____ C. Temperature (heat) and pressure rises. 4. Weathering: ____ D, Cooling rock or forming crystals. 5. Erosion: ____ E. Moving of sediments. 6. Transport: ____ F. Rock that has been cooled underground. 7. Deposition: together 8. Compaction & Cementation: ____ G. When sediments get closer and stick ____ H. Rock that has been cooled on the surface. 9. Increased P& T: ____ I. Breaking down of rock into smaller pieces. Fill out your review worksheet as you travel around the rock cycle. When you successfully answer a review question you may move your game piece. Tally where you have been in the rock cycle and draw an arrow if you move to a new location. Igneous Rock To The Surface Cooling & Hardening Magma Weathering & Erosion Melting Sediments Metamorphic Rock Compaction & Cementation High Temp & Pressure Sedimentary Rocks Simplified Guided Notes: 1. Fill in the blank: Rocks are made up of Minerals 2. Be able to Circle the following Characteristics of a mineral: -Luster - Mineral Structure -Hardness -Color -Streak -Cleavage/Fracture -Density 3. Minerals help humans for example: A quartz is used in a time-keeping instrument 4. Talc is the softest: Hardness of 1 and Diamonds are the hardest: Hardness of 10. (To find out if a diamond is fake Scratch it against glass) 5.-14. Be able to draw this rock cycle and what process makes each type of rock Weathering Melting & Cooling 14. The rock cycle can be summarized as “Rocks can change from one form to another” 15- 25 . Rock Cycle Diagram: Extrusive Intrusive 26. Essay: Gravity plays a role in the rock cycle by breaking larger rocks into small pieces call sediments. This makes Sedimentary Rocks. Essay: 27. Mechanical Weathering is when rocks break into small pieces 28. Chemical Weathering is when rocks change chemically into a new substance. Essay: 29. Soil formation is when small rocks (sediments), water and humus (once living things) accumulate (or come together) to make soil. 20. Fossil formation is when hard parts of animals get trapped in sediment along with water and minerals to preserve the bone for a very long time. Know that: 31. Sedimentary Rocks: means that smaller pieces have been stuck together , it was once made of a living thing, or it has chemicals alter it on the surface 32. Metamorphic: have been squished under heat and pressure (it is sparkly, has lines or blotches) 33. Igneous rocks: have cooled quickly (glassy or gas pockets) or have cooled slowly (big crystals)\ THE HALF WORKSHEET: (If the student was absent, the back side was not necessary to complete). Name: _______________________________ Match each Rock Cycle Word with a Definition 1. Crystalization: _D__ A. Ice, wind, snow, rain, etc. alter the rock. 2. Intrusive: _F_ B. Sediments get placed in one spot. 3. Extrusive: _H__ C. Temperature (heat) and pressure rises. 4. Weathering: _A__ D, Cooling rock or forming crystals. 5. Erosion: _I__ E. Moving of sediments. 6. Transport: _E__ F. Rock that has been cooled underground. 7. Deposition: together _B__ G. When sediments get closer and stick 8. Compaction & Cementation: _G__ H. Rock that has been cooled on the surface. 9. Increased P& T: _C__ I. Breaking down of rock into smaller pieces.







