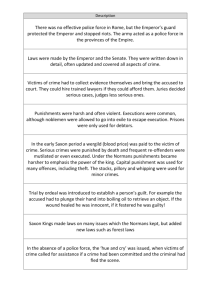
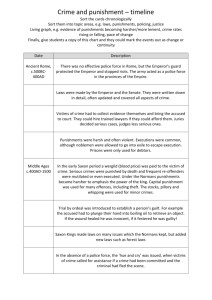
Introduction to Criminal Justice, First Edition
advertisement

Introduction to Criminal Justice, First Edition Table of Contents Part 1: Crime, Law, Criminals, and Victims Chapter 1 - Criminal Justice in Society Themes in Criminal Justice The Problem of Crime Thinking About Crime, Defining the Crime Problem, The Problem of White Collar Crime, Changing Demands on the Criminal Justice System Controlling Crime in a Democratic Society Discretion and Criminal Justice The Criminal Justice System Police, Courts, Corrections, Careers in Criminal Justice The Criminal Justice Process Initial Contact with the Police, Investigation, Arrest, Booking, Charging, Grand Jury, Initial Appearance, Preliminary Hearing and Arraignment, Bail/Detention, Plea Bargains, Trial, Sentencing, Postconviction Remedies, Corrections, Institutional Release and Postrelease Supervision Perceptions and Criminal Justice Defining Situations, What are Perceptions? Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 2 - Criminal Law: The Foundation of Criminal Justice Origins of Criminal Law Early Codifications of Law, Common Law and the Concept of Stare Decisis, Contemporary Sources of Criminal Law Conceptualizing Crime Relation of Civil Law to Criminal Law, Seriousness of Crime, Legal Definition of Crime Functions of Criminal Law Defining Socially Unacceptable Behavior, Controlling Behavior and Maintaining Social Order, Regulating the Punishment of Behavior Elements of a Crime Actus Reus, Mens Rea, Concurrence of Actus Reus and Mens Rea Criminal Responsibility Self-Defense, Duress, Age, Mistake, Necessity, Consent, Intoxication, Insanity, Legal Exemptions Due Process and the Rights of the Accused The Bill of Rights, The Fourteenth Amendment, Incorporation of the Bill of Rights Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 3 – Measuring Crime Measures of Crime Uniform Crime Reports, Victimization Surveys, Self-Report Studies, Comparing the UCR, NCVS, and NYS, Sourcebook of Criminal Justice Statistics Extent and Nature of Crime Ecological and Seasonal Differences, Age and Crime, Gender and Crime, Race and Crime, Social Class and Crime Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 4 – Theory and Policy Supernatural Explanations The Classical and Neoclassical Schools of Criminology Cesare Beccaria, Jeremy Bentham, Demise of the Classical School, Policy Applications of the Classical and Neoclassical Schools The Positive School Biological Positivism, Psychological Positivism, Sociological Positivism The Critical School Labeling Theory, Conflict Theory, Policy Applications of the Critical School Female Criminality Biological Explanations, Psychological Explanations, Sociological Explanations Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 5 – Crime Victims The Study of Crime Victims The Extent and Nature of Victimization Group Differences, Victimization Trends, Cumulative Risks, International Survey of Crime Victims Costs of Victimization Economic Costs, Psychological Costs Types of Victims Children, Teenagers, The Elderly, Women, Minorities, Workplace Crime Victims Accounting for Criminal Victimization Fixing Responsibility, Victim Facilitation, Victim Precipitation, LifestyleExposure Theory Crime Victims and the Criminal Justice System Police, Prosecutors, Defense Attorneys, Judges, Parole Boards Victim-Oriented Reforms Restitution and Compensation Programs, Victim Impact Statement Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Part 2: Police Chapter 6 – Police History and Systems Our English Heritage The Kin Police System, The Frankpledge Police System, The ParishConstable Police System, The Uniformed Police System American Policing The 1700s to the 1790s: The Origin of Organized Policing, The 1800s to the 1890s: Growth, Brutality and Corruption, The 1900s to the 1930s: Building Organizations and Technology, The 1940s to the 1980s: Testing the Reform Model, The 1990s and Beyond: A Quiet Revolution Police Systems Public Law Enforcement, Private Security Police, International Policing: Interpol Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 7 – Police Organization and Functions The Structure of Police Organizations Formal Structure: Police Bureaucracy, Informal Structure: The Police Subculture and Police Personality Functions of the Police Police Discretion, Order Maintenance, Service, Law Enforcement Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 8 – Police and the Law Policing in a Democratic Society The Exclusionary Rule Establishing Probable Cause, Searches and Seizures Warrantless Searches Search Incident to Arrest, Stop and Frisk, Automobile Searches, Plain View, Open Fields, Consent Searches, Abandoned Property, High-Speed Pursuit, Boarder Searches, Electronic Surveillance Arrest The Arrest Warrant, Warrantless Arrests, Arrests in the Home Booking Lineups Interrogation and Confessions Coerced Confessions, The Nature of Coerced Confessions, Confessions and Counsel, In Support of Miranda, Erosion of Miranda Politics, the Police, and the Law Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 9 – Critical Issues in Policing Discretion The Reason for Discretion, Factors Influencing Discretion, Pros and cons of Discretion, Controlling Discretion Corruption A Continuum of Corruption, Corrupt Police Officers, Corrupt Police Departments, Explaining Corruption, Controlling Police Corruption Force Police Brutality, Deadly Force, High-Speed Pusuits Stress Stress Inherent in Police Work, Internal Stressors, External Stressors, Impact of Stress, Controlling Stress Women in Policing History of Women in Policing, Policewomen Today Minorities in Policing History of Minorities in Policing, Redressing Problems in Recruiting and Promoting Minorities Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Part 3: The Courts Chapter 10 – The Criminal Courts: History, Structure, and Participants History of Criminal Courts The Emergence of Criminal Courts, The American Colonial Court System, Post-Colonial Developments, Slave Courts, Frontier Justice Jurisdiction of the Criminal Courts The Dual System of Courts State Court Systems Courts of Limited Jurisdiction, General Trial Courts, Intermediate Appellate Courts, Courts of Last Resort, Unification of Courts The Federal Courts U.S. Magistrate Judges, United States District Courts, United States Courts of Appeals, United States Supreme Court Court Participants Clerks, Bailiffs, Reporters, and Court Administrators The Judge The Role and Responsibilities of Judges, Background of Judges, Selection of Judges, Removing Judges from Office The Prosecutor Selection of Prosecutors, Responsibilities of the Prosecutor, Prosecutorial Discretion Defense Attorneys The Role of the Defense Attorney, The Right to Counsel, Representing Indigent Defendants, Competence of Defense Attorneys Courtroom Workgroups Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 11 – Prosecuting the Accused: From Initial Appearance to Plea Bargain Initial Appearance Notification of Defendant’s Rights, Timing of the Initial Appearance, The 48-Hour Rule The Grand Jury History of the Grand Jury, The Grand Jury Today, Selection of Jury Members, Grand Jury Hearings, Criticisms of the Grand Jury System The Prosecutor’s Charging Decisions Influences on the Charging Decision, Models of Prosecutor Charging, Public Perceptions of Prosecutors’ Charging Decisions, Patterns of Charging Preliminary Hearings The Format of Preliminary Hearings, Discovery, Pretrial Release, Preventive Detention, Predicting Dangerousness Entering Pleas The Guilty Plea, The Plea of Nolo Contendere, The Not Guilty Plea, The Plea of Not Guilty by Reason of Insantiy, Can a Defendant Withdraw a Not Guilty Plea? Plea Bargaining History of Plea Bargaining, Types of Bargains, The Judge’s Role in Plea Bargains, Are Plea Bargains Constitutional?, Who Wins with Bargained Justice?, Who Loses with Bargained Justice?, Attempts to Control Plea Bargaining Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 12 – The Trial Pretrial Motions Motions for Dismissal of Charges, Motion for Change of Venue, Motion for Severance of Defendants or Charges, Motion for Discovery, Motion for a Bill of Particulars, Motion for Suppression of Evidence, Motion of Intention to Provide Alibi, Motion for Determination of Competency, Motion for Continuance The Right to a Speedy, Public, and Fair Trial The Right to a Speedy Trial, The Courts, the Public and the Press, Cameras in the Courtroom Bench Trial versus Jury Trial Constitutional Right to a Jury Trial, Size of Juries, Selecting the Jury The Trial Opening Statements, Presentation of Evidence, Closing Arguments, Judge’s Instructions to the Jury, Jury Deliberations, Judgment or Verdict Appeal of Verdict The Right to Appeal, The Appeal Process Other Postconviction Remedies Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 13 – Sentencing The Goals of Sentencing Retribution, Deterrence, Incapacitation, Rehabilitation Types of Sentences Intermediate Sentences, Indeterminate Prison Sentences, Determinate Prison Sentences, Concurrent, Consecutive and Mandatory Sentences Arriving at an Appropriate Sentence The Presentence Investigation Report, The Sentencing Hearing, The Role of the Victim in Sentencing Disparity and Discrimination in Sentencing Disparities and Sentencing, Discrimination and Sentencing, Consequences of Disparities and Discrimination in Sentencing, Race and Ethnicity, Gender, Socioeconomic Status, Age Capital Punishment The Supreme Court and Capital Punishment, Characteristics of Death Row Inmates, Public Opinion and the Death Penalty, Arguments Over Capital Punishment Appeal of Sentence Grounds for Appellate Review of Sentence, The Appeal Process Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Part 4: Corrections Chapter 14 – Corrections History and Structure Colonial Punishments The Death Penalty, Fines and Corporal Punishment, Opposition to Corporal Punishment Early American Prisons The Pennsylvania Model, The New York Model, Comparing the Two Models The Reformation of Penology Creation of the Mark System, The Irish System, The Birth of Reformatory, The Elmira Reformatory The Rebirth of the Prison Emergence of the Medical Model, Other Correctional Innovations Structure of Modern Prisons Prison Security Levels, Coeducational Prisons, Boot Camps, Military Prisons The Federal Prison System Early History of Federal Prisons, Federal Bureau of Prisons Privatization of Correctional Services Prisons for Women English Servitude, Colonial Treatment, Reform Efforts Jail Systems The Colonial Jail, The Modern Jail Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 15 – Prisons Prisons and Prisoners Classifications of Prisoners, Characteristics of Prisons, The Inmate Population, Prison Programs Managing Prisons Prison Personnel, Custody Staff, Female Correctional Officers, Prison Discipline, Managing Special Populations Life in Prison Inmate Order, Inmate Subculture, Prison Gangs, Coping in Prison, Sex in Prison, Prison Violence Women in Prison Social Order of Women’s Prisons, Programs for Women, Mothers in Prison Prisoners’ Rights Freedom of Religion, The Right to Privacy, Mail and Access to the Media, Access to Courts and Legal Services, Protection Against Cruel and Unusual Punishment, Medical Care, Prison Conditions Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Chapter 16 – Corrections in the Community Probation The Emergence of Probation, The Rationale Behind Probation, Probation Administration, Assignment to Probation, Conditions of Probation, Supervisory Styles, Specialized and Generalist Models of Probation, Revocation of Probation, Effectiveness of Probation Supervision Intermediate Sanctions Intensive Probation Supervision, House Arrest and Electronic Monitoring, Fines, Forfeitures, Restitution, Community Service Parole and Other Prereleases The Emergence of Parole, Types of Prison Release, Characteristics of Offenders on Parole, Modern Parole Administration, Parole DecisionMaking, Leaving Prison, Parole Supervision, Revocation of Parole Furloughs and Other Temporary Prison Releases Furloughs, Work and Educational Release Evaluating Community-Based Sanctions Balancing Sanctions Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Part 5: Juveniles and Criminal Justice Chapter 17 – Juveniles in the Justice Systems The Legal Status of Juvenile Offenders Early Control of Juvenile Crime, The Child Saving Movement, Status Offenders, Juvenile Delinquency Today Overview of the Juvenile Justice System Arrest, Detention, Juveniles in Adult Jails, The Juvenile Court, Juvenile Corrections Waiver of Jurisdiction to Criminal Court Reasons for Transferring Juveniles, Legal Criteria for Transfer, The Transfer Process, Double Jeopardy, Who is Transferred? Prosecuting Juveniles Sentencing the Convicted Juvenile Sentencing Alternatives, Severity of Sentences in Adult Court The Juvenile Offender in Prison Separating Juvenile and Adult Inmates in Prison, Adjusting to the Institution The Death Penalty and Juveniles Characteristics of Juveniles on Death Row, Should Juvenile Offenders be Executed? Summary Key Terms Discussion Questions Class Activities Further Reading Notes Epilogue: Confronting Crime at the Turn of the Century – The Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act of 1994 Recent Federal Efforts to Control Crime The Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act of 1994 Police and Law Enforcement, Assault Weapons Ban and Other Gun Provisions, “Three Strikes” Sentencing, Prisons and Prisoners, Death Penalty, Youth and Crime, Violence Against Women, Crime Prevention Final Comments Notes Appendix A: Constitution of the United States Appendix B: Documents Glossary Legal Case Glossary and Index Name Index Subject Index