Set2.doc - E

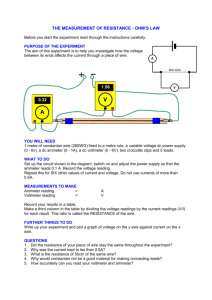
1. Ammeter in Figure 2.1 and Figure 2.2 are used to measure electric current in the circuits.
Constantan wire
A
6 V
V
A
6 V resistor
V
FIGURE 2.1 FIGURE 2.2
Circuit
Current
/ A
Potential difference /
V
2.0
Circuit
Figure
2.1
0.4
0.6 3.0
TABLE 2.1
(a) What is meant by electric current?
Figure
2.2
Current
/ A
0.3
0.5
TABLE 2.2
Potential difference /
V
3.0
5.0
[1 mark ]
(b) Based on Figure 2.1, Figure 2.2, Tablel 2.1 and Table 2.2, state the same caracteristics for:
(i) constantan wire and resistor,
(ii) readings of ammeter and voltmeter.
Then, relate all the characteristics to deduce a physics’s law.
State the physics’s law.
[5 marks ]
Dry cell
FIGURE 2.3
(c) Figure 2.3 shows a filament bulb connected to a dry cell which its internal resistance cannot be ignored. What will happen to the brightness of the bulb if a same filament bulb is connected in parallel to the first bulb.
Explain your answer.
[4 marks ]
(d) Figure 2.4 shows a cabin wiring consisting of a filament lamp, an air
conditioner and an electric kettle. The electric supply enters the cabin via
meter and fuse box.
Fuse box
Kotak fius
L
N
E
L – Live wire
Wayar hidup
N
– Neutral wire
Wayar neutral
E
– Earth wire
Wayar bumi
Filament lamp
Lampu filamen
To an air conditioner
FIGURE 2.4
To an electric kettle
Using your knowledge on electricity and Figure 2.4, suggest and explain suitable designs or ways to
(i) make the cabin wiring more effective
(ii) protect electric appliances from damage
(iii) prevent electric shock
(iv) increase energy efficiency
[10 marks ]
2. Figure 2(i) shows an electrical circuit consisting of a constantan wire, an ammeter, a voltmeter and a rheostat which are connected to a potential difference of 6V.
Figure2(ii) shows an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor, ammeter, voltmeter and rheostat which is connected to a potential difference of 6V. The readings from the ammeter and voltmeter are recorded in table 1.The rheostat was adjusted for both circuits and the ammeter and voltmeter readings are recorded in table 2.
Circuit
(i)
(ii)
Circuit
(i)
(ii)
FIGURE 2
I / A
0.2
0.3
TABLE 1
I/A
0.3
0.5
TABLE 2
V/V
1.0
1.5
V/V
1.5
2.5
(a)(i) What is potential difference?
[ 1 mark ]
(ii) From Figure 2(i), 2(ii), table 1 and table 2, relate the similarity in the ammeter reading and the voltmeter reading observed to deduce a relevant physics concept.
Name the physics concept.
[ 5 marks ]
(b) Figure 3(i) and Figure 3(ii) each shows two pieces of resistor connected in a series circuit and a parallel circuit respectively.
FIGURE 3
(i) State the difference in the ammeter reading and the voltmeter reading in Figure 3(i) and Figure 3(ii).
(ii) Explain your answers in b(i).
[ 2 marks ]
[ 2 marks ]
(d) Using the appropriate physics concept, suggest and explain suitable modifications to an iron so that ironing clothes can be done in short time.
[ 10 marks ]
First Situation Second Situation
First situation:
After the switch of a CRO is on, a light spot is formed on the CRO screen as shown in
Figure7(a).
Second situation:
When the television is on, the screen of the television displays a TV programme as shown in Figure 7(b).
3. The figure shows a starter motor of a car connected to a 12 V battery.
When the starter motor is switched on, high current flows from the battery to the motor through a wire. To reduce energy in it, the wire used is thick and short.
Using this information;
(a) make one suitable inference, [ 1 mark ]
(b) state one appropriate hypothesis that could be investigated.
[ 1 mark ]
(c) describe how would you design an experiment to test your hypothesis using constantan wire and other apparatus .
In your description, state clearly the following:
(i) aim of the experiment
(ii) variables in the experiment
(iii) list of apparatus and materials
(iv) arrangement of the apparatus
(v) the procedure of the experiment which include the method
of controlling the manipulated variable and the method of
measuring the responding variable
(vi) the way you would tabulate the data
(vii) the way you would analyse the data
[ 10 marks ]
4
.Diagram 7.1 and 7.2 shows two roadside stalls selling “ABC” and “PAU”.
Both stalls are using the same bulbs and batteries that are new. The bulb at the “ABC” stall is brighter than the bulb at the “PAU” stall.
Battery
Battery
DIAGRAM 7.1
DIAGRAM 7.2
Based on the above information and observation:
(a) State one suitable inference.
[1 mark]
(b) State one suitable hypothesis.
[1 mark]
(c) With the use of apparatus such as dry cells, a constantan wire and other apparatus, describe an experiment framework to investigate the hypothesis stated in 5(b).
(i) Aim of the experiment.
(ii) Variables in the experiment.
(iii) List of apparatus and materials.
(iv) Arrangement of apparatus.
(v) The procedure of experiment which include the method of controlling the manipulated variable and the method of measuring the responding variable.
(vi) The way you would tabulate the data.
(vii) The way you would analyse the data.
[10 marks]
5.Diagram 9.1 shows a bar magnet is pushed slowly into the solenoid.
Diagram 9.2 shows a bar magnet is pushed quickly into the solenoid
magnet
solenoid
DIAGRAM 9.1
Based on the observations:
DIAGRAM 9.2
(a) State one suitable inference that can be made. [ 1 mark ]
(b) State one appropriate hypothesis for an investigation. [ 1 mark ]
( c ) By using the apparatus like magnet, meter ruler, coil and
others, describe an experimental framework to test your
hypothesis.
In your description, state clearly the following:
(i) Aim of the experiment
(ii) Variables in the experiment
(iii) List of apparatus and materials
(iv) Arrangement of the apparatus
(v) The procedure of the experiment which include the method
of controlling the manipulated variable and the method of
measuring the responding variable
(vi) Way you would tabulate the data
(vii) Way you would analyse the data [ 10 Marks]