Density Lab

Determining the Density of Solids
Background Information:
Density is a physical property of a substance that is often useful in identifying the substance. This is because the density of a substance always remains the same at a given temperature and pressure. Density may be thought of as how heavy an object is for its size, or the ratio of an object’s mass to its volume.
In this investigation, you will determine the density of several objects by measuring their mass and volume by methods that you have used in previous experiments and then using the formula
D=M/V
.
Problem: How is the density of a solid object determined?
How is mass of a solid object determined?
How is volume of a determined?
r
Volume of a cylinder
h
=
3.14 x r 2 x h
(measured in cubic units)
H
L
Volume of cubic shaped object
= L x W x H
(measured in cubic units)
W
Part A: Regular Solids
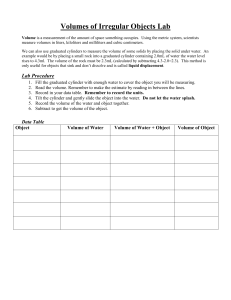
Find the mass and volume of the regular solids by measuring their dimensions to the nearest .01 cm and calculating their volumes with the appropriate formulas. Round your answer to the nearest 0.1 cm 3 . Then, use the balance to determine their mass to the nearest 0.1g. Calculate the density and round your answer to the nearest 0.1g/mL.
Object Dimensions Volume Mass Density (D=M/V)
Cube 1 ____________
Cube 2 ____________
_______ ______ ______
_______ ______ ______
Cube 5 ____________
Cube 7 ____________
Cube 9 ____________
Light Cube ____________
Heavy Cube____________
Cylinder 1 ____________
Cylinder 2 ____________
Cylinder 3 ____________
Cylinder 4 ____________
_______ ______ ______
_______ ______ ______
_______ ______ ______
_______ ______ ______
_______ ______ ______
_______ ______ ______
_______ ______ ______
_______ ______ ______
_______ ______ ______
Metal Bar ____________ _______ ______ ______
Part B: Irregular Solids
Determine the density of
marble chips
and
metal nuts
:
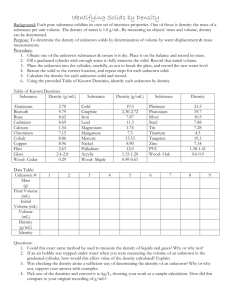
Put 40-50mL of water into a 100mL graduated cylinder. Accurately record the volume of water to the nearest 0.1mL. Obtain the mass of the graduated cylinder and water with your balance and record the mass to the nearest 0.1g. Add 20-30 marble chips to the graduated cylinder and gently tap out any air bubbles. Record the new volume level in the graduated cylinder to the nearest 0.1mL. Obtain the mass of the graduated cylinder and its contents and record the mass. Calculate the density of the marble chips to the nearest 0.1g/mL. Repeat the experiment with the metal nuts.
1. Starting volume of water:
2. Mass of graduated cylinder and water:
3. Volume of water and objects:
4. Mass of graduated cylinder, water and objects: ________
5. Volume of objects: (#3 - #1)
6. Mass of objects: (#4 - #2)
7. Calculate the density of the marble chips (show your work):
8. Calculate the density of the metal nuts (show your work):
Conclusions:
Marble Chips Metal Nuts
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
1. How do the densities of the small cubes (light and heavy) compare?
2. How do the densities of metal cylinders compare?
3. Are there any similarities between the large cubes and the light cube?
4. Are there any similarities between the large cubes and the heavy cube?
5. Which cube(s) could be made of the same material as the metal bar? Why?
6. Which cylinder(s) could be made of the same material as the metal bar? Why?
7. Could Cube 2 and the metal bar be made of the same metal? Why or why not?
8. Determine the probable identities of the substances that comprise the 4 metal cylinders (look at the know densities at the bottom of the lab):
9. What effect does the shape of an object have upon its density?
10. Based upon your data, what can you conclude about the density of an object that floats in water?
11. Based upon your data, the metal nuts are probably composed of what material?
Why?
MATERIAL
Aluminum
Brass
Cobalt
Copper, Pure
Gold, Pure
Iron, wrought
Lead
Tantalum
Magnesium, Pure
Kevlar 49
Silicon carbide
Rubber
Graphite
Steel
Water
Density (g/cm 3 )
2.643
8.553
8.8
8.9
19.32
7.658
11.37
16.6
1.7
1.44
3.2
1.506
2.163
7.85
1.00