Unit 3

Unit 3 Study Guide
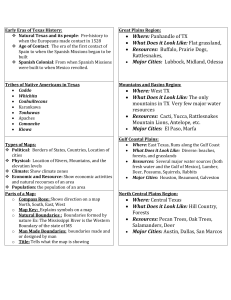
Explorers, Missions, & Colonization
Vocabulary conquistadores - one of the Spanish soldiers who sought riches and power for themselves, and wealth and glory for Spain, in the conquest of the Americas. Simplified definition : Spanish explorer looking for gold and glory. missions - a religious settlement. presidio - a Spanish military base. empresarios - the Spanish word for a land agent whose job it was to bring in new settlers to an area.
Simplified definition : people who brought and settled people in Texas. filibuster - an individual who carries out rebellious activities in a foreign country.
Important Dates
1519 - Alvarez de Pineda maps the Texas coast and Hernan Cortes conquers the Aztec
1718 - San Antonio de Valero, also known as the Alamo, is founded
1821 - Stephen F. Austin brings first U.S. settlers to Texas
Three G's
It was a massive undertaking for Spain to explore and conquer large parts of North & South America - as it took months to travel there by boat and large sums of money to fund expeditions. There were three main factors that lead the Spanish to explore in the New World (North & South America) and they were:
1. Gold - This brought not only wealth to the Spanish, but also led to the conquistador to be rewarded for his service to the Spanish empire.
2. Glory - All conquistadors sought glory, not only for Spain, but for themselves - if successful in finding riches for Spain in the New World they would be famous throughout the empire.
3. God - The Spanish were also concerned with converting Native Americans to the Catholic religion and making them more like themselves. They saw the Native Americans as children and it was their job to teach them how to live a "normal" life.
Columbian Exchange
New World
North & South America
Old World
Europe, Asia, Africa
Food Plants: avocados, beans, cashews, cassava roots, cocoa beans, corn, papayas, peanuts, pecans, peppers, pineapples, potatoes, squash, tomatoes, vanilla beans, wild rice
Food Plants: barley, oats, rice, wheat, bananas, chickpeas, coffee, grapes, lemons, lettuce, okra, olives, onions, oranges, peaches, pears, radishes, soybeans, sugarcane, watermelons
Other Plants: tobacco cotton, marigolds, rubber,
Other Plants: bluegrass, couchgrass, crabgrass, daisies, dandelions, roses
Animals & Insects: gray squirrels, guinea pigs, hummingbirds, muskrats, potato beetles, rattlesnakes, turkeys
Animals & Insects: chickens, cows, domestic cats, goats, hogs, honey bees, horses, Japanese beetles, mice, rabbits, rats, sheep, sparrows, starlings
Spanish Conquistadors and French Explorers
Alvarez de Pineda
Pineda was the first European to map the coast of Texas and claim Texas in the name of Spain.
Hernan Cortes
Sailed to eastern coast of Mexico & conquered the Aztecs. Montezuma drove Spanish out of Aztec capital on June 30, 1520, but Cortes later took control of the capital and the Aztecs surrendered on August
31, 1521. As a result of the expedition more Spanish conquistadors came to America to search for gold and glory.
Cabeza de Vaca
Shipwrecked on coast near Galveston possibly due to a hurricane -- he survived with the Karankawas for
8 years serving as a trader and shaman. He later traveled and lived among various Indian villages before finally reaching Mexico City and then returning to Spain. Once back home he wrote a book describing his experiences, plant, animals (buffalo), and rumored cities of gold in Texas.
Coronado
Conquistador that went exploring to find Cibola, the rumored seven cities of gold Cabeza de Vaca had written about, only to find poor Indian villages. In the course of his exploration he did explore the Texas
Panhandle and wrote back to the King of Spain about the rich fertile soil of the area and "strange cows"
(buffalo).
La Salle
Explored the Mississippi River to its mouth at the Gulf and claimed Louisiana for the French. On his return journey back to the mouth of the Mississippi river La Salle was thrown off course and instead landed near present-day Matagorda Bay in Texas. La Salle's established a settlement known as Fort St.
Louis that was eventually overrun by Karankawa Indians and La Salle was killed by his own men after going to find the Mississippi river and get help for the settlement. La Salle's establishment of a settlement in Texas convinced the Spanish that they had to take action to protect their claim to Texas.
Spanish Texas and Spanish Missions
Ysleta - first Spanish mission in Texas, which was established east of El Paso and is the oldest European town in Texas.
San Francisco de los Tejas - first mission in East Texas, which was established east of the Neches River.
It was built to convert the Tejas Indians living in the area to Catholicism.
San Antonio de Valero - established in 1718 along the San Antonio River to serve as a half-way point between the missions in East Texas and the missions below the Rio Grande in Mexico.
Purpose of Mission in Texas
1. Convert Native Americans to Christianity and to teach them to be good Spanish citizens
2. Represent Spanish government
3. Help to develop settlement within Texas
Daily Life in a Mission
A regular day at a mission in Texas would keep missionaries and Native Americans busy from dawn to dusk.
1. Start day with prayers
2. After breakfast, children would attend school, including classes in religion
3. The women wove cloth, molded pottery, or cooked
4. Men worked in the fields or learned a trade, such as, carpentry or blacksmithing
5. After supper came more religion classes for adults, followed by prayers
Reasons why Spanish missions failed in Texas
1. Little Indian interest in the missions
2. Lack of money from the Spanish government
3. Drought that killed crops
4. Disease
5. Conflicts with Native Americans
6. Conflicts with the French
Mexican Independence from Spain
Causes of Mexican Revolution Effects of Mexican Revolution
1. Economic & Social division between the rich
& poor in New Spain
2. American Revolution & other revolutions in
Latin America show Mexico they can also win their independence
3. Father Hidalgo called for an end to Spanish rule when he delivered his "Grito de Dolores"
4. Corrupt Spanish Officials
1. Mexico becomes and independent, but unstable, republic
2. Ruined economy and drained resources
3. Greatly decreased Tejano population
4. Led to increased moves to colonize Texas with immigrants from Europe and the
United States
5. Worsened relations with Texas Indians
Empresarios
Moses Austin - the first American to secure a land grant contract from the government of Spain to bring
300 families from the United States to Texas. Unfortunately, he died before ever bringing one family to
Texas.
Stephen F. Austin - took over his father's land grant when Moses died. He confirmed the legality of the contract with the new Mexican government. The 300 families that settled in his first colony became known as the "Old Three Hundred". Due to his continued efforts to settle the territory Stephen F. Austin became known as the "Father of Texas".
Martin de Leon - empresario and cattle rancher that brought primarily Mexican settlers into Texas.
Mexican Constitution of 1824
The Mexican Constitution of 1824 set up a federalist government. It was modeled after the Constitution of the United States and divided Mexico into 19 separate states. Texas was not its own state - Mexican authorities believed that Texas did not have the economy or population to become an individual state so they joined it to Coahuila forming the state of Coahuila y Tejas .
National Colonization Law of 1824
1. No empresario could receive more than 48,708 acres of land.
2. Colonies could not be established within 30 miles of coast or 60 miles of international border without permission from Mexican government.
3. To receive land contract you had to plan to stay permanently in Texas.
State Colonization Law of 1825
1. Foreigners were invited to settle in Texas.
2. Could receive title to land as individuals or through an empresario.
3. After a payment of $30, a family could receive as much as 4,428 acres of land.
4. Colonist did not have to pay taxes for a set number of years.
5. Colonists had to show evidence of good moral character and also had to become Catholic.