ws_ ch.4 ex.doc
advertisement

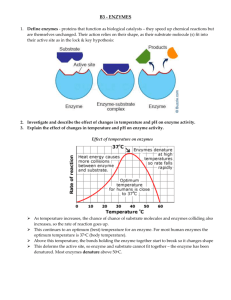
4 4.1 Enzymes and metabolism Metabolism (Book 1A, p. 4-3) Metabolism (新陳代謝) refers to the (1) _______________ of the chemical reactions that take place in an organism to keep it alive. Catabolism (分解代謝) All the (2) _______________ reactions Anabolism (合成代謝) within an organism (3) _______________ energy All the (4) _______________ reactions within an organism (5) _______________ energy 4.2 Properties and actions of enzymes (Book 1A, p. 4-4) A What is the role of enzymes in metabolism? (Book 1A, p. 4-4) To start a chemical reaction, enough energy must be supplied to the reacting molecules so that they can overcome the (1) _______________ _______________ (能障). Enzymes (酶) are (2) _______________ which act as biological (3) _____________ (生物催化劑). Enzymes can speed up the rate of chemical reactions by (4) _______________ the energy barrier so that reactions can take place at body temperature. Metabolic reactions would proceed very (5) _______________ or even stop without enzymes. B How do enzymes work? (Book 1A, p. 4-6) Each enzyme molecule has an (6) _______________ _______________, which is (7) _______________ (專一的) in shape. The active site of an enzyme molecule combines with the substrate molecules that fits the active site to form an (8) ______________________ _______________. The formation of the complex lowers the energy barrier of the reaction. In catabolic reactions, the enzyme helps to (9) _______________ the substrates apart. Ch.4 Enzyme / P.1 In anabolic reactions, the enzyme helps to (10) _______________ the substrates together. The complex then breaks down to give the (11) _______________. The enzyme is released in its (12) _______________ form. Specificity of enzyme: The (13) _______________ hypothesis (鎖鑰假說) explains the specificity of enzyme action. Enzymes combine with particular (14) _______________ only, like a key only fits in a particular (15) _______________. What are the properties of enzymes? (Book 1A, p. 4-7) C 1 Enzymes are biological catalysts. 2 They can (16) _______________ _______________ metabolic reactions. Enzymes can be (17) _______________. They combine temporarily with the substrates during reactions, but return to the original form and released after reaction. 3 Enzymes are required in relatively (18) _______________ amount. 4 Enzymes are (19) _______________. 5 Their structures and functions are easily affected by (20) _______________ and pH. The actions of enzymes are (21) _______________. Each enzyme catalyses only one type of reaction. Ch. 4 Enzyme / P.2 4.3 Factors affecting the rate of enzymatic reactions (Book 1A, p. 4-9) Enzyme activity is usually expressed in terms of (1) _______________ _______________ of an enzymatic reaction, which is the rate at which the substrates are used up or broken down, or the rate of the formation of product(s). A Temperature (Book 1A, p. 4-9) Effect of temperature on the rate of enzymatic reaction Temperature Effect on the rate of enzymatic reactions Low temperatures At around 0°C, enzymes become (2) inactive/active and the reaction rate is (3) low/high. As temperature rises, the molecules have (4) less/more kinetic energy and collide (5) less/more frequently. This leads to a (6) lower/higher chance to form an enzyme-substrate complex. Optimum (7) minimum/maximum. temperature High Enzymes work best and the reaction rate reaches a temperatures Enzyme molecules change shape and denatured (變性), so the rate of reaction (8) decreases/increases. Misconception Some students wrongly think that enzymes are killed by heating so the rate of enzymatic reaction decreases. Enzymes are NOT living things. They cannot be killed. They are denatured (their shapes are changed) at very high temperatures. Ch.4 Enzyme /P.3 B pH (Book 1A, p. 4-11) Effect of pH on the rate of enzymatic reaction Each enzyme works in a (9) _______________ range of pH. An enzyme works best at its (10) _______________ pH. C Enzymes become (11) _____________ at unsuitable pH. Therefore enzyme activity decreases. Inhibitors (Book 1A, p. 4-12) Enzyme activity can be slowed down or even stopped by (12) _______________ (抑制劑). (13) ______________________ (14) ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ (競爭性抑制劑) (非競爭性抑制劑) Similar to substrate molecules Not similar to substrate molecules Shape of molecule Action inhibitor substrate inhibitor (15) _______________ with the Attaches to other parts of the substrate molecules for active site enzyme to change its by binding to the active site of the (16) ______________, so that the enzyme substrate molecules can no longer fit into the active site Ch. 4 Enzyme / P.4 substrate substrate substrate enzyme inhibitor enzyme inhibitor Effect of The rate of enzymatic reaction The rate of enzymatic reaction does increasing (17) _______________ not increase substrate concentration 4.4 Applications of enzymes (Book 1A, p. 4-16) Enzymes are widely used in industrial processes to produce useful products. For example: Washing powder Meat tenderizer (鬆肉粉) Cheese Proteases and lipases are Papain extracted from papaya is added to remove stains. added to (1) ____________ meat. (2) _______________ milk. Bread Juice Proteases are used in Leather Enzymes modify the Enzymes are used to break down Enzymes are used to remove (3) ____________ in bread, plant cell walls in fruit juices, so hairs from hides (牛皮) and so that the bread can keep that the juices look less cloudy. (4) ___________ the leather. softer for a longer time. Ch.4 Enzyme /P.5 Advantages of using enzymes in industrial processes: Production of unwanted products can be reduced due to the (5) _______________ of enzyme action. Cost of production can be (6) _______________ as enzymes are efficient in small amounts. Extreme and expensive conditions are not required because enzymes can work at (7) _______________ conditions. Exercise A student carried out an investigation to study the effect of temperature on amylase activity. He prepared 5 test tubes, each contained 5 cm3 of starch solution and 1 cm3 of amylase solution. He put the tubes in water bath of different temperatures (0°C, 20°C, 40°C, 60°C and 80°C). He measured the time for all the starch in the test tubes to disappear. The results are shown in the graph below. time needed for the disappearance of all starch 0 a 20 40 60 80 temperature / °C Suggest a method to test for the presence of starch in the test tube. (1 mark) ____________________________________________________________________________ b Describe and explain the results at the following temperatures: i below 60°C (3 marks) ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ii above 60°C (2 marks) ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ c State two variables that should be kept constant in the above investigation. (2 marks) ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ d If acid is added to the test tubes, the starch will not disappear. Why? (2 marks) ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Total: 10 marks Ch. 4 Enzyme / P.6 Answers Ch 4 Enzymes and metabolism 4.1 1 sum 2 breaking-down 3 Releases 4 1 energy barrier 2 proteins 3 catalysts 4 6 active site 7 specific 8 enzyme-substrate complex 10 join 11 products 12 original 13 15 lock 16 speed up 17 reused 20 temperature 21 specific 1 reaction rate 2 inactive/active 3 low/high 6 lower/higher 7 minimum/maximum 10 optimum 11 denatured 14 Non-competitive inhibitor building-up 5 Requires 5 slowly 9 split lock-and-key 14 substrates 18 small 19 proteins 4 less/more 5 less/more 8 decreases/increases 9 4.2 lowering 4.3 12 inhibitors 13 Competitive inhibitor 15 Competes 16 shape 17 3 starch 4 soften 5 narrow increases 4.4 1 soften 2 coagulating 6 lowered 7 moderate specificity Exercise a Iodine test 1m b i At below 60°C, the amylase activity increases and reaches a maximum at about 60°C. 1m At low temperature, the enzymes are inactive and the reaction rate is slow. 1m As the temperature rises, the kinetic energy of the enzyme molecules increases, so they vibrate more frequently. This ii increases the chance to form an enzyme-substrate complex. 1m At above 60°C, the amylase activity decreases with the increase in temperature. 1m Enzymes become denatured at high temperatures.The active sites of the enzymes can no longer fit the substrate molecules. c Any two from: 1m 1m × 2 Concentration of amylase solution Concentration of starch solution pH of the reaction mixtures d Amylase is denatured at very low pH. 1m Reaction rate becomes very slow, so starch remains in the solution. 1m Ch.4 Enzyme /P.7