Causes of World War One - olivia
advertisement

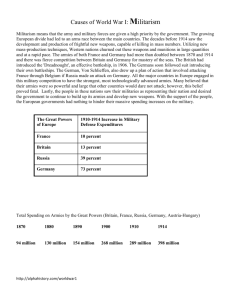
Causes of World War One There are a number of causes both Long term and Short Term. The ones below are the longer term causes Alliances An alliance is an agreement made between two or more countries to give each other help if it is needed. When an alliance is signed, those countries become known as Allies. A number of alliances had been signed by countries between the years 1879 and 1914. These were important because they meant that some countries had no option but to declare war if one of their allies declared war first. Imperialism Imperialism is when a country takes over new lands or countries and makes them subject to their rule. By 1900 the British Empire extended over five continents and France had control of large areas of Africa. The amount of lands 'owned' by Britain and France increased the rivalry with Germany who had entered the scramble to acquire colonies late and only had small areas of Africa. Pink = British Blue = French Red = German Militarism Militarism means that the army and military forces are given a high profile by the government. The growing European divide had led to an arms race between the main countries. The armies of both France and Germany had more than doubled between 1870 and 1914 and there was fierce competition between Britain and Germany for mastery of the seas. The British had introduced the 'Dreadnought', an effective battleship, in 1906. The Germans soon followed suit introducing their own battleships. The German, Von Schlieffen also drew up a plan of action that involved attacking France through Belgium if Russia made an attack on Germany. Nationalism Nationalism means being a strong supporter of the rights and interests of one's country. The Congress of Vienna, held after the Napoleonic wars left both Germany and Italy as divided states. It was nationalism the re-unification of Italy in 1861 and Germany in 1871. France was angry because the settlement at the end of the Franco-Prussian war had given AlsaceLorraine to Germany. Large areas of both Austria-Hungary and Serbia were home to differing nationalist groups, all of whom wanted freedom from the states in which they lived. Crises The Moroccan Crisis - In 1904 Morocco had been given to France by Britain, but the Moroccans wanted independence and were supported by Germany. War was avoided, but in 1911, the Germans were again protesting against French possession of Morocco. Britain supported France and Germany was persuaded to back down for part of French Congo. The Bosnian Crisis - In 1908, Austria-Hungary took over Bosnia. This angered Serbians who felt the province should be theirs. Serbia threatened Austria-Hungary with war, Russia, allied to Serbia, mobilised its forces. Germany, allied to Austria-Hungary mobilised its forces and prepared to threaten Russia. War was avoided when Russia backed down. In 1911 and 1912 there was war in the Balkans when the Balkan states drove Turkey out of the area. The states then fought each other over which area should belong to which state. Austria-Hungary intervened and forced Serbia to give up land. Tension between Serbia and Austria-Hungary was high. Activities – The Long Term Causes of WW1 Use the information on the left and further research of your own to determine the following. 1. The two main alliances at the time were called the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. Which countries belonged to each, and why was this such a difficult situation. In the Triple Entente the countries were Russia, France and Britain. In the Triple Alliance the countries were Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy. This was a difficult situation because if one country in an alliance declared war, for example Austria-Hungary, then all the other countries in that alliance would have to help out that country during the war. 2. How did imperialism contribute towards Germany’s increasing anger with Britain and France? Imperialism contributed towards Germany’s increasing anger with Britain and France because the British Empire ruled five continents. France ruled many areas in Africa such as Madagascar. Germany did not own many places and was trying to rule places and only got a small portion of Africa. 3. Why was nationalism an important factor? Nationalism is an important factor because without it people would not fight for their country. If nobody was a believer in their countries rights and the interests of their country then that country would not move forward in the world in terms of owning more land etc. Also people would not fight for the freedom of their country (if they were under another country’s power) if they did not have nationalism. 4. Describe the part played by Germany in increasing European militarism. Germany had doubled the size of its army between 1870 and 1914. When Britain brought out a battleship which it called the “Dreadnought” Germany created more battleships. After introducing the battleships Germany devised a plan to attack France in case Russia attacked Germany. 5. What links were there between the two crises and: a. Alliances: The link between alliances and the Moroccan Crisis is that because France had alliances with Britain, they had someone supporting them to keep ownership of Morocco. Morocco wanted to be independent and Germany agreed. Since the Triple Entente existed though, Germany could not fight against France and Britain. The link between alliances and the Bosnian Crisis is that since AustriaHungary had alliances with Germany it was able to stop a war from occurring between them and Russia. b. Imperialism: The link between imperialism and the Moroccan Crisis is that Morocco was now governed and ruled by France. They wanted independence and freedom but were not able to gain any since Germany was forced to back down from standing up for Morocco. The link between imperialism and the Bosnian Crisis is that Austria-Hungary now had control over Bosnia. Serbians wanted control of Bosnia but did not get it when Russia decided not to fight in the war to get control of Bosnia. When Turkey was no longer there a fight broke out between the Balkan states over who would own the land. c. Militarism: The link between militarism and the Moroccan Crisis is that since Germany’s army was not as strong as the British army they were forced to back down from fighting for Morocco’s freedom. The link between the Bosnian Crisis and militarism is that when Germany and Austria-Hungary allied they formed a stronger army then Russia and Serbia. This caused Russia to back down from the war. d. Nationalism: The link between nationalism and the Moroccan Crisis is that the Moroccan people wanted freedom for their country because they knew that it was in the country’s best interest. Germany also wanted Morocco to be free and independent. The link between nationalism and the Bosnian Crisis is that Serbians wanted Bosnia to be theirs. Also when the Balkan states fought each other for who should own which parts of Turkey shows nationalism because people were thinking that their country deserved the right to own more land.