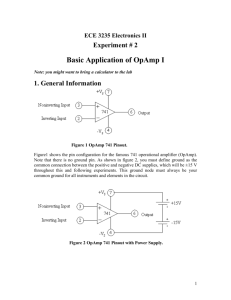
©IPK02/12/00 Op-amp Test. Decide whether each of the statements
advertisement

©IPK02/12/00 Op-amp Test. Decide whether each of the statements below is True or False and shade in the box corresponding to your answer on the marking sheet. PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS QUESTION PAPER. USE SCRAP PAPER FOR YOUR WORKING OUT. A correct answer gains 1 mark, an incorrect answer loses 1 mark and no attempt gains 0 marks. 1). An op-amp has a differential input. 2). An op-amp needs a dual power supply. 3). An op-amp has a very large voltage gain at high frequencies. 4). The voltage gain of an op-amp decreases with frequency. 5). The output voltage of an op-amp cannot exceed the supply voltages. 6). Voltage gain is the ratio 7). Power gain is the ratio 8). Bandwidth is the range of frequencies over which the power gain does not fall below 50% 9). Bandwidth is the range of frequencies over which the voltage gain does not fall below 50% 10). The circuit diagram below is of an inverting amplifier. V in V out Pout Pin Rf P R1 _ + Vin Vout 0V 11). The input resistance of the circuit in Qu10 is R1. 12). Point P in the diagram for Qu10 is called a virtual earth point. 13). The output resistance of the inverting amplifier is Rf. ©IPK02/12/00 Rf R1 14). The voltage gain of the circuit diagram in Qu10 is 15). For the circuit diagram in Qu10, if R1 is 10k, Rf is 220k, and the input voltage is 0.1V, then the output voltage will be -2.2V if the power supply voltage is greater than + 5V. 16). For the situation on Qu15, if the input voltage is increased to 0.3V, then the output voltage will be -6.6V. R3 Rf R2 V3 _ R1 V2 + Vout V1 0V 17). The diagram above is the correct diagram for a summing amplifier. 18). V V V The output voltage of a summing amplifier is given by Vout Rf 1 2 3 . R1 R 2 R 3 19). R For a summing amplifier if R1 = R2 = R3 = R then Vout f V1 V2 V3 R 20). For a summing amplifier if R is 10k, Rf is 220k, V1 = -2.5V, V2 = 4V and V3 = -1.5V then Vout = 0. 21). A summing amplifier can be used as a DAC if all of the resistor values are equal. 22). A summing amplifier does not have a virtual earth point. _ + Rf Vin Vout R1 0V 23). The circuit diagram above is for a non-inverting amplifier. ©IPK02/12/00 24). A non-inverting amplifier does not have a virtual earth point. 25). The input resistance of a non-inverting amplifier is equal to R1. 26). The minimum voltage gain of a non-inverting amplifier is -1. 27). For a non-inverting amplifier, if Rf = R1 then the voltage gain is 2. 28). The voltage gain of a non-inverting amplifier is given by 29). For a non-inverting amplifier, the output voltage is in phase with the input voltage. 30). A non-inverting amplifier has Rf = 30k, R1 = 10k, Vin = 0.1V and a power supply of +5V. The output voltage will be 0.4V 31). If the power supply voltage in Qu30 is increased to +15V, then the output voltage will increase to 1.2V. 32). If the input voltage in Qu30 is increased to 2V, the output voltage will be 8V. 33). A voltage follower can be made from a non-inverting amplifier by making Rf = 0 and R1 = infinity. 34). The voltage gain of a voltage follower is equal to +1. 35). The input resistance of a voltage follower is very large. 36). The amplitude of an alternating voltage is equal to the peak voltage. 37). The period of an alternating voltage is equal to the time between adjacent peak voltages. 38). The frequency of an alternating voltage that has a period of 20ms is 500Hz. 39). An op-amp with a voltage gain-bandwidth product of 106 will have a bandwidth of 1000 when used to make an inverting amplifier with a voltage gain of 102. 40). The output of an amplifier with a voltage gain of -100 is connected to the input of a second amplifier with a voltage gain of -100. This is equivalent to a single non-inverting amplifier with a voltage gain of 104. Vout R 1 f Vin R1