Chem Rev #2.doc

Name : ________________
Date : _________
Chemistry Of Life : Review #2
Biological Molecules (Learning Outcomes C1-C6)
L.O. C-1 Synthesis vs. Hydrolysis
___ 1. For something to be considered "Organic" in chemistry, what two elements must
it possess?
___ 2. Carbon (#6) must share electrons to become stable, therefore, it forms what type
of chemical bonds with the other atoms it bonds with?
___ 3. How many extra electrons must carbon share to reach the octet rule?
___ 4. A large molecule made up of several smaller unit molecules (monomers) is called
a…?
___ 5. The process of joining one monomer to another monomer, requires that an "H" is
removed from one monomer, while an "OH" is removed from the other
monomer. In the process water forms (HOH). Give the two scientific names for
this process.
___ 6. The reverse process, when large polymers are broken down into their individual
monomers requires the input of a water molecule. Give the scientific name for
that type of reaction.
___ 7. When 5 monomers (for example 5 amino acids) are linked together to form a
small protein (polymer). How many water molecules would be formed in the
process?
____8. When a starch molecule (polymer) consisting of 10 glucose molecules is broken
down to release all 10 glucose molecules, how many water molecules are produced?
L.O. C-2 Chemical structure of Polymers – See "polymer-monomer table" on p. 31
___ 1. What are the unit molecules (monomers) of a protein?
___ 2. When building large carbohydrate molecules (polymers) like starch and
glycogen, what monomers are required?
___ 3. A nucleotide is the unit molecule (monomer) of what type of polymer?
___ 4. What is the more scientific name for a large complex carbohydrate? P. 32
L.O. C-3 Empirical Formula of a Carbohydrate
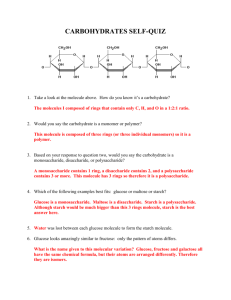
___ 1. List the three key elements that make up a carbohydrate.
___ 2. What important ratio must be seen in the formula of a typical carbohydrate?
___ 3. What is the more scientific name for a simple sugar (carbohydrate)?
L.O. C-4 Types of Saccharides
___ 1. Draw one of the common representations of glucose. – See fig. 2.17
___ 2. What is the chemical formula for glucose?
___ 3. Give the generic name for any simple sugar containing 6 carbons.
____4. Give the generic name for any simple sugar containing 5 carbons.
___ 5. Give the name for three specific mono-saccharides mentioned in the notes.
___ 6. What is a disaccharide?
___ 7 Give the name of three specific disaccharides mentioned in the notes.
___ 8. For the three disaccharides mentioned above, list the two mono-saccharides for
each..
___ 9. Give the names of the three specific examples of polysaccharides.
___ 10. Use a diagram to illustrate how two glucose molecules can be joined to form a
single maltose molecule.
___ 11. Give a specific example of a pentose sugar.
___ 12. Give a specific example of a hexose sugar.
L.O. C-5 Starch, Cellulose and Glycogen
___ 1. What is the primary function of Starch in plants?
___ 2. What is the primary function of glycogen in animals?
___ 3. Both starch and cellulose are produced and used by plants. How do these
polysaccharides differ in their structure and in their function.
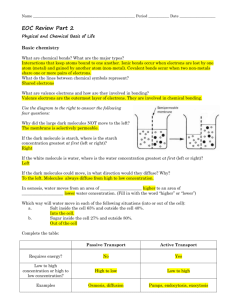
___ 5. How can you tell the difference between starch and glycogen if given a diagram
of the two?
___ 7. What benefits might cellulose have in our diet?
L.O. C-6 Functions of Carbohydrates
___ 1. What is the main function of carbohydrates in living things?
___ 2. What type of reaction is responsible for breaking down polysaccharides?
___ 3. What two functions do carbohydrates have in plants?
Practice Quiz: