Government Systems and Citizen
Participation and Rights
__________________________________________
__________________________________________
Regions and People of the World
Sixth Grade
Standards-based Lesson Plan
_____________________
2007-2008
Developed by the Hamilton City School District, All Rights Reserved
Page 1 of 26
Lesson Summary / Overview
Title: Government Systems and Citizen Participation and Rights
Duration: 3-4 Days / Class Periods
Targeted Benchmarks and Indicators
Responsibilities
Responsibilities
Citizenship
Rights and
Citizenship
Rights and
Government
Standard
Benchmark
Indicator
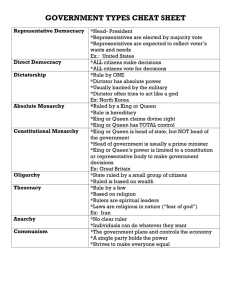
Gv6C. Compare the defining characteristics of
democracies, monarchies and dictatorships.
Gv6C4. Describe the defining characteristics of democracies,
monarchies and dictatorships.
C6A. Show the relationship between civic
participation and attainment of civic and public
goals.
C6A1. Explain how opportunities for citizens to participate in
and influence the political process differ under various systems
of government
C6B. Identify historical origins that influenced the
rights U.S. citizens have today.
C6B2. Compare the rights and responsibilities of citizens living
under various systems of government.
Final Assessment:
Students will complete a traditional test to culminate work on the benchmarks and
indicators. Questions are written in OAT style –Multiple Choice, Short Answer, and
Extended Response.
Optional Final Assessment or Extension Activity
To complete this optional extension activity, students will construct an essay in
response to the following quote from Winston Churchill: "Democracy is the worst form
of government on earth except for all the rest."
Essential Questions – Focus Questions:
1. What are the defining characteristics of democracies, dictatorships, and
monarchies?
2. What is the difference between a direct and representative democracy?
3. How are monarchies and dictatorships alike? How are they different?
4. Which government system allows its citizens the most opportunities to participate
and influence the political process?
5. Which government system does the best job of providing and protecting it’s
citizen’s rights?
Page 2 of 26
6. Who decides a citizen’s rights and responsibilities in a dictatorship?
7. Which two government systems are most alike?
Key Vocabulary
Democracy
Direct Democracy
Representative Democracy
Republic
Monarchy
Absolute Monarchy
Constitutional Monarchy
Empire
Kingdoms
Dictatorship
Oligarchy
Majority Rule
Civic Participation
Rights
Responsibilities
Divine Right
Preview Activities (Pre-Assessment or “Before” Activity)
To get a sense of the students understanding of governments systems before the
lesson, perform a Pre/Post Learning Concept Check. This information can be helpful on
selecting groups or knowing where to focus during the course of the lesson. This preassessment can also be revisited at the end of the lesson to informally measure
learning or to be used for a final writing assignment to answer the following BIG IDEA
QUESTION: What are the defining characteristics of democracies, monarchies, and
dictatorships and how do they compare to one another?
Following the Pre/Post Learning Concept Check, preview Governments and the World
Today (pages 500 – 506) in your Harcourt Horizons Ancient Civilizations text with your
students. A Preview Map is provided with this lesson, which helps you guide students
through the reading and models how an active reader asks themselves questions and
makes predictions or inferences about the section that they are about to read. It would
be a good idea to make transparencies of the Preview Map and briefly go through the
pages with your students. The key is to familiarize the reader with the main ideas, titles,
bold words, italicized words, maps, graphs, pictures, quotes, and diagrams before they
read and work on an assignment. “Previewing Non-fiction Text” is a quick, simple, and
powerful “before” strategy helps students practice active reading skills and prepare for
the main part of the lesson.
Engaging Activity 1 – Creating Illustrated Dictionary Entries for Democracies,
Monarchies, and Dictatorships
During this activity, Students will be broken up into three groups to research the basic
types of governments -- Democracy, Monarchy, and Dictatorship. The result of this
research is an illustrated dictionary entry. This process allows the students to look at
the different types of government more critically as they make their way through the
various levels of Blooms Taxonomy. Once each student has all or most of their
illustrated dictionary entry complete, they will briefly meet in groups to share there
thoughts and results with other students with the same type of government. Then each
group of students will take turns share their findings to the whole class. The students in
the audience need to fill in their chart based on the presenting group’s findings and
teacher direction. This will help prepare the students for their next activity where they
Page 3 of 26
compare and contrast the types of governments in a schematic feature analysis chart
(the state uses the word “compare” to ask students for both similarities and differences).
Engaging Activity 2 –Comparing Democracies, Monarchies, and Dictatorships
(with a Schematic Feature Analysis Chart)
To compare the defining characteristics of major types of governments (and the major
subgroups that need to be taught in the 6-8 grade-band), the students will complete a
schematic feature analysis chart. If the type of government is associated with a defining
characteristic, then the students will write a “+” (plus-sign) in the grid where that column
and row intersect; if the type of government is not associated with the defining
characteristic, a “-“(minus-sign) is placed in the corresponding square on the grid. By
the end of the activity students will be able to see on one sheet the similarities and
differences between the three types of governments and citizens’ rights and
opportunities for civic participation under each.
Authors notes:
Page 4 of 26
Final Assessment
1. Which is a characteristic of a direct democracy?
A.
B.
C.
D.
All eligible citizens can assemble and vote on government issues.
Citizens elect representatives and officials to government offices.
Common Citizens can petition the king or queen.
Citizens can vote for the dictator’s political party.
2. Which defining characteristic is common to both monarchies and
dictatorships?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Both governments are ruled by a king or queen.
Both governments are ruled by one national leader.
Both governments allow citizens to actively participate through elections.
Both governments have a variety of political parties.
3. Which two types of government allow citizens to vote for representatives to a
national legislature?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Direct Democracy and Dictatorship
Constitutional Monarchy and Absolute Monarchy
Oligarchy and Theocracy
Representative Democracy and Constitutional Monarchy
4. Which person or group is sovereign in a democracy?
A.
B.
C.
D.
The Dictator
The Politburo
The People
The Monarch
5. An incomplete outline is provided.
I. __________________
A. Usually a single leader
B. Ruler’s will is law
C. People have limited or no
rights
D. Leader has total authority
over citizens’ lives
Which types of government best completes the outline?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Absolute Monarchy
Dictatorship
Representative Democracy
Constitutional Monarchy
Page 5 of 26
6. Which statement is a defining characteristic of a monarchy?
A.
B.
C.
D.
The ruler is elected by the people.
The ruler inherits his or her power.
The ruler is a military leader who seizes power.
The ruler is elected by the national legislature.
7. Which type of government is similar to a form of dictatorship, where a small
group of people controls the government of a country?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Anarchy
Absolute Monarchy
Representative Democracy
Oligarchy
8. What typically happens to people who do not support a dictator’s policies or
political party?
A.
B.
C.
D.
They are rewarded for their independent thinking.
They arrested and given a fair trial with a jury of their peers.
They are punished, jailed, and sometimes executed.
They are ignored and not paid any attention.
9. Around the world, countries and people are governed by a variety of different
types of governments, such as democracies, dictatorships and monarchies.
Select one of these types and describe two of its defining characteristics
(2 points).
Page 6 of 26
Final Assessment Key with Exemplar Answers
1. Which is a characteristic of a direct democracy?
A.
B.
C.
D.
All eligible citizens can assemble and vote on government issues.
Citizens elect representatives and officials to government offices.
Common Citizens can petition the king or queen.
Citizens can vote for the dictator’s political party.
2. Which defining characteristic is common to both monarchies and
dictatorships?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Both governments are ruled by a king or queen.
Both governments are ruled by one national leader.
Both governments allow citizens to actively participate through elections.
Both governments have a variety of political parties.
3. Which two types of government allow citizens to vote for representatives to a
national legislature?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Direct Democracy and Dictatorship
Constitutional Monarchy and Absolute Monarchy
Oligarchy and Theocracy
Representative Democracy and Constitutional Monarchy
4. Which person or group is sovereign in a democracy?
A.
B.
C.
D.
The Dictator
The Politburo
The People
The Monarch
5. An incomplete outline is provided.
I. __________________
A. Usually a single leader
B. Ruler’s will is law
C. People have limited or no
rights
D. Leader has total authority
over citizens’ lives
Which types of government best completes the outline?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Absolute Monarchy
Dictatorship
Representative Democracy
Constitutional Monarchy
Page 7 of 26
6. Which statement is a defining characteristic of a monarchy?
A.
B.
C.
D.
The ruler is elected by the people.
The ruler inherits his or her power.
The ruler is a military leader who seizes power.
The ruler is elected by the national legislature.
7. Which type of government is similar to a form of dictatorship, where a small
group of people controls the government of a country?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Anarchy
Absolute Monarchy
Representative Democracy
Oligarchy
8. What typically happens to people who do not support a dictator’s policies or
political party?
A.
B.
C.
D.
They are rewarded for their independent thinking.
They arrested and given a fair trial with a jury of their peers.
They are punished, jailed, and sometimes executed.
They are ignored and not paid any attention.
9. Around the world, countries and people are governed by a variety of different
types of governments, such as democracies, dictatorships and monarchies.
Select one of these types and describe two of its defining characteristics
(2 points).
Possible Answers:
Democracy
Government Authority is based on the consent of the people
Elections for representatives and issues
Majority Rule
Multiple Political Parties
Rights are protected by a Constitution and a Bill of Rights
Civic Participation is encouraged
o Staying informed on issues
o Writing representatives
o Joining political parties
o Running for office
o Voting in elections
o Serving in Government
o Volunteering in the local community
Dictatorship
Elections are not held or tightly controlled
Leaders are typically military leaders who seize power
Sometimes a leader passes power onto a son or brother, like in a monarchy
National leader is the sovereign power
The leader has nearly total control of people’s lives
The dictator’s will is law
Oligarchy is a dictatorship by a small group of leaders.
Page 8 of 26
Liberties and rights are granted by the dictator
One Ruling Political Party – the dictator’s party
Limited Citizen Participation, unless supporting the dictator’s party
Monarchy
Elections are not held or tightly controlled in an absolute monarchy
Election are free and open in a constitutional monarchy
Leaders inherit their throne or power from a family member
Sometimes leaders seize power from a family member or opponent (several
historical examples)
King, Queen, Emperor, Empress, or Sultan is the sovereign power
The leader a high degree of power over people’s lives (authoritarian) in an absolute
monarchy
The leader is more of figure head in a constitutional monarchy
The absolute monarch’s will is law
A Prime Minister runs the country in a constitutional monarchy
Liberties and rights are granted by the absolute monarch
Liberties and rights are guaranteed by a constitution, bill of rights, and common law
in a constitutional monarchy.
Limited Citizen Participation in an absolute monarchy
Citizen Participation is encouraged in a constitutional monarchy
* Other possible defining characteristics exist, especially if the student provides an
example. Please use your professional opinion and mark accordingly.
Scoring Rubric
Points
Student Response
2
Student accurately describes 2 defining characteristics of a democracy,
dictatorship or monarchy.
1
Student accurately describes 1 defining characteristic of a democracy,
dictatorship or monarchy.
0
Student did not accurately describe any defining characteristics of a
democracy, dictatorship or monarchy.
Page 9 of 26
Optional Final Assessment or Extension Activity
Winston Churchill was Prime Minister of
Great Britain during World War II and
during the early years of the Cold War. He
is also a celebrated artist, author, and
orator. Over his long and distinguished
career, he has also made several memorable
statements about government, life, and war.
When speaking about governments, he once
said, “"Democracy is the worst form of
government on earth except for all the
rest.”
Based on the Churchill quote about democracy and your knowledge of the different
types of government, write an essay where you
Construct a thesis statement and explain the meaning of the quote.
Give details and examples to support your thesis in your main body
paragraphs.
Conclude your essay by explaining whether you agree or disagree with
the author of the quote and why.
Page 10 of 26
Preview Activity: Pre-Post Concept Check
Name __________________________________
Using the symbols listed to the left rate
your current understanding of the
terms and concepts below. Please
write the symbols on the blanks to the
left of each term. We will return to this
page at when we complete our
activities on Government Systems and
Citizen Interactions to answer the BIG
IDEA QUESTION and to see how much
you have learned.
Date _______________________
+ = Expert
= Some experience and still learning
- = Heard of it
N = New to me / Need more information
______________________
Direct Democracy
______________________
______________________
Representative Democracy
______________________
______________________
Absolute Monarchy
______________________
______________________
Constitutional Monarchy
______________________
______________________
Dictatorship
______________________
______________________
Oligarchy
______________________
BIG IDEA QUESTION - What are the defining characteristics of democracies, monarchies,
and dictatorships and how do they compare to one another?
After we finish the Pre/Post Learning Concept Check, we will be previewing
“Governments and the World Today” (pages 500 – 506) in your Harcourt Horizons
Ancient Civilizations Text. Please wait for your teacher to give you further directions.
Page 11 of 26
Preview Activity: Previewing Non-fiction Text with Preview Maps
Chapter/Section: _Chapter 12/Section 3________
What is the focus of the
Lesson?
What is the main idea?
Page: _500_________________
What are the main Governments of the World Today?
Democracy
What is a Democracy?
What are the important
Terms?
Where did democracy originate?
What type of democracy existed in Ancient Rome?
What’s the difference between a Direct and Representative
Democracy?
What type of government
does the U.S. Capital
Building symbolize?
Page 12 of 26
Chapter/Section: _Chapter 12/Section 3________
Page: _501_________________
Thinking about the Branches of Government
Do all governments
have a Constitution?
What powers does
each government have?
I wonder who makes
laws in a dictatorship.
If the president is the
top executive in a
democracy, who would
it be in an oligarchy?
What type of government did Romans
eventually adopt?
I know that courts
interpret laws in the
U.S. Who is
responsible for this in
a monarchy?
How many countries are democracies
today?
I wonder if all democracies operate like
the United States’ government.
What document put England on the part
to democracy?
How did Abraham Lincoln define
Democracy in the Gettysburg Address?
Page 13 of 26
Chapter/Section: _Chapter 12/Section 3________
How does Canada’s Parliament work?
Page: _502_________________
Does Canada’s parliament operate like the
U.S. Congress?
What makes Democracies work?
I wonder if Canada’s Parliament Building
was once a church.
Page 14 of 26
Chapter/Section: _Chapter 12/Section 3________
Page: _503_________________
Does Queen Elizabeth or Sultan Qaboos bin Said have
more power?
Monarchy
What does monarchy mean?
What is the difference between an
absolute monarchy and a constitutional
monarchy?
There is document the Magna Carta again.
Is this a term I should remember?
Is the British Bill of Rights similar to the
one in the U.S. Constitution?
What are some examples of absolute and
constitutional monarchs today?
Page 15 of 26
Chapter/Section: _Chapter 12/Section 3________
Page: _504_________________
Was the Nazi party,
the only political
party in power during
World War II?
Why did so many
people salute and
follow Hitler?
Dictatorship
How are absolute monarchs and
dictators similar?
The root word of Totalitarianism is
“total.” I wonder if that has anything to
do with the words meaning.
How long to dictators rule?
How do dictators come to power?
Who is Fidel Castro?
Who are some recent or
present dictators?
Page 16 of 26
Chapter/Section: _Chapter 12/Section 3________
What are some examples of
dictatorships today?
Page: _505_________________
Oligarchy
Is an oligarchy a type of dictatorship?
Where all communist governments
dictatorships?
This sounds similar to Hitler and the Nazi
party. I wonder how many political parties
dictatorships and oligarchies typically have?
Is Iraq still a dictatorship, like it says in
the text?
According to the map in the text, it appears that almost every continent has seen a dictator
rise to power during the 20th century. What conditions allow a dictator to seize power in a
country?
Page 17 of 26
Chapter/Section: _Chapter 12/Section 3________
How does China’s People’s Republic of China
fit in to the oligarchy category?
Page: _506_________________
Do dictators usually pick their successors?
How easy it for a common person to
influence or participate in the current
Chinese government?
LESSON REVIEW
I should probably look over these questions.
They may give me some direction as a read
the section and complete my assignment.
Do these questions align with the academic
content stanadards?
Gv6C. Compare the defining characteristics of
democracies, monarchies and dictatorships.
Gv6C4. Describe the defining characteristics of
democracies, monarchies and dictatorships.
C6A1. Explain how opportunities for citizens to
participate in and influence the political process
differ under various systems of government
C6B2. Compare the rights and responsibilities of
citizens living under various systems of
government.
Page 18 of 26
Engaging Activity 1: Creating Illustrated Dictionary Entries for
Democracies, Monarchies, and Dictatorships
Through this activity you will be explaining the major types of government systems in
the world today by making your own illustrated dictionary entries. A complete
illustrated dictionary entry includes:
Define each type of term in your own words
Draw an illustration that represents the term and how it works
Provide an Synonym and Antonym
Provide 1-2 related terms or forms
Identify one negative and one positive point about each term
Explain why it is important to know about this term
Example
Monopoly
Source: Bring Learning Alive!
Definition
to have total control of something, such as an industry
Synonym
Cartel
Antonym
Competition
Related Terms or
Forms of the Term
Positive and
Negative Points
Why is it import to
know this Term
1.
2.
3.
4.
Holding Companies
Trusts
Vertical Integration
Horizontal Integration
“+” – limits overlap of the same products, like electric service.
“-“ – limits competition in the market.
Knowledge of what a monopoly is helps us maintain competition and
promote innovation in the marketplace.
Page 19 of 26
Democracy
Definition
Synonym
Antonym
Related Terms or
Forms of the Term
Positive and
Negative Points
Why is it import to
know this Term
Page 20 of 26
Monarchy
Definition
Synonym
Antonym
Related Terms or
Forms of the Term
Positive and
Negative Points
Why is it import to
know this Term
Page 21 of 26
Dictatorship
Definition
Synonym
Antonym
Related Terms,
Forms of the Term
Positive and
Negative Points
Why is it import to
know this Term
Page 22 of 26
Engaging Activity 2: Comparing Democracies, Monarchies, and
Dictatorships
Name
_______________________________________
You have been provided with a list of defining characteristics of governments and types of governments. If the type of
government is associated with a defining characteristic, then record a + (plus-sign) in the grid where that column and
row intersect; if the type of government is not associated with the defining characteristic, a - (minus-sign) is placed in
the corresponding square on the grid.
Types of Governments
Defining
Characteristics
Direct
Representative Constitutional Absolute
Democracy Democracy
Monarchy
Monarchy Dictatorship Oligarchy
All eligible citizens
can assemble and
vote on issues
Elections are free and
open
Elections are not held
or tightly controlled
Leaders seize power
National Leaders
inherit their position
Rulers claim power by
“divine right”
People elect
representatives
People are the
sovereign power
National leader or
leaders are the
sovereign power
Liberties and rights
protected by a
constitution
Commoners can
petition the King
Nobles serve and
advise the Queen
Liberties and rights
granted by the
national leader(s)
One Political Party
System
Multiple Political
Party System
Encourages Free
Citizen Participation
Limited Citizen
Participation
Page 23 of 26
Engaging Activity 2: Comparing Democracies, Monarchies, and
Dictatorships – Answer Key
Types of Governments
Defining
Characteristics
Direct
Representative Constitutional Absolute
Democracy Democracy
Monarchy
Monarchy Dictatorship Oligarchy
All eligible citizens
can assemble and
vote on issues
Elections are free
and open
+
-
-
-
-
-
+
+
+
-
-
-
Elections are not
held or tightly
controlled
-
-
-
+
+
+
Leaders seize
power
-
-
-
+/-
+
+
National Leaders
inherit their position
-
-
+
+
-
-
Rulers claim power
by “divine right”
-
-
-
+
-
-
People elect
representatives
-
+
+
-
-
-
People are the
sovereign power
+
+
+/-
-
-
-
National leader or
leaders are the
sovereign power
-
-
+/-
+
+
+
Liberties and rights
protected by a
constitution
+/-
+
+
-
-
-
-
-
+
+
+
-
-
-
-
-
+
+
+
-/+
+
-
+
+
-
+
+
-
+
+
+
+
+
Commoners can
petition the King
Nobles serve and
advise the Queen
Liberties and rights
granted by the
national leader(s)
Multiple Political
Party System
One Political Party
System
Encourages Free
Citizen Participation
Limited Citizen
Participation
* NOTE – If a grid square has a “+/-,” that means that it can go either way, because there are examples of countries and governments that
have used this defining characteristics in different ways.
Page 24 of 26
Connections
Differentiated Instructional Support (Scaffolds)
The terms (types of governments) explored in this lesson need to be mastered, because they
will be used by the students in all of their Social Studies classes up through 12 th Grade.
Pairing students and giving extended time is an excellent way to scaffold the activities in this
lesson to ensure that students have learned these important concepts.
Extensions (Gifted)
To extend Engaging Activity 1, the teacher can ask the students to complete an illustrated
dictionary entry or cubing exercise (see MAX Teaching Book) for all of the types of
governments listed on the pre/post learning concept check.
To extend the Engaging Activity 2, the teacher can ask students to provide examples for each
defining characteristic.
To culminate the lesson, teachers can assign the “Churchill” writing assignment in place of or
in addition to the standards-based test questions on the Final Assessment.
Homework Options and Home Connections
Any of the activities can be given as homework, which leaves final determination of when and
how these exercises up to the classroom teacher.
Interdisciplinary Connections
Use the Four Square Writing Approach to answering an extended response item with supports and details.
Technology Connections
This lesson could easily be adapted into a power point slide show or used with a smart board.
Educational Research Connections and other Sources
Bower, B, Lobdell, J., Owens, S. Bring Learning Alive!: The TCI Approach for Middle and High
School Social Studies, Palo Alto, CA: Teachers Curriculum Institute, 2005.
Forget, M. MAX Teaching with Reading and Writing: Classroom Activities for Helping Students
Learn New Subject Matter While Acquiring Literacy Skills, Victoria, British Columbia: Trafford
Publishing, 2004.
Marzano, R. et al. Classroom Instruction that Works: Research-based Strategies for Increasing
Student Achievement, Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum
Development, 2001.
Ogle, D., Klemp R., McBride W. Building Literacy in Social Studies: Strategies for Improving
Comprehension and Critical Thinking, Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and
Curriculum Development, 2007.
Page 25 of 26
Page 26 of 26