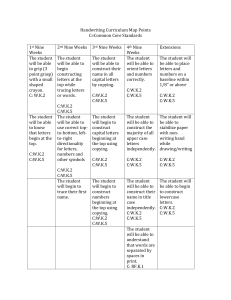
Ardenne High School Grade 9 Curriculum Guide
advertisement

Ardenne High School Curriculum Guide Grade 9 Revised 2013 Table of Contents Language Arts and Literature Department English Language ……………………………………………..…………………………………….2 English Literature ……………………………………….…………………………………………6 Modern Languages Department French……………………………………………………………………………………………….10 Spanish………………………………………………………………………………………………17 Mathematics Department Mathematics……..……………………………………………………………………………….….25 Science Department Physics…………………………………………………………………………………………….….34 Biology ……………………………………………………………………………………….........41 Chemistry ………………………………………………………………………………………….…46 Agricultural Science ……………………………………………………………………………..…..52 History Department History…………..……………………………………………………………………………………56 Personal Development Department Personal Development…..……………………………………………………………………..……62 Home Economics / Industrial Arts Department Design Technique ……………………………………………………………………………………66 Home and Family ……………………………………………………………………………………70 Religious Education Department Religious Education……………………………………………………………………..……………73 Visual Arts Department Visual Arts……………….……………………………………………………………….…………..78 Physical Education Department Physical Education……….………………………………………………………………..……….…82 Geography Department Geography ………………………………………………………………………………………….…86 Business Information Technology ………………………………………………………………………………95 © 2011 Ardenne High School ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE ENGLISH LANGUAGE DEPARTMENT ENGLISH LANGUAGE CURRICULUM Introduction This English Language Curriculum is created with the view of fostering in Grade 9 students an extensive appreciation of language learning and language use. The guide is structured to allow for the development of competence through the acquisition of the five basic literacy skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing and viewing. Upon completion of this course of study, all grade 9 students are expected to communicate more effectively in Standard Jamaican English through the use of more complex structures in speech and writing. © September 2 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE ENGLISH LANGUAGE Grade 9 Topic/Content 1. MECHANICS – Revision of: *Parts of speech *Figures of speech *Subject-verb Agreement *Spelling 2. VOCABULARY *Using the dictionary *Prefixes and suffixes *Forming adjectives 3. GRAMMAR *Verb tenses *Error Recognition *Homophones 4. TYPES OF WRITING *Descriptive Writing *Narrative Writing 5. COMPREHENSION SKILLS © September SEMESTER ONE : September - January Objectives Students should be able to: Recognize the different parts of speech Recognize different figures of speech Use different parts of speech and figures of speech Spell given words Select correct forms to complete given sentences Students should be able to: Identify and define prefixes and suffixes Add prefixes and suffixes to existing words to make new words Students should be able to: Use tenses appropriately and consistently Identify and explain grammatical errors in sentences Differentiate between words which are similarly spelt Students should be able to: Identify elements of a descriptive passage Write descriptive passages Differentiate between a descriptive passage and a narrative passage Identify the elements of narrative writing Write narrative passages Students should be able to: Identify main ideas Respond appropriately to literal, inferential and critical level questions Decipher unfamiliar words using context clues 3 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 6. MECHANICS *Synonyms *Antonyms *Sentence Completion *Clauses/Phrases Topic/Content 7. MECHANICS/ERRORS IN WRITING *Direct and Indirect Speech *Redundancy *Clichés *Idioms *Slang *Usage Students should be able to: Select the correct synonym/antonym for given words Use given words to complete given sentences Recognize clauses and phrases Use given words correctly SEMESTER TWO : February - June Objectives Students should be able to: Change sentences from direct to indirect speech and vice versa Recognize and correct repetition of words, ideas and word meanings Recognize and avoid clichés, idioms, slang Use words in proper context 8. LETTER WRITING *Formal Letters *Report Writing Students should be able to outline: Kinds of formal letters Parts of a formal letter Tone and content of a formal letter Tone, content and format of a simple report 9. TYPE OF WRITING *Persuasive Writing Students should be able to: Identify and use persuasive techniques © September 4 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 10. COMPREHENSION 11. MECHANICS *Synonyms *Antonyms *Spelling *Sentence Completion Write persuasive pieces Participate in debating competitions Refer to #5 Students should be able to: Select the correct synonym/antonym for given words Use given words to complete given sentences Use given words correctly Spell given words ASSESSMENT: A unit test will be done at the end of each unit. For each sub-topic students will be assessed using graded class work and homework assignments along with any other form of assessment the teacher may devise. Homework : 25% of the overall grade for the semester Class Work : 25% of the overall grade for the semester Tests : 50% of the overall grade for the semester RECOMMENDED TEXTS A Comprehensive English Course Book 3 Grammar and Composition 3 by Nancy Cox et al Longman Study Dictionary and Thesaurus © September 5 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE ENGLISH LANGUAGE DEPARTMENT ENGLISH LITERATURE CURRICULUM Introduction Literature provides an approach to the three genres - drama, prose and poetry and the interaction with varying literary works as an active enterprise involving thought and feeling. Students should be encouraged to consider why they respond as they do and how these responses change as they engage in subsequent readings of these pieces. Students should be encouraged to relate their experiences in reading literature to their experience of living. They should be encouraged moreover, to see literature as a significant reflection of life and also an imaginative extension of its possibilities. This is the premise on which this guide is constructed. Consequently, the aims and objectives are selected with the view that the lessons will be so structured that students will have an opportunity to vicariously experience other ways of life, culture, beliefs, language and practices through literature teaching. Aims: To develop an appreciation for literary works To sensitize students to the differences in the genres To develop the habit of critically evaluating and questioning situations and events in the texts and by extension real life To develop an appreciation for differing cultures, languages, practices and beliefs. © September 6 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SEMESTER ONE – SEPTEMBERJANUARY CONTENT 1. STUDYING THE GENRES OF LITERATURE Prose Poetry Drama 2. INTRODUCTION TO DRAMA Studying Elizabethan Drama Prescribed text The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare OBJECTIVE Differentiate between the various literary genres Discuss the elements of each genre Appreciate the different forms of literature Features of Drama Revise the elements of Drama Examine the use of dialogue in drama Examine the presentation of the characters Examine the use of setting in the play Examine the presentation of mood and atmosphere Analyze the writer’s style Identify and examine the themes in the play. 3.THE SHORT STORY Areas of study Examine the presentation of characters Story comprehension and Explore the presentation of themes analysis Examine the use of setting in the story Selected Stories from A World Examine the structure of the story (plot, conflict, climax and resolution) of Prose Analyze the writer’s style Substantiate interpretations of texts with adequate and relevant detailsorally and written © September 7 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 4. POETRY Poetry comprehension and analysis Selected poems from A World of Prose SEMESTER TWO - FEBRUARYJUNE CONTENT 5.THE NOVEL The West Indian Novel Prescribed Text Miguel Street by V.S Naipaul 6. THE SHORT STORY Story comprehension and analysis Selected Stories from A World of Prose © September Areas of study Identifying types/forms of poems Uncovering the meaning of poems Examining the use of diction (denotative/connotative language) Examining the poets’ use of rhythm and rhyme Examining the use of imagery Examining the use of figurative language Examining the thematic significance of each poem OBJECTIVES Areas for Analysis Examine the presentation of characters Discuss the development of each character and the effect they have on the main character Explain how setting influences the character’s actions Identify and discuss the main themes Identify the narrative technique Examine the structure and its relationship to the presentation of issues Areas of study Examine the presentation of characters Explore the presentation of themes Examine the use of setting in the story Examine the structure of the story (plot, conflict, climax and resolution) 8 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 7. POETRY Poetry comprehension and analysis Selected poems from A World of Prose Resources The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare A World of Prose edited by David Williams and Hazel SimmonsMcDonald A World of Poetry edited by Mark Williams and Hazel SimmonsMcDonald Miguel Street by V.S Naipaul © September Analyze the writer’s style Substantiate interpretations of texts with adequate and relevant detailsorally and written Areas of study Identifying types/forms of poems Uncovering the meaning of poems Examining the use of diction (denotative/connotative language) Examining the poets’ use of rhythm and rhyme Examining the use of imagery Examining the use of figurative language Examining the thematic significance of each poem ASSESSMENT: A unit test will be done at the end of each unit. For each subtopic students will be assessed using graded class work and homework assignments along with any other form of assessment the teacher may devise. Homework : 25% of the overall grade for the semester Class Work : 25% of the overall grade for the semester Tests : 50% of the overall grade for the semester 9 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE MODERN LANGUAGES FRENCH CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The third year of the French foreign language programme is designed to help students to continue the development of their foreign language skills. They will be taught not only the grammatical structures that will enable them to pass written exams but will also be able to speak the language in a wide range of situations at an intermediate level. © September 10 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE TOPIC/CONTENT OBJECTIVES LISTENING Students will be able to: Read, sing and perform other forms of oral interactions. Understand regular classroom instructions. SPEAKING Students will be able to: Talk about themselves, their family, friends, pastime or leisure activities Do dramatization where they act out various scenes in the foreign language Carry out basic conversations using learned sounds and phonetic patterns. Ask and answer questions. Talk about school describing in more details the subjects they do and how well they do them. READING WRITING © September Students will be able to: Read short passages in French using correct pronunciation and intonation. Read and write basic instructions. Students will be able to: Write short compositions and/or letters where they express ideas using the past tense. Complete written grammar and vocabulary exercises from different sources. 11 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE CULTURE Students will be able to: Develop an appreciation of the French language and of people of francophone culture. SEMESTER I (SEPTEMBER – JANUARY) TOPIC/CONTENT OBJECTIVES 1. A GENERAL REVISION OF GRAMMAR - Present Tense of Regular & Irregular Verbs -General revision of Vocabulary Students should be able to: Use tenses correctly to describe their actions orally Talk in more detail about themselves, their family and friends Talk about school: describe in more details the subjects they do and how well they do in them - The passé composé of verbs that take Students should be able to: avoir - To form the past participle of regular Say more about what they did and irregular verbs Say what has happened and what they have done -To conjugate more irregular verbs in Talk about a place they have recently visited the present tense: ouvrir, souffrir, offrir Ask and answer questions about past events - To use more negative expressions Ask and answer negatively to questions © September 12 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE October – December 2007 -To form the past tense of verbs that are conjugated with être that is, reflexive verbs and those from the acronym DR MRS VANDER TRAMP. - To form the past participle of verbs that take être and distinguish between these and the ones that take avoir -Use negative expressions with verbs in the past tense -Conjugate some rare irregular verbs such as partir, sortir, couvrir. Students should be able to: - Use qui/que/qu’ in sentences. - Revise object pronouns Say more about what they did using other verbs Describe past actions. Use these pronouns in simple sentences. Recall the use of object pronouns in simple sentences. Use object pronouns appropriately. January General Revision Semester II (February – June) The imperfect tense The imperfect and together © September passé Students should be able to : Talk about their daily routine composé Say what they prefer. Talk about things in the past 13 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE The comparison of adjectives/ adjectives that precede the noun. Write about what they used to do and places they used to visit. Describe people or themselves in the past. Discuss past holiday activities. Compare the past and the present. Use the imperfect tense to describe an outing etc. Compare persons in the past Superlative of adjectives Relative pronouns: lequel, laquelle, lesquels, lesquelles Demonstrative Pronouns celui, celle, ceux, celles Rare irregular verbs offrir, craindre, couvrir Two pronouns together JUNE: General Revision © September 14 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE RESOURCE MATERIAL USED IN GRADE 9 Main texts Hexagone 2 by Ken Foden Encore Tricolore: Examination Grammar in Action by Sylvia Honnor and Heather Mascie- Taylor Other material to be used Encore Tricolore 2: nouvelle edition by Sylvia Honnor and Heather Mascie-Taylor French First Year by Eli Blume and Gail Stein Deuxième Livre: Third Edition by Eli Blume French Grammar: 11 – 14 by Rosi McNab Assessment © September Classwork: 25% Homework 25% Test 50% 15 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE MODERN LANGUAGES DEPARTMENT SPANISH CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The goal of the curriculum is for Spanish is mainly to: Further the development of the four skills of listening, reading, speaking and writing by allowing students to: carry out instructions given orally respond accurately to situations arising from context taught e.g. travel, sports, accident read with understanding, correct pronunciation, intonation and fluency role play situations arising from topics taught describe things and persons and weather conditions in the past talk about things they did, were doing or used to do in the past give commands and instructions to family, friends and strangers follow simple instructions/commands given continue presenting the Spanish language as an integral element of the culture and to show the similarities of that culture and the Jamaican culture. continue to encourage an appreciation of Spanish by way of: o inter-school activities such as Spanish Festival © September 16 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE o cultural activities such as Spanish Week, Spanish Carol service, Spanish Awards Ceremony SEMESTERS 1 & 2 TOPIC / CONTENT 1. PERCEPTIVE LISTENING 2. PERCEPTIVE READING 3. PRODUCTIVE SPEAKING 4. PRODUCTIVE WRITING © September OBJECTIVES Students should be able to: 1. carry out instructions given orally 2. answer comprehension questions after listening to simple statements, the listening of a dialogue and or passage Students should be able to: 1. read with correct pronunciation and intonation 2. comprehend what is read Students should be able to: 1. give appropriate responses to situations arising from contexts taught 2. role-play in situations arising from topics 3. give and ask for opinions 4. answer in the negative 5. make comparisons 6. understand and respond to commands 7. give commands to different individuals 8. talk about what people like and do not like 9. tell what they used to do in the past 10. talk about what was happening in the past 11. relate what happened in the past Students should be able to: 1. give responses to situations from topics taught 2. relate past events 3. write dialogues based on the traveling experience 17 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 5. CULTURE 6. GRAMMAR 7. VOCABULARY Students should become more familiar with the Latin American culture. Emphasis will be placed on the types of sports practiced. 1. Students should learn the grammar rules arising out of the contexts taught, thus improving their receptive and productive skills. a. revise, learn and practice required tenses with correct conjugation: Present Continuous, Past Continuous, Preterit, Imperfect Tenses 2. Students should expand their vocabulary, thus enabling them to: a. function in the context taught b. write on the subject area taught SEMESTER 1 (September – January) General Revision: - Useful classroom expressions - Present tense of irregular verbs Students should be able to: 1. introduce themselves e.g. name age, career choice, e.g. 2. revise grammar areas from previous year group. e.g. – stem-changing verbs, tener que + infinitive 3. Orals 4. talk about themselves 5. talk about their daily routine ¿Qué Hay? Libro del Alumno 3 – Students should be able to: © September 18 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Units 1-4 Theme – Travelling Topics: - Modes of transportation -Planning a trip -Booking a flight -Going through customs - Asking for/giving directions - Commands – Singular and Plural/ Polite and Familiar (including stemchanging and irregular verbs) -Reserving a hotel -Making complaints about things and services at the hotel -Street signs Vocabulary - vocabulary related to being at customs, the airport, at the travel agency 1. discuss different modes of transportation 2. respond appropriately to questions at the airport, travel agency, customs, immigration 3. ask and respond correctly to the arrival and departure of flights 4. say where they plan to stay in the country 5. ask for and list places of interest in an area 6. ask for and give directions 7. book rooms in a hotel 8. make complaints about things and services at a hotel Orals 1. role play at the travel agency/airport/customs/hotel lobby 2. interviews about hobbies Students should be able to: 1. fill out travel related forms 2. respond to situations on traveling 3. write dialogue on traveling - personal travel information e.g. place of birth, accommodation at destination, length of stay, etc. 4. PRODUCTIVE WRITING 5. CULTURE © September 1. Design signs/commands to the general public 2.Write dialogues making use of commands 3.Design fliers advertising modes of transportation 1. Students should become familiar with some places of interest in Mexico – 19 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE La Torre Latinoamericana; El Zόcalo 6. GRAMMAR Students should learn the grammar rules arising out of the contexts taught, thus improving their receptive and productive skills. Polite and Familiar, Singular and Plural Commands 7. VOCABULARY Students should expand their vocabulary, thus enabling them to: 1. function in the context taught 2. write on the subject area taught SEMESTER 2 (February – June) Students should be able to: ¿Qué Hay? Libro del Alumno 3 – Units 5 - 8 Topics: -discussing past vacations -discussing past actions -shopping in the market Grammar -Preterite Tense of regular AR, ER and IR verbs © September Talk/write about times of year they take trips Talk/write about trips they had taken Talk/write about activities they had done on trips Talk/write about places of interest they had visited on trips Talk/write about persons they had visited on trips Pronounce high numbers in Spanish Deal in different weights and currencies from Latin-American countries and Spain 20 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE -Preterite Tense of GAR, CAR and ZAR verbs -Preterite Tense of verbs with spelling changes -Preterite Tense of irregular verbs -Preterite Tense with direct object pronouns -Demonstrative adjectives -Demonstrative pronouns -Superlatives – el más/ ísimo Learn how to buy food in different situations Orals 1. Carry out conversation with store/market clerks 1. PERCEPTIVE LISTENING Students should be able to: 1. carry out instructions given orally 2. answer comprehension questions after listening to simple statements, the listening of a dialogue and or passage 2. PERCEPTIVE READING Students should be able to: 1. read with correct pronunciation and intonation 2. comprehend what is read 3. PRODUCTIVE SPEAKING © September Students should be able to: 1. give appropriate responses to situations arising from contexts taught 2. role-play in situations arising from topics 3. tell what happened in the past 4. ask for various shopping items 5. make comparisons about food items 21 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 4. PRODUCTIVE WRITING Students should be able to: 1. give responses to situations from topics taught 2. write about past experiences 3. write dialogues based on the shopping experience 4. write a shop list in Spanish 5. CULTURE Students should become more familiar with the Latin American culture in terms of some food items and currencies. 6. GRAMMAR Students should learn the grammar rules arising out of the contexts taught, thus improving their receptive and productive skills. 1. revise, learn and practice required tenses with correct conjugation: Preterite Tense, Object Pronouns 7. VOCABULARY Students should expand their vocabulary, thus enabling them to: 2. function in the context taught 3. write on the subject area taught GENERAL REVISION OF THE AREAS TAUGHT IN SEMESTERS ONE AND TWO STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO: HAVE A CLEAR UNDERSTANDING AND REMEMBRANCE OF THE AREAS TAUGHT IN SEMESTERS ONE AND TWO! Assessment © September Classwork: 20% Homework 20% Test 60% 22 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE MATHEMATICS DEPARTMENT MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The purpose of the mathematics curriculum is to help students acquire a range of mathematical techniques and skills to foster and maintain the awareness of the importance of accuracy. make Mathematics relevant to the interest and experience of the students, helping them to recognize Mathematics in their environment. cultivate the ability to apply mathematical knowledge to the solution of problems which are meaningful to students as citizens help students think logically and critically prepare students for the use of Mathematics in further studies. NB: Algebra (Unit 8) is to be done one day per week © September 23 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SEMESTER 1 (SEPTEMBER – JANUARY) OBJECTIVES CONTENT UNIT 1 – NUMBER INDICES Students should be able to 1. State the meaning of a m , where a and m are whole numbers. 2. Evaluate expressions of the form a m and a m b n where a, b, m and n are whole numbers APPROXIMATION AND STANDARD FORM 1. Round off any decimal number to a given number of decimal places. 2. Write any number to a given number of significant figures. 3. Write any given number in standard form RATIO 1. Identify quantities in proportion 2. Solve problems involving direct or indirect proportion. © September 24 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE UNIT 2 – MEASUREMENT AREA Students should be able to 1. Convert from unit of area to another 2. Use Area s(s a)( s b)( s c) where s abc to 2 find the area of a triangle. 3. Calculate the area of the region enclosed by a parallelogram, rhombus, trapezium and circle and any combination of them. 4. Calculate the length of an arc of a circle using angles at the centre that are factors of 360º 5. Calculate the area of sectors as in specific objective 3 above. 6. Calculate the surface area of simple right prisms, pyramids and spheres VOLUME 1. Find the volume of right prisms using Ah [area of crosssection x length (height) ] 2. Convert from unit of volume to another 3. Find the volume of composite solids 4. Find the capacity of any solid container in litres. © September 25 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE PYTHAGORAS’ THEOREM 1. Use an investigative method to derive Pythagoras’ theorem. 2. Use Pythagoras’ theorem to find the length of sides in right-angled triangles. UNIT 3- GEOMETRY 1 ANGLES AND STRAIGHT LINES Students should be able to 1. Identify angles formed when a transversal cuts parallel lines. 2. Solve problems involving properties of angles and straight lines TRIANGLES 1. Identify the types of triangles and state the number of lines of symmetry 2. Use the angle properties of triangles to solve problems QUADRILATERALS 1. Identify the different types and quadrilaterals and state the number of lines of symmetry that each has. 2. Use angle properties of quadrilaterals to solve problems OTHER POLYGONS 1. Calculate the sum of interior and exterior angles of polygons of n sides. 2. Use the angle properties of these polygons to solve problems. © September 26 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SEMESTER 2 (FEBRUARY – JUNE) UNIT 4- GEOMETRY 2 TRANSFORMATIONS Translations Reflection Rotation Enlargements Students should be able to x 1. Translate any shape using a column vector T = y 2. State the relationship between an object and its image after it undergoes a translation 3. Reflect any in a given line 4. State the relationship between an object and image after a reflection 5. Rotate any shape given a centre, angle of rotation and the specified direction. 6. State the relationship between an object and its image after a rotation 7. Locate the image of an object under an enlargement 8. State the relationship between an object and its image after an enlargement. 9. Identify and describe a transformation given an object and its image. © September 27 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE UNIT 5-TRIGONOMETRY THE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS Students should be able to 1. Identify the three sides of a right-angled triangle in relation to a given angle. 2. Determine the sine, cosine and tangent of acute angles in right-angled triangles. 3. Use the sine, cosine or tangent ratios in the solution of right angled-triangles ANGLES OF ELEVATION AND DEPRESSION 1. Read and interpret worded problems identifying a. Where the person is standing b. The location of the object c. Line of sight d. The angle of elevation or depression. 2. Draw the right-angled triangle and insert data from the problem given 3. Use an appropriate trigonometric ratio to find the required height or distance BEARINGS 1. Identify the starting point and general direction of any three-figure bearing. 2. Draw diagrams to illustrate bearing problems. 4. Use the trigonometric ratios to solve problems involving bearings © September 28 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE UNIT 6- CONSUMER ARITHMETIC PERCENTAGES Students should be able to 1. Calculate profit or loss as a percentage 2. Calculate discount, sales tax and profit or loss when these are given as a percentage 3. Solve problems involving marked price (or selling price), cost price, percentage profit, loss or discount HIRE PURCHASE 1. Solve simple problems involving payments by installments (hire purchase/mortgages) 2. Identify ‘best buys’ 3. Calculate total hire purchase costs 4. State the advantages or disadvantages of buying goods on hire purchase versus cash FOREIGN EXCHANGE 1. Recognize the concept of exchange rate 2. Convert between currencies in the operations of buying, selling and earning INTEREST AND BANKING Calculate simple interest, principle, time rate or amount SIMPLIFICATION 1. Use the four operations to simplify algebraic expressions 2. Use the distribution law to expand algebraic expressions. 3. Simplify algebraic fractions 4. Factorize simple algebraic expressions © September 29 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE EQUATIONS 1. Solve linear equations in one unknown (review) 2. Solve equations involving fractions 3. Solve simultaneous equations using the elimination and substitution methods 4. Change the subject of simple formulae INEQUALITIES 1. Use inequalities to solve story related problems 2. Devise simple problems which give rise to inequalities 3. Solve simple inequalities © September 30 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE ASSESSMENT: A unit test will be done at the end of each unit. For each sub-topic students will be assessed using graded class work and homework assignments along with any other form of assessment the teacher may devise. Homework : 20% of the overall grade for the semester Class Work : 30% of the overall grade for the semester Tests : 50% of the overall grade for the semester MATERIAL AND EQUIPMENT: Oxford Mathematics for the Caribbean Book 3 Sturdy notebook Set of Mathematical instruments Large graph book Scientific calculator © September 31 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SCIENCE DEPARTMENT PHYSICS CURRICULUM Introduction Apart from developing a knowledge base in physics in preparation for eventually qualifying for the entry to the course of preparation for the CSEC examination in Grades 10 and 11, this course is designed to develop students’ interest in the subject, as well as an understanding of its relevance to the everyday life. GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of the course, students should be able to a) Recall some basic laws, principles, data and experiments. b) Understand the concepts associated with the said laws and principles. c) Apply the laws and principles to simple everyday phenomenon (e.g. machines, electricity, temperature) d) Use the data to solve problems related to the laws and principles. e) Demonstrate acquired experimental skills including the ability to © September 32 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE (i) Manipulate simple apparatus, given the necessary instructions (ii) Observe, record and report, in a logical and systematic format, in relation to investigations performed or demonstrated (iii) Analyze simple data and draw inferences from such analysis, bearing in mind limitations, as well as steps need to be taken to improve the quality of these experiments. (iv) Plan and design ways for investigating simple everyday observation related to the principles of physics. It is the intention that, at the end of the course, students will be better able to make more informed choices toward their future development in the higher Grades and their careers. © September 33 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Physics Topic/ Content MECHANICS / HYDROSTATICS (1) MOMENTS © September Objectives Students should be able to: 1. Associate the moment of force with its ability to turn an object about a point or axis. 2. Define moment of force about a point or axis as the product of force and perpendicular distance from the point or axis to the line of action of force. 3. Do a simple calculation to determine the moment of force. 4. Recall and understand the terms, fulcrum, balance point, clockwise moments, anti clockwise moments, equilibrium. 5. State the two conditions for equilibrium about a point, namely that (i) The sum of clockwise moments must balance(must be equal to) the sum of the anti clockwise moments about that point. (ii) The sum of forces in any given direction must be equal to the sum of forces in the opposite direction. 6. Apply the condition for equilibrium to the cause of a simple leaver, appreciating that there is force acting at the fulcrum or balance point. 7. Define the three classes of leavers and give at least two examples of each class. 8. Determine the unknown value of a mass, using the principle of moments and construction. 9. Understand the concept of center of gravity. 10. Understand the concepts stable, und\stable, neutral equilibrium. 11. Apply the concept of center of gravity to object in (a) stable, (b) und\stable, (c) neutral equilibrium. Determine the center of gravity of a lamina 34 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE (2) DENSITY Students should be able to: 1. Students should be able to appreciate that different substances (e.g. iron, wood) contain different amounts of matter in equal volumes. 2. Define density as the amount of mass (matter) in unit volume (1 cubic meter) 3. Recall the S.I. unit for mass, volume and density. 4. Do calculations related to mass, volume and density. 5. Use a “eureka can”/ “overflow can” and a balance to determine / compare the densities of different solid irregular substances. 6. Use venier calipers to determine the volume of regularly shaped substances and hence determine the density of substances. Use measuring cylinders to determine volume and hence determine density of substances. MECHANICS (3) KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY Students should be able to: 1. Define Energy, Potential Energy, and Kinetic Energy. 2. Identify situations in which Potential Energy, and/or Kinetic Energy apply (swing pendulum, vibrating mass at the end of the spring, stretched elastic band, etc.) – moving objects. 3. Appreciate that to make an object move faster implies that it must have been given more energy, hence can do more work (damage). © September 35 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE HEAT AND KINETIC THEORY (4) HEAT TRANSFER Students should be able to: 1. Differentiate between Heat and Temperature. 2. Appreciate that heat can be transferred without change in temperature such as in evaporation and melting. 3. Recall that heat can be transferred by conduction, convection and radiation. 4. Explain how heat is transferred by conduction, convection and radiation. With the aid of a diagram explain how a “thermos Flask” is able to keep hot liquids hot or cold liquids cold, by limiting transfer by conduction, convection and radiation. (5) EXPANSION DUE TO HEAT Students should be able to: 1. Understand the principle of operation of a bimetallic strip. 2. Explain the use of a bimetallic strip as a thermostat in household appliances and alarm systems. 3. Describe at least 3 situations in everyday life where expansion is a problem/undesirable and how correction is made for this in each case, e.g. telephone wires, walls, roads, train lines. 4. Describe 3 situations where heat expansion useful (e.g. thermometers, thermostats). (6) KINETIC THEORY Students should be able to: 1. Out line the simple Kinetic theory as related to solids, liquids, gases. 2. Recall evidence for such a theory. © September 36 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 3. Use the theory to explain a) Evaporation b) Electricity and heat transfer. c) Pressure in a car tyre due to air inside. (7) PRESSURE Students should be able to: 1. Define pressure. 2. Do simple problems based on the definition of pressure, including variation in pressure exerted by a cuboid with its various sides resting on a flat surface. (8) ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM (9) ARCHIMEMDES’ PRINCIPLE © September Students should be able to: 1. Define a magnetic field as the space where a magnetic force exists. 2. Understand the concept that a magnetic field can be pictured as being made up of lines of force (flux). 3. Plot the magnetic field due to a bar magnet, using a plotting compass. 4. Draw magnetic fields due to magnets “end-on”, “parallel”, “with like”, or” unlike” poles adjacent. 5. Understand Ohm’s law and do simple calculations based on the law. Students should be able to: 1. Understand Archimedes Principle. 2. Demonstrate, experimentally, Archimedes Principle. 3. Understand why a weather balloon rises, a ship, made of steel is able to float; a small sewing made of steel sinks, yet a large wooden log floats. 37 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE EXPERIMENTS/DEMONSTRATIONS MM / ORR 1. Moments MM / ORR 2. Center of Gravity - Lamina MM / ORR 3. Density - Eureka Can / Displacement Can, liquid. MM / ORR 4. Density - Measuring Cylinder, liquid, regular or irregular solid. MM / ORR 5. Density - Vernier Calliper, irregular solid. MM / ORR / PD 6. Elasticity - AI 7. Pendulum - ORR 8. Melting point of Wax. (Graph) DEMO 9. Convection in Liquids. DEMO 10. Force on a current carrying conductor by a Magnetic field. © September - Fulcrum, meter rule and known mass to determine unknown. P.D. Does an elastic band stretch uniformly when loaded with different weights? (Graph) (a) Does amount of displacement affect time ? (b) Does mass of bob affect time ? (c) Does length of string affect time? How? (i) Linearly? (ii) T2 ? 38 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE DEMO 11. Magnetic fields using iron filings. MM 12. Magnetic field due to bar magnet using plotting compass. DEMO 13. Ohms Law (Graph) DEMO 14. Electromagnetic Induction. MM / AI 15. Archimedes Principle. Graphs : Students should be given the scales to be used. Resource A Concise Revision Course for CXC by Anne Tindale © September 39 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SCIENCE DEPARTMENT BIOLOGY CURRICULUM Introduction Apart from developing a knowledge base in biology in preparation for eventually qualifying for the entry to the course of preparation for the CSEC examination in Grades 10 and 11, this course is designed to develop students’ interest in the subject, as well as an understanding of its relevance to the everyday life. © September 40 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Topic Objectives; Students Should be able to: LIVING ORGANISIMS: What is biology Classifying organisms using observable characteristics Using standard classifying schemes Characteristics of living organisms Pg 1 - 3 LIFE AND THE ENVIRONMENT: Definitions of some ecological terms Food chains and food webs Nutrient cycles Relationships Pg 115 -119 text. © September Suggested activities State the definition of biology Have students Place organisms into categories using collect samples and observable characteristics such as presence classify them. of wings, number of legs, segmented body Possible group etc. work. List and describe the six kingdoms of living Or use pictures of organisms. organisms. List in order the seven hierarchical Use role play. E.g. classifications of organisms starting from each student could kingdom to specie. be a particular List the main groups of plants and animals. group and they Describe the features of each main group and research on it and give three examples of each. act it out in class. Describe the characteristics of all living Concept mapping organisms Work sheets, concept maps, Define the following terms and give etc. examples where applicable: ecology, environment, abiotic factor, biotic factor, habitat, population, community, ecosystem, and niche. Construct the following types of food chains terrestrial, marine and aquatic that contains at least four organisms. Define trophic levels, and give examples for each level. Construct a food web given a list of organisms and their eating habits. Describe the carbon cycle Describe the nitrogen cycle Describe and explain the following giving 41 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE THE CELL: Plant cell Animal cells Unspecialized cells and specialized cells Pg. 4 – 5 text CHEMISTRY OF LIFE Organic versus inorganic substances. Main elements found in living organisms Macromolecules Pg. 6 – 7 text NUTRITION: Types of nutrition Nutrients Deficiency diseases Water © September examples where necessary: prey/predator relationships, symbiosis, Parasitism, commensalisms, mutualism State the definition of a cell Draw a plant cell and label the parts as seen under a light microscope Draw an animal cell and label the parts as seen under a light microscope. Compare and contrast the features of a typical plant and animal cell. Define what specialized is a cell Give three plant and animal examples of specialized cells and their functions. Draw examples of specialized cells. Distinguish between organic and inorganic substances. Give examples of each type of substances State the elements that are mainly found in living organisms. Describe what carbohydrates are. Describe what lipids are. Describe what proteins are. State the functions of each macromolecule to humans. Carry out simple tests to identify the presence of starch, simple sugars, protein and lipids. Define the following: nutrition, autotrophic nutrition, heterotrophic nutrition. List the nutrients and their function to the human body. State the deficiency diseases of the above Labs, games etc. Worksheets, research class discussions group work. 42 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Roughage Pg. 6 – 13 text DRAWINGS AND GRAPHS FOR CXC SBA drawings Constructing graphs Pg. vii – viii text DISEASE AND MAN Types of diseases Vectors Life cycle of the mosquito Drug abuse Pg. 91 – 98 text Practical work worksheets © September nutrients. State the mineral elements required by plants. Describe the symptoms of mineral deficiency in plants. Describe the importance of water to living organisms. Describe what is roughage Describe the importance of roughage to humans. Draw simple structures using CXC guidelines Calculate magnification of drawings and diagrams given the necessary information. Construct graphs given a set of data Interpret information from a graph. Describe the following types of diseases: deficiency, physiological, hereditary, pathogenic State that STDs are a type of pathogenic disease since they are caused by pathogens. Give three examples of each type of disease, their symptoms and method of control. Describe what are vectors and their importance in the transmission of diseases. Describe the life cycle of a mosquito. Define drugs Describe the symptoms associated with Group project, role play, games: guess my disease! Guest lecture: nurses, doctors other health care workers, police etc. 43 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE alcohol abuse Describe the effect of the excessive use of alcohol. Ref. drinking and driving, aggressiveness violence etc. Describe the use and abuse of cocaine Describe the symptoms associated with cocaine abuse ASSESSMENT: A unit test will be done at the end of each unit. For each sub-topic students will be assessed using graded class work and homework assignments along with any other form of assessment the teacher may devise. Homework : 10% of the overall grade for the semester Class Work : 30% of the overall grade for the semester Tests 60% of the overall grade for the semester : Recommended Text Biology: A Concise Revision Course for CXC © September 44 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SCIENCE DEPARTMENT CHEMISTRY CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The study of Chemistry involves an investigation into chemical reactions and processes. It attempts to provide students with an understanding of the nature of matter and the behaviour of substances. It is intended that during this year, students will be able to appreciate and understand the ways in which materials behave and be aware of the influence and impact which Chemistry has in a modern and scientific world. © September 45 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Chemistry SEMESTER 1 (September – January) Topic/ Content © September Objectives 46 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE NIT 1 Topic: A Study of Matter Students should be able to: a) Define matter as anything that has mass and volume b) Describe matter as being made up of tiny particles (atom etc.), which are in constant random motion c) Discuss the assumptions of the Kinetic Theory of Matter. d) Use experimentation to prove the Kinetic Theory of Matter with reference to (1) Brownian Motion (2) Diffusion (3) Osmosis e) Describe experiments to show how matter changes from one state to the next. f) Define the terms evaporation, boiling, sublimation, condensation, freezing and melting g) Differentiate between the processes evaporation and boiling h) Compare the solid, liquid and gaseous states using 1) arrangement of particles (2) motion of particles (3) shape (4) volume © September 47 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE UNIT 2 Topic: A Study of Elements and Compounds Students should be able to: a) Define an atom. b) Carry out detailed study of an atom c) Describe an atom as containing sub-atomic particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. d) State the charge and mass of each sub-atomic particle. e) Explain why an atom has no net electrical charge. f) Discuss the development of the periodic table, g) Define an element h) Locate the position of the first twenty elements on the periodic table i) Classify elements into metals, non-metals and metalloids, j) State the properties of metals, non-metals and metalloids. k) two, Distinguish between the elements in-group one, three, seven and eight of the periodic table, © September 48 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SEMESTER 2 (February – June) l) Interpret the symbol Z AX, where: (1) X represents the element (2) A represents the mass number of the element (3) Z represents the atomic number m) Calculate the number of protons, neutrons, electrons and mass number of an atom given specific conditions n) Define an isotope, o) Give at least two examples of isotopes, p) Calculate the number of protons, neutrons, electrons and mass number of an isotope given specific conditions, q) Draw electronic diagrams to represent the atoms of the first twenty elements of the periodic table. r) Write the electronic configuration of the first twenty elements of the periodic table s) Define the terms period, group and valency, t) Use electronic configurations to determine; the period, group and valency of elements u) Define a compound v) List the name of the elements that make up a compound, given the formula for the compound w) Define the terms ions, cations and anions © September 49 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE x) Explain how cations and anions are formed y) Describe the following compounds (electrovalent/ionic compound, simple covalent compound and giant covalent compound. z) Use a simplified approach to refer to the formation of ionic and covalent compounds © September 50 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE UNIT 3 (1) Topic: Physical and chemical change Students should be able to a) Define and describe a physical change. b) Give examples of a physical change c) Define and describe a chemical change d) Give examples of a chemical change (2) Topic: Chemical reaction and equation Students should be able to a) Define a chemical reaction b) Define a chemical equation c) Write simple word equations coming from the topics, Elements and Compounds, Acids, Bases and Salts. ASSESSMENT: A unit test will be done at the end of each unit. For each sub-topic students will be assessed using graded class work and homework assignments along with any other form of assessment the teacher may devise. Homework : 10% of the overall grade for the semester Class Work : 30% of the overall grade for the semester Tests : 60% of the overall grade for the semester Recommended Text Chemistry, A Concise Revision Course for CXC by Anne Tindale © September 51 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SCIENCE DEPARTMENT AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE CURRICULUM The general aim of the Agricultural Science Department is to engage students in learning activities that will allow them to be sensitized to the importance of agriculture in our everyday lives. The gains to be derived from agriculture will also be examined. © September 52 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Topic / Content 1. (a) Planning and Planting - (b) Caring for crops 2. Tillage 3. Soils © September Objectives: Students should be able to: Students should be able to : Outline the steps in land preparation Describe requirements for crops Plant seeds using proper technique Transplant seedlings Describe and carry out the steps in vegetative propagation Explain cropping Carry out the following procedures: weeding thinning cropping mulching watering fertilizing shading pruning protection harvesting define tillage Describe the purpose of tillage Outline methods of methods of tillage Carry out methods of tillage Define erosion List agents of erosion Describe the types of erosion. 53 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 4. Plants Explain the effects of erosion Describe the following soil conservation practices (a) Terracing (b) Barriers (c) Contours (d) Cover cropping (e) Afforestation (f) Compost (g) Mulch (a) Describe the following cropping systems Mixed farming Subsistence farming Shiffing cultivation Monocropping Crop rotation (b) Define each system (c) Give the advantage and disadvantages each type of cropping systems (a) Poultry 5. Animal Identify, describe and name types of the following Egg producers eg. Leghorn Meat producers eg. Vantres cross Dual purpose eg. Rhode Island Red, New Hampshire Red, Bored Plymouth Rock (b) Housing and Equipment Describe the steps to site selection Explain deep litter system Determine the space requirements for different types Describe the roofing and ventilation systems © September 54 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Describe waterers, feeders, laying box ASSESSMENT: A unit test will be done at the end of each unit. For each sub-topic students will be assessed using graded class work, practical assignments and homework assignments along with any other form of assessment the teacher may devise. Homework : 10% of the overall grade for the semester Class Work : 30% of the overall grade for the semester Tests 60% of the overall grade for the semester : Recommended Texts Senior Secondary Agricultural Science Agricultural Science for The Caribbean © September 55 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE HISTORY DEPARTMENT HISTORY CURRICULUM The aim of the Grade 9 History Curriculum is designed To provide students with the basic knowledge of how the plantation system has shaped contemporary society To provide students with knowledge and understanding of resistance as a means of transformation and change in the Western Hemisphere. To discover and clarify their individual aptitudes, interest and aspirations. For students to develop civic pride and to become worthwhile citizens through the study of civics To develop and hone their critical thinking skills To develop a sense of community spirit. © September 56 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Semester 1 September - January Topic/ Content UNIT 1 The Plantation System Physical layout of a typical 18th century West Indian Plantation Social relations on a typical 18th century West Indian Plantation Resistance to slavery Types of Resistance 1. The Maroons 2. The Haitian Revolution 3. The Christmas Rebellion Objectives Students should be able to: © September Define the concepts – enslavement, plantation, plantation system, selfsufficiency, domination, subjugation, resistance, gender, revolution, maroon, maroonage List the main land divisions and buildings which were found on a typical 18th century sugar estate Construct a mural of an 18th century sugar plantation Describe the social hierarchy which existed ion 18th century West Indian slave societies Identify the roles associated with each social group which formed 18th century West Indian societies Outline the reasons why slaves resisted enslavement Explain the various methods used by the enslaved to free themselves Assess the impact of resistance on the system of slavery in Jamaica and the wider Caribbean. Identify Maroon settlements in Jamaica – location and reasons for establishment Outline the First and Second Maroon War – causes, key personalities, course, effects Appreciate the role of slavery in shaping Caribbean societies. 57 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE UNIT 2 Students should be able to: POLITICAL REVOLUTIONS The American Revolution 1. Causes 2. Course 3. Effects Latin American Revolutions - Mexico Define the terms mercantilism, exclusivism, mother country, independence, colonialism,’ minute men’, ‘red coats’. Outline the push and pull factors which led to the formation of the original thirteen North American seaboard states, Locate the original North American seaboard states on a map of the united States Assess the issues which gave rise to the outbreak of the American Revolution Describe the Boston Tea Party Evaluate the role of John Hancock, George Washington, William Dawes and John Adams Outline the main reasons for the defeat of the British Analyze the social, political and economic changes which independence brought to America Assess the main problems which the Americans experienced after Independence Construct a timeline of the main events leading up to the outbreak of the Revolution and to Indpendence Students should be able to: - Chile - Peru 1. Causes 2. Course Define terms – creoles, Peninsulares, Mestizos, enlightenment, Latin America, Junta, counter-revolution Identify the main countries which constituted the Latin American empire in the 18th century Outline the main administrative divisions which made up Latin America in the 18th century 3. Effects © September 58 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Assess the socio-economic, religious, ethnic and political factors which led to the outbreak of revolutions in Latin America in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Evaluate the roles of Simon Bolivar, Bernardo Hidalgo, Jose de San Martin, and Bernardo O’Higgins in the Wars of Spanish American independence. Identifyt he main issues which Independence broght to the independent republics of Mexico, Chile and Peru. Appreciate the role of ideology in influencing revolutions Semester 2 FEBRUARY - JUNE Topic/ Content Objectives UNIT 3 CIVICS The Community Students should be able to: © September Define the term civics, community, institutions, social groups, socialization, culture, co-operation, society, List the types of communities – home, school, church, country, region, global Evaluate the role/ functions of the main communities – home, school, and church. Explain why the home is considered to be the first community Describe the characteristics of each family structure Identify the different types of social groups – formal and informal 59 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Citizenship Students should be able to: Define the term citizenship, citizen, alien, democracy, rights, responsibilities List at least three ways a person can become a citizen of a country. Identify at least six rights of a citizen Classify responsibilities according to legal and voluntary responsibilities Discuss responsibilities to self – good health practices; to community ; to country Appreciate that with rights comes responsibilities Government Students should be able to © September Classify different types of groups according to their functions, characteristics and composition. Appreciate their role as social beings and recognize the need to cooperate and respect each other. Define the terms government, fiscal duty, budget, taxation, voting, the electoral system Identify the various types pf governmental systems Illustrate by way of a time line the historical pattern of the Jamaican government Describe the functions/role of the government Outline the electoral process Identify factors influencing voter behaviour in Jamaica Describe the fiscal duties of the Government 60 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE ASSESSMENT: A unit test will be done at the end of each unit. For each sub-topic students will be assessed using graded class work and homework assignments along with any other form of assessment the teacher may devise. Homework: 20% of the overall grade for the semester Class Work: 30% of the overall grade for the semester Tests : 50% of the overall grade for the semester RECOMMENDED TEXTS Honychurch Lennox, The Caribbean People, Bk. 3, 3rd ed., United Kingdom: Nelson Thornes, 2006. Carlong Secondary Social Studies – Book 3B: Jamaica: Citizenship and Government (formerly New Civics for Young Jamaicans) © September 61 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT CURRICULUM Introduction This Guide is meant to be used as a tool to help Grade nine parents and students keep abreast of the required learning outcomes for the academic year. The guide outlines the topics, objectives, activities and resources that are used at this level. It is by no means exhaustive, but simply representative of the syllabus for this level. © September 62 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT SEMESTER 1 (September – January) and SEMESTER 2 (February – June) Topic/ Content 1. Transition period from 2nd to 3rd form Objectives Students should be able to: (a) Evaluate 2nd form obstacles and positive points - “Looking back for a while”. (b) Choose subjects according to career options – More on visioning and goal setting, my dream portfolio. (See grade eight assignment.) (c) Research the ‘new’ subjects I might be pursuing in grade 10 by interviewing grade 12-13 students. The number of SBA’s and the careers associated with each should be noted. (d) Analyse “I need to be responsible for my life”: Making space in my life - Pg 16 Bk 2 Discovering my gifts- Pg 15– 20 Bk 2 Overcoming laziness- Pg 14– 20 Bk 2 What motivates me? - Pg 14– 20 Bk 2 I need help - Pg 14– 20 Bk 2 I want to be a successful person – Pg 8– 13 Bk 2. © September 63 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 2. Enhancing relationship between Discuss the role of parents in their lives parents and children “I heard my (a) (b) parents and teacher say” Complete assignments on page 82 – 91, Bk 2 Complete Projects - Pg 80–81 Bk 2. presenting neat homework . See page 72 in Bk 1 re Parent week - Pg 23 – 25 Bk 1 (a) Establish positive values – Pg 28-36 Bk 2. 3. Revision of study topics (b) Practise abstinence (c) Complete 2 words each A- Z in Bk. 2. Page 38-49 4. I will say yes to …………….. and I will say no to …………….. (a) Discuss employment as a basic need (b) Examine the consequences of unemployment and under-employment (c) Define Work and leisure (d) Demonstrate Team work – Do practical example – The geese story. 5. Employment (a) Discuss how to make a decision? (b) Discuss Decision making techniques © September 64 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE (c) Research career choices before making a decision 6. Decision Making (a) Define career terms (b) Set goals (c) Understand occupational clusters 7. Career Talk – ties in with dream book assignment (a) Set realistic goals (b) Identify the limitations of setting goals (c) Examine hobbies and extra-curricular activities as contributors to goal attainment (d) Discuss community service as a contributor to goal attainment 8. Goals/Values/Resources page: 21 - 27 (e) Determine subject choices and goals (a) Demonstrate taking responsibility – “Being away from it all”; demonstrate acceptable behaviour with or without teachers being present. (c ) ‘Release’ -5 things I need to release in order to achieve my goals. Bk. 2, Page 5-7 and ‘Start’ 9. Do's and don'ts © September Bk. 2 Page 10- 12 65 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE INDUSTRIAL ARTS DEPARTMENT DESIGN TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION It is generally recognized that Technical Drawing is the language of communication of technical/vocational occupations and as such, has widespread applications in the life of consumers. It is therefore recommended that students have a basic knowledge of Technical Drawing. © September 66 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SUBJECT : DESIGN TECHNIQUES (TECHNICAL DRAWING) . TOPICS OBJECTIVES At the end of the lesson students should be able to: Introduction Identify common drawing instruments and equipment and state their uses Drawing Equipment Layout drawing paper on table. Lettering, Title Block. Draw and state the name and application of the types of line used in drawing. Bisect straight line, arcs and angles. Erect a perpendicular to a given line. Divide straight lines equally and proportionally. Construct a line parallel to a given line. Construct various angles. Lettering and dimensioning of drawing. Line Types Lines © September 67 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Triangle Construction Construct triangles given; Two angles and one side, three sides, two sides and included angle, perimeter and proportional of sides, altitude and base angles, Quadrilateral and Polygons Construct inscribed and circumscribe circles Construct a square given the length of one side. Construct a rectangle given the length of two sides. Construct a rhombus given a diagonal and the length of one side. Construct a parallelogram given two sides and an angle. Construct a trapezium given the length of the two parallel sides, perpendicular distance between them and one angle. Isometric Projection Orthographic Views © September A regular octagon within a square given the length of one side of the square. Construction isometric blocks Draw orthographic projections of geometric solids and simple solids using first angle and third angle of projection. 68 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE ASSESSMENT: A unit test will be done at the end of each unit. For each sub-topic students will be assessed using graded class work and homework assignments along with any other form of assessment the teacher may devise. Homework : 20% of the overall grade for the semester Class Work : 30% of the overall grade for the semester Tests 50% of the overall grade for the semester : Recommended Text Technical Drawing Workbook for Grade Nine Available at the Industrial Arts Department © September 69 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Home Economics Department Food and Nutrition Curriculum CONTENT OBJECTIVE Students should be able to: Review Food and Nutrition Section of grade 8 past paper 1. Nutrition Overview Terms – Food, nutrition, nutrient, nutritional status, diet, balanced diet, malnutrition. Signs of good and poor nutrition, methods used to assess nutritional status Home Economics for the Caribbean Schools Chapters 1-3 Food and Nutrition Workbook pages 71-90 2. The Cooker Describe List 3 types of cookers Name 4 main parts of the cooker Outline 3 points to bear in mind when using the cooker Explain how to care for the cooker State 3 specific features of a modern cooker Food and Nutrition Workbook pages 41-42 Caribbean App. Book 2 pages 75-77 3. Methods of cooking and heat transfer © September Define cooking State five reasons for cooking List five methods of cooking - Steaming, boiling, grilling, baking, frying Explain each method State two advantages and disadvantages of each method Name three types of heat transfer 70 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Describe three methods of heat transfer using labeled diagrams Practical - Grilled chicken/burger/fish Boiled/baked potatoes Simple vegetable salad Workbook pages 65-69 Home Economics for the Caribbean Schools Chapter 5 4. Vegetables Define vegetables List four (4) classifications of vegetables. State two (2) examples of each classification. State three (3) factors to consider when choosing vegetables. Explain the conservative method of cooking vegetables. Caribbean Approach, Bk.2, pages 19 – 24. Food and Nutrition Workbook, pages 110 – 111 5. Cake Making State five methods of mixing List the basic ingredients used State the function of each ingredient State the position in oven and suitable temperature Home Economics for Caribbean Schools Chapter 15 Practical 6. Nutrients – Fat soluble vitamins ADEK Water soluble vitamins B1, B2, B3, C © September - Rock cakes (rubbed in method) State the sources, functions deficiencies and excesses of each. 71 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 7. Nutrients coagulation, Terms- amino acids, gelatinization, dextrinization, caramelization, low and high biological value, complete and incomplete protein Protein, Carbohydrates, Fats State the sources, functions, deficiencies and excesses 8. Egg Cookery Draw and label the diagram of a hen’s egg State the function of the parts Tell five uses of egg in food preparation State at least TWO methods of testing an egg for freshness Discuss the effects of heat on egg State THREE points to bear in mind when storing eggs Discuss the nutritive value of egg Demonstrate the use of eggs in groups Practical - Egg Dishes 9. Nutrients – Minerals (Iodine, calcium and Iron) Water State the sources, functions, deficiencies and excesses 10. Milk Define Milk State the nutritive value of milk State four uses of milk in food preparation List four guidelines for storing milk Discuss briefly how milk is processed to produce milk powder, evaporated milk and condensed milk Field trip – © September 72 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE RELIGIOUS EDUCATION CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION The Religious Education Curriculum is designed to inculcate the concept of Stewardship so that students may develop and possess qualities namely honesty, integrity, industry and loving-care for that over which he or she is placed. It is important for students to recognize that one of their responses to the deity within their religion is to acknowledge the various gifts given to them and to be good stewards of those gifts. It is hoped that from exposure to this subject students will become aware of the different social issues in our world and to acknowledge their responsibility as corporate stewards. © September 73 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SEMESTER I September-January TOPIC / CONTENT OBJECTIVES 1. THE NATURE AND PURPOSE OF STEWARDSHIP Students should be able to: Define the concepts steward, talent, pollution, environment, stewardship, natural world Discuss the importance of a Khalifa List three Christian teachings about the responsibilities of God’s stewards Examine the impact of deforestation and global warming on the environment Write three ways in which man is responsible for the world Read and relate the parable of the talents told by Jesus Design a poster showing the impact of pollution on the world Demonstrate ways in which we can care for the environment Develop awareness of their capabilities and their responsibilities as stewards Be willing to explore ways in which religion acts as motivating factor influencing every area of human life Develop a sense of personal and corporate ownership and desire to care for the physical environment 2. PERSONAL STEWARDSHIP Students should be able to: Define the concept symbolism, pre-marital, extra-marital Sexual Relationships Contraception, Marriage and Divorce ,Homosexuality, Abuse, Abortion, ,Prostitution Discuss the difference between pre-marital and extra-marital sex Describe what is a Chuppah and explain its symbolism Explain the different religious views pertaining to marriage Role play a given human relationship issue © September 74 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Write down three pieces of information about the Jewish attitude to abortion Compose a poem about marriage in any religion Be willing to assert themselves in maintaining their rights and to recognize that with every right comes responsibilities Develop a positive attitude to self and others. SEMESTER 2 - FEBRUARY-JUNE TOPIC / CONTENT CORPORATE STEWARDSHIP OBJECTIVES Students should be able to: a) Define the concepts cloning, infertility, sexually transmitted infections, disability euthanasia, Hospice Movement, ageism, sexism, racism , suicide. Name two types of disabilities Discuss what is the Hospice Movement List and explain two reason for racism Outline factors in society that can be classified as sexism Write four methods used to help persons who are infertile Present arguments for and against Euthanasia Compare and contrast the different religious views pertaining to Organ Transplants Compose a song or poem to educate young people about sexually transmitted diseases Identify at least four reasons why a person might want to commit a suicide Be challenged to think through the values that have either a negative or positive influence on their own lifestyles and those of others Develop respect for people who hold beliefs and views which differ from their own © September 75 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE TOPIC / CONTENT 4. CORPORATE STEWARDSHIP II © September OBJECTIVES Students should be able to: Define key terms of wealth and poverty, time, work and leisure, crime and punishment, capital punishment, war and peace, human rights, animal rights, substance abuse Identify causes and effects of poverty Examine reasons for people breaking the law Present arguments for and against capital punishment Write five reasons why substance abuse occur Develop and express personal views on animal rights Design a poster entitled ‘ Human Rights’ Identify the effects of abusing drugs Develop an understanding that with every human right comes a responsibility Develop respect for people who hold beliefs and views which differ from their own 76 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE ASSESSMENT: A unit test will be done Prescribed text at the end of each unit. For each sub-topic Michael Keene, New Steps in Religious education for the Caribbean, students will be assessed using graded Book 3 class work and homework assignments The Bible along with any other form of assessment the teacher may devise. Homework : 20% of the overall grade for the semester Class Work : 30% of the overall grade for the semester Tests : 50% of the overall grade for the semester © September 77 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE VISUAL ARTS DEPARTMENT ART AND DESIGN CURRICULUM RATIONALE: Education in Art and Design offers opportunity for students to enjoy and participate in a range of expressive media that facilitate the creative exploration of processes and forms of two and three dimensional art and design. It also offers significant exposure to research methodologies and to cultural appreciation and criticism that are shared by a wide range of subject areas. Some of these are design formations, drawing and painting, three dimensional handmade crafts among others. In addition, it provides one with the knowledge and skills necessary in the entertainment, creative production, marketing, as well as commercial and manufacturing industries. AIMS The syllabus aims to: 1. To further build on students knowledge, skills and attitude acquired in grades seven and eight. 2. Encourage experimentation with materials, various processes and methods. 3. Convey concepts and ideas through the manipulation of materials; 4. Develop critical thinking through research; © September 78 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 5. Expose students to the use of art and design as an investigative tool; 6. Motivate the students in the area of the Visual Arts, so that they may see it as an option when choosing their career path. In all the areas presented students will be tested in the areas of 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Craftsmanship Design and Composition Innovation Enquiry Critical Thinking Semester 1 September - January Topic/ Content Objectives At the end of the unit students should be able to: Unit One - September to November Introduction to Advanced Designs and Design Techniques. Lettering and Logos Formatting Designs and Mounting Critical Analysis 1. appreciate the Visual Arts as an important part of every day life 2. define art and list the various areas in the arts and the career opportunities 3. differentiate decorative and functional art 4. link the five modules in Resource and Technology 5. use the design cycle to solve design problems 6. select appropriate tools for a particular job 7. understand the elements and principles of design Resources: paint, pencils, cardboard, rules, scissors, paint brushes, mat board, fabric, text book (Art Craft Design) UNIT TEST © September 79 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Unit Two – November - January Introduction to ADVANCED DRAWING Shading Techniques and Application Finishing techniques Presentation and mounting Unit Three – February - June Introduction to advance three dimensional forms Mobiles Printing Figure Drawing Landscape © September Resources: paint, pencils, pastel, chalk pastel, fabric, paper,text book (Art Craft Design) Resources: paper, paint, industrial waste, dyes, paint brushes, strings, pencils crayons, cardboard (Art Craft Design) UNIT TEST 80 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE PHYSICAL EDUCATION DEPARTMENT INTRODUCTION The aim of the Physical Education Curriculum is to allow students to: 1. Get together and have fun 2. Experience success and achievement. 3. Keep fit and healthy. 4. Learn physical and technical skills. 5. Improve their mental skills. 6. Cooperate and communicate with others. It is also geared to enhance motivation, organization, leadership and interpersonal skills. © September 81 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Physical Education SEMESTER 1 (September – January) and SEMESTER 2 (February – June) Topic/ Content NETBALL - Theory- rules, dimension of court Revision of passes - Marking & dodging - Passing . Straight Line . Zig Zag Objectives Students should be able to: - 2. Receiving both from goal & side lines Center pass Game - Draw and label the netball court Answer questions regarding dimensions and rules governing netball Demonstrate marking, dodging and passing. Execute the shoulder, chest, bounce overhead, underarm and side passes accurately. Describe the skills above when called upon to do so and apply technique of the skills effectively. Show reasonable competence in taking & receiving the center pass. Use knowledge of the skill taught to perform effectively in the game situation FOOTBALL (BOYS) - 3. - Revision of grade 7 & 8 Rowing Long pass Goal keeping Rules TRACK & FIELD Relays 4 x 100m 4 x 400m Check marks Lung jump © September Students should be able to: - Applying rules in a game situation - Demonstrate competence in skills taught. - Describe the field dimension, number of players, and positions Students should be able to: - Demonstrate fluency in running speed, during the exchange of the locations in the 4 x 100 relay. - Exchange batons without risk of collisions. - Distinguish between the pattern of 4 x 100 relays & 4 x 400m relays. 82 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE - Participate in competitions for all events at class, grade, house and extramural competitions. Coordinate the run up, take off, flight and landing to get maximum height and distance while jumping. SEMESTER 2 TRACK & FIELD CONTD. - High jump - Shot putt - Discus 2. - VOLLEY BALL Conditioning Setting Spiking Blocking Rules of the game Game © September Students should be able to: - Coordinate the run up, take off, flight and landing to achieve maximum height in high jumping. - Combine training and skills development to accurately throw the discus and shot putt. - Demonstrate the basic technique for putting the shot. - Demonstrate the basic technique for throwing the discus. Students should be able to: - Show by illustration, at least two playing patterns used for volleying. - Perform conditioning exercises to develop strength, endurance, speed, flexibility and power. - Demonstrate competence in setting, spiking and blocking. - Apply rules in game situation. - Accept constructive criticisms from peers. - Use knowledge of skills taught to perform effectively in the game situation. 83 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 3. - BASKETBALL Advance dribbling Playing position Defence Shooting Rules dimension of court Game 4. CRICKET (BOYS) - Revision of 7 & 8 - Bowling styles - Batting strokes - History of cricket - Laws of cricket N.B THEORY SESSIONS a. Research b. Notes c. Handouts d. Practical Students should be able to: Demonstrate competence in dribbling the ball. - Identify playing position. - Develop the skill of shooting accurately - Apply tactics and strategies in the game situation - Apply rules in the game. Students should be able to Show mastery of skills taught - Explain how the game of cricket was formed and developed - Accept constructive criticism from peers and teacher. - To test and measure students’ critical, analytical and comprehensive skills Students should be able to correctly answer short multiple choice test on aspects of the various sports Assessment will be both physical and theory © September 84 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE GEOGRAPHY DEPARTMENT GEOGRAPHY CURRICULUM INTRODUCTION This Guide is meant to be used as a tool to help Grade nine parents and students keep abreast of the required learning outcomes for the academic year. The guide outlines the topics, objectives, activities and resources that are used at this level. It is by no means exhaustive, but simply representative of the syllabus for this level. © September 85 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SEMESTER 1 (September – January) and SEMESTER 2 (February – June) Topic/ Content Objectives 1. STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH At the end of the unit students should be able to: Key Terms Asthenosphere, Hydrosphere, Lithosphere, Name and describe the different layers of the earth. Oceanic Crust, Continental Crust, Crust, Mantle, Draw and label a diagram showing the layers of the earth. Inner Core, Outer Core, Convection Current Name and explain at least two (2) evidences to support the Layers of the earth: crust, asthenosphere, earth’s internal structure. Mohorovicic Discontinuity, mantle, Gutenberg Discontinuity, outer core, inner core State of each layer i.e. are they solid, semisolid, liquid Temperature of each layer Rocks & minerals found in each layer Evidence to support the internal structure of the earth. 2. TYPES AND ORIGIN OF ROCKS Key Terms Rock, Minerals, Gem, Rock Cycle, Metamorphic, Igneous, Sedimentary The Rock Cycle Types of Rocks Igneous, Metamorphic, Sedimentary. How are they formed? Name and describe the different layers of the earth. Draw and label a diagram showing the layers of the earth. Name and explain at least two (2) evidences to support the earth’s internal structure. Physical characteristics of the rocks. Example of each rock type © September 86 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE . PLATE TECTONICS A brief introduction on Wegner’s Continental Drift Theory What is plate tectonics? The earth’s crustal plates What is a plate margin/plate boundary? The three types of plate margins Direction of movement at each plate margin An examination of the activities at each plate margin and features produced Tectonic activities in the Caribbean 4. VOLCANISM What is a volcano? The structure of volcanoes The life cycle of volcanoes Conditions under which volcanoes are formed Intrusive volcanic features e.g. batholith, sill, dyke etc. Materials ejected from volcanoes e.g. ash, cinder, lapilli etc. Types of volcanic lava i.e. acid and basic lava Types of volcanic eruptions Types of volcanic cones Characteristics of volcanic cones Warning signs that volcanoes may erupt Positive factors resulting because of volcanic eruptions Negative impact volcanic eruptions have on the environment © September Define all the terms related to plate tectonics as outlined in the course outline. Name the type of plate margins and state the directions they move in. Explain the activities that occur at plate margins and the landforms that may be formed (if any) at each. Define all the terms related to volcanism as outlined in the course outline. Draw and label a diagram showing the structure of a volcano. Name and identify on a map of the world, active volcanic zones around the world. Explain with the aid of diagrams how volcanoes are formed. Name and describe the intrusive features of a volcano. Describe the life cycle of a volcano. Name and describe at least three (3) volcanic cones, and state the type of eruptions associated with each. State at least five (5) signs given by volcanoes that they may erupt. Name the materials ejected from volcanoes and explain how these ejected material affect the physical environment and humans. State at least three (3) reasons why people live in areas prone to volcanic eruptions. .Explain three (3) positive and three (3) negative impact volcanic eruptions have on the environment 87 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Why people live in volcanic zones around the world EARTHQUAKES How earthquakes occur How earthquakes may be predicted Effects of earthquake on the environment Measures to reduce the effects of earthquakes Why people live in earthquake prone areas 6. FOLDING AND FAULTING What is folding Types of folds- simple folds, Asymmetrical fold etc. What is faulting Types of faults – Normal fault, Reverse faults etc. © September Define all the terms related to earthquake, as outlined in the course outline. Explain with the aid of diagrams how earthquakes occur. Identify and locate on a world map, earthquake zones around the world. State at least three (3) precautions that should be put in place, should earthquakes occur. Name and identify the measurements on the Richter Scale and explain the damages associated with the different magnitudes. Explain the impacts earthquake activities have on the earth’s physical environment. Explain why people live in areas around the world prone to earthquakes. State the difference between folding and faulting. Name and describe with the aid of fully labeled diagrams the different types of folds and faults. Explain how folding and faulting aids in the formation of natural landforms. 88 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE LONGITUDES AND TIME What are lines of longitude Importance of the Prime Meridian and the International Date Line, in understanding time around the world How the earth's rotation influence time Lines of longitude east and west of the Prime Meridian - 15° apart. Using mathematical formulae to calculate the difference in time, from one place to another. 8. STATISTICAL REPRESENTATION Differentiate between data and information Sources for collecting information- primary and secondary sources Instruments use to collect data Statistical methods of presenting data Presenting data on tables, bar graphs, line graphs, pie charts etc. MAP SKILLS REVIEW State how many degrees of latitude is equivalent to- one hour and how many is equivalent to four minutes. Explain how time changes as one travels east or west of the Prime Meridian and or east or west within a given zone. Calculate the time (a.m./p.m.) at places east and / or west of the Prime Meridian. Differentiate between data and information State the different sources of information State at least three (3) ways in which geographical data/information is presented. Collect data and present such, using various statistical instruments Students should be able to recall previous map skills taught at the seventh and eighth grade. At the end of the unit students should be able to: Define all the key terms related to resources outlined in the © September 89 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE The impact of mining on the environment i.e. impact on land, the atmosphere, fresh water sources and the Marine environment The attempts at conservation and preservation of minerals by the mining industry in Jamaica Careers in the mining industry course outline. Name the two types of physical resources and explain the importance of each. Identify and locate on a map of Jamaica, where its nonrenewable physical resources are located. Explain why it is important to carefully manage the utilization of a country’s resources. Identify and locate on a map of Jamaica, where bauxite deposits and mining areas are located Name and describe the type of bauxite mining method used in Jamaica. Explain how bauxite is processed into alumina in Jamaica. Explain the benefits of bauxite mining to the Jamaican economy. Explain the impact of mining physical resources have on the humans and the physical environment. Industries Key Terms: Industry Primary Industry Secondary Industry Tertiary Industry Assembly Manufacturers Manufacturing Industries. Examples of primary, secondary and tertiary industries in Jamaica Factors, which have influenced the development of industries in Jamaica. E.g. raw materials, large labour force, seaport facilities. Site - flat land etc. Industrial centres in Jamaica © September 90 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SETTLEMENT The three types of settlement pattern and their characteristics Advantages and disadvantages of each settlement type The site and situation of settlements Functions of settlements Factors to be considered for the development of settlements What is a central business district? What is urbanization? Problems of urbanization Define the key terms related to the unit Name and describe the three settlement patterns and outline their characteristics and advantages and disadvantages. Discuss the factors that influence the settlement at specific locations State what is the Central Business District and describe its characteristics. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of urbanization. CONTOURS Review contour lines Types of slopes Identifying types of landforms using contour lines Drawing cross sections LAND USE ON MAPS © September Name and identify physical landforms on a map using contour lines. Draw cross sections of an area on a map, and describe its slopes. State whether places/features, based on their slope formation is visible from the next List the various ways land space is utilized on a given O.S. map. Identify and explain the factors (using map evidence when asked)that may have influenced the type of land use seen on a given map. 91 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE Resource Skills in Geography 3 by C. Myers Assessment: A unit test will be done at the end of each unit. For each sub-topic students will be assessed using graded class work and homework assignments along with any other form of assessment the teacher may devise. Homework : 20% of the overall grade for the semester Class Work : 30% of the overall grade for the semester Tests : 50% of the overall grade for the semester © September 92 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE REVIEW FOR SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS In reviewing for this examination, the following points should be considered: Review all assignments and test papers. Many times the exam items are based on these exercises. It is advisable to make corrections to any errors on these papers so as not to repeat the same mistakes on the major examinations. Make sure all class notes are in order in your note book (s). Follow the syllabus guide/course outline if you are unsure of what you may have missed. Use other geography books and your prescribed texts to help you prepare you own notes. Remember to carry all your tools you will need for the examination. These include; crayons, rulers, graph paper, a clean sheet of paper for measuring distances, calculators etc. All questions on the exam paper will be compulsory, so review all content areas/topics covered in class. The exam paper is usually divided into three (3) section, they are – A multiple Choice section, - A map Reading section, - A structured questions section that require the student to answer questions in complete sentences. These questions will range in difficulty from simple recall to higher order reasoning, for example to explain what factors determine a named situation. The items tested in the structured section of the examination are usually based on content covered in a given semester. The map reading, multiple choice and statistics (grade 9 only) sections of the examination are usually a reflection of the content done in a given semester and an overview of the previous semester’s work. Length of examination papers vary for each grade level, grade 7 may have papers in duration of 1 hour to 1 hour forty five minutes, grade 8 examination papers may be for 2 hours and grade 9 may be as long as 2 ½ hours. No student will be exempted from doing a Geography examination, unless such instructions are given by the principal of the school. Where a student entered the school in the middle of and/ or near end of a semester, before the sitting of a semester examination, the onus is on the student to acquire the content done before he/she joined the school/class, and prepare his/her self for the examination. © September 93 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE BUSINESS AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT THEORY AND PRACTICAL CURRICULUM – INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION The need to prepare our students for the change in global world necessitates that Information Technology is taught at all levels in the Secondary School System. This is the basis for developing a curriculum in Information Technology for Grade 9. The Computer, the vehicle by which the skills in Information Technology are transmitted, will also be used to integrate other subject areas within the curriculum. In a global economy with the emphasis on technology, Information Technology must be given priority. This course seeks to allow students to develop an appreciation for Information Technology in terms of its history and its application and implication to today’s society. Knowledge and skills obtained by students in the practical component will allow them to create professional looking documents using the software program Microsoft Word. © September 94 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE AIMS OF THE GRADE 9 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CURRICULUM This Information Technology curriculum aims to have students: 1) Achieve computer Literacy by the end of Grade 9 2) Use the computers for communication 3) Use computers to create graphics 4) Use computers for problem solving 5) Use computer software to assist learning in other subject areas 6) Use computers for report writing 7) Use computer to achieve enrichment activities 8) Develop the awareness of different types of technology by utilizing them to enhance information transfers 9) Use computers for report writing and information gathering 10) Commit themselves to a belief in independent life-long learning CURRICULUM DESCRIPTION: This curriculum is designed to be an introduction to computers. It includes an introduction to the components and usage of a computer and it provides the student with enough knowledge to gain a level of computer competency. The curriculum will provide the students with a theoretical and practical framework to enable them to participate in the information age. © September 95 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SEMESTER 1 (September – January) and SEMESTER 2 (February – June) TOPIC /CONTENT 1. INTRODUCTION TO THE COMPUTER OBJECTIVES Students should be able to: The Computer -The Components of a Computer -The Processing Cycle - Data and Information - Users of Computers 1. define the computer 2. tell the components of a computer 3. draw the processing cycle 4. distinguish between data and information 5. list the different users of computers 2. EARLY COMPUTER DEVELOPMENT Students should be able to: - Early Computer Development - Generations of Computers -Types of Computers Supercomputer, Mainframe computer, Minicomputer, Microcomputer, Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) 1. explain the early development of computers 2. differentiate between the different generation of computers 3. list the different generation of computers 4. differentiate between the different types of computers 5. list the types of computer UNIT TEST 1 TOPIC /CONTENT OBJECTIVES 3. COMPUTER SYSTEMS HARDWARE Students should be able to: a. Input Devices Categories of Input Devices - Keyboard Entry Devices - Pointing devices - Source Data Entry Devices - Multimedia Devices b. Output Devices Types of Output Devices - Disk or Tapes - Modem - Hardcopy: - printers, microfiche - Softcopy:- monitor(CRT), audio, voice, sound and 1. distinguish between the terms input and input devices © September 2. distinguish between the different categories of input devices 3. give examples of input devices Students should be able to: 96 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE video output - Multifunction devices 1. distinguish between the terms output and output devices 2. distinguish between the different types of output devices 3. give examples of output devices TOPIC /CONTENT c. Storage 1) Types of Storage: - Primary Storage memory chips:- RAM, ROM, Cache and Buffer - Secondary Storage Devices and Media Types of Secondary Storage Media:- Magnetic Storage, Disk, Tape and Optical Storage 2) Categories of Secondary Storage - Serial Access for example, magnetic tape - Direct Access for example, floppy disk 3) Other types of Storage devices - PC Cards - Smart Cards -Microfilm/Microfiche OBJECTIVES Students should be able to: 1. distinguish between different memory chips 2. distinguish between the two types of RAM chips 3. explain the different variations to Read Only Memory (ROM) 4. distinguish between a storage medium and a storage device 5. distinguish between the two categories of secondary storage 6. give examples of the categories of secondary storage 7. distinguish between a PC card and a Smart card 8. list the two types of smart cards © September 97 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 9. list the uses of a smart card 10. tell the use of a microfilm/microfiche TOPIC /CONTENT OBJECTIVES d. Processing - System Unit - Central Processing Unit (CPU) - Components of the CPU - The Machine Cycle Students should be able to: UNIT TEST 2 3. distinguish between the different functions of the machine cycle © September 1. distinguish between a system unit and a central processing unit 2. list the components of the central processing unit (CPU) 98 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 4. draw the machine cycle Students Textbook: Information Technology Made Simple by George King and Tiffany Forbes Assessment Procedures include: Learning Experiences include: 1. Two Unit Tests 1. Small group assignments 2. Class Work 2. Individual assignments 3. Home Work 4. Project © September 99 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE PRACTICAL © September 100 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE SEMESTER 1 (September – January) and SEMESTER 2 (February – June) TOPIC /CONTENT 1. INTRODUCTION TO THE COMPUTER SYSTEM OBJECTIVES Students should be able to: 1. define the term computer - The Computer 2. identify the main components of the computer system - Main components of the computer system 3. tell the different parts of the keyboard - Parts of the keyboard 4. turn on the system unit and the monitor - Turning on the system unit and monitor 5. apply typing skills when typing a document - Typing Skills 6. identify different parts of the Microsoft Word Window - Parts of the Microsoft Word Window 7. define different terms associated with the word window - Terms associated with the word window 8. save a document - Saving a document 9. closing a document and exit word - Closing and Exiting Word 10. create a Header and Footer - Headers and Footers 11. use Superscript and Subscript to text - Superscript and Subscript 12. © September 101 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE © September 102 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE CREATING A WORD DOCUMENT - Overtyping Text Students should be able to: 1. overtype text in a document - Deleting Text 2. delete text from a Word Document - Undo and Redo Functions 3. use the Undo and Redo functions - Closing a Word Document 4. close a Word Document - Retrieving a Word Document 5. - Page Numbering 6. apply page numbering 3. FORMATTING WORD DOCUMENTS - I - Spell Check Function - Highlighting Text - Cut and Paste Text retrieve a Word Document Students should be able to: 1. use the spell check Function 2. highlight Text 3. cut (remove) text and paste - Coping and Pasting of Text - Underlining Text 4. copy text and paste 5. underline Text © September 103 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE OBJECTIVES FORMATTING WORD DOCUMENTS - I - Bolding Text - Applying Italics Students should be able to: 6. bold text 7. apply italics to text - Font Style, Size and type 8. change font style, type and size - Alignment of Text 9. change the alignment of text - Changing the Case of Text 10. change case of a text - Finding and Replacing Text 11. find and replace text in a document - +-. 12. change the line spacing of a paragraph - Line Spacing UNIT TEST 1 4. INSERTING ITEMS IN A DOCUMENT - Inserting Page Breaks - Inserting Pictures or Graphics - Inserting Word Art - Inserting Bullets and Numbering - Inserting Border around a page or text © September Students should be able to: 1. insert a page break 2. insert a page break and section break 3. insert a picture or graphic into a document 4. insert word art into a document 5. insert Bullets and Numbering 6. insert a border around a page and text 104 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE OBJECTIVES 5. FORMATTING WORD DOCUMENTS – II INSERTING COLUMNS AND CREATING TABLES - Creating a two column document Students should be able to: 1. create a two column document - Inserting a column break 2. insert a column break - Creating tables of different size and width 3. create tables of different size and width - Splitting cells of a Table 4. split cells of a Table - Rotating text in a table 5. rotate text in a table - Centering text in a cell horizontally and 6. center text in a cell horizontally vertically 7. center text in a cell vertically - Adding Columns and Rows 8. add a column and row to a table - Deleting Columns and Rows 9. delete a column and row in a table UNIT TEST 2 TOPIC /CONTENT 6. SPECIAL DOCUMENTS: BUSINESS LETTERS - A business letter © September OBJECTIVES Students should be able to: 105 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE - Basic parts of a business letter Examples of a business letter Styles of writing business letters Producing a letterhead using Word Art Preparing business letters 1. define the term ‘business letters’. 2. identify the basic parts of a business letter. 3. state at least four (4) examples of business letters. 4. state two (2) styles of writing business letters. 5. distinguish between the blocked and indented styles of business letters. 6. produce a letterhead using word art feature. 7. prepare accurate examples of business letters © September 106 ARDENNE HIGH SCHOOL GRADE NINE CURRICULUM GUIDE 7. MAIL MERGE Students should be able to: - The concept of mail merge 1. explain the concept of mail merge - The steps involved in performing a mail merge 2. merge a document following the steps involved in mail - Creating a Main Document merge - Creating a Data Source 3. create and work with a main document - 4. create a data source for the mail merge Insertion of Merge Fields - Merging a document with its data source 5. enter information to the data source 6. insert merge fields created from data source into the main document 7. perform a mail merge to produce personalized documents. Students Textbook: Ardenne High School Grade 9 Information Technology Instructional Manual by the Business and Technology Department Assessment Procedures include: 1. Two Unit Tests 3. Home Work 2. Class Work 4. Quiz © September Learning Experiences include: 1. Question and Answer Sessions 2. Drilling Exercises 3. Class Reading 4. Computer Oriented Exercises 107