Electricity Summary Notes: Circuits, Current, Voltage, Safety
advertisement
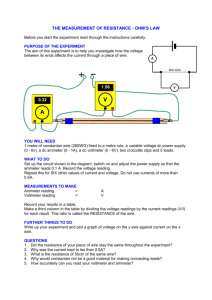
ELECTRICITY Summary Notes 1.REVISION OF PS ELECTRICITY (A) When drawing components in an electric circuit, SYMBOLS are used component symbol energy change wire none cell chemical to electrical battery chemical to electrical switch none buzzer electrical to sound lamp electrical to light motor M electrical to movement 2.REVISION OF PS ELECTRICITY (B) In a series circuit components are connected one after another with no branching: Examples of series circuits include: Christmas tree lights Switches and fuses Electric current WILL pass through a conductor and will NOT pass though an insulator. 3. SIMPLE CAR CIRCUITS In a parallel circuit components are connected “side-by-side” so that the circuit branches. Examples of parallel circuits include: House circuits Car circuits 4. MEASURING ELECTRIC CURRENT (A) An ammeter is used to measure current in units of amps (A). An ammeter is always connected in series 2A 2A 2A 2A A The current is the same at every point in a series circuit. 4. MEASURING ELECTRIC CURRENT (B) The currents in the branches of a parallel circuit add up to the current from the source. 3A 3A 1A 1A 1A 5. MEASURING ELECTRIC VOLTAGE (A) A voltmeter is used to measure voltage in units of volts (V). A voltmeter is always connected in parallel. V 5. MEASURING ELECTRIC VOLTAGE (B) The voltage across each branch in a parallel circuit is equal to the voltage across the battery. 3V 3V 3V 3V 5. MEASURING ELECTRIC VOLTAGE (C) The voltages across each component in a series circuit add up to the voltage across the battery. 3V 1.5V 1.5V 6. ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE Circuit components resist current. The greater the resistance the smaller the current. A thin wire has more resistance than thick wire. A long wire has a greater resistance than short wire 7. STAYING SAFE WITH ELECTRICITY Passing a current in a wire causes it to heat up. If the current in a wire gets too high, fuses are used to protect the wire. the fuse melts and breaks the circuit. this stops the current and keeps the wire safe.