Chapter 17
advertisement

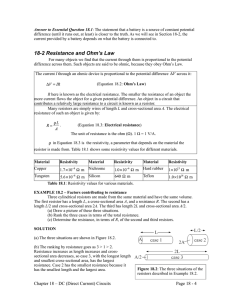
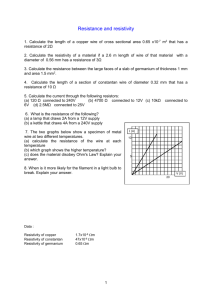
February 12, 2009 PHY 2054 Discussion Spring ‘09 Conceptual Review: Chapter 17 A. Electric Current & Drift Speed 1. An electron is circling around a nucleus with a frequency f. What is the effective current? 2. Express number density in terms of Avogadro’s number NA, density and atomic mass M. B. Resistance & Ohm’s law 1. A steady current is flowing in a resistor R. (A resistor is a conductor.) According to the Ohm’s law, voltage across it is not zero. We already know the potential is constant in a conductor in equilibrium. What’s wrong? 2. What is the difference between Ohm’s law and the definition of resistance? C. Resistivity 1. What factors determine the resistance of a conductor? 2. A tension is applied to a wire and the length of the wire is doubled. By what factor does the resistance of the wire increases? D. Temperature Variation of Resistance 1. Can you choose the reference temperature on your own? 2. Why does the resistance of many materials increase as its temperature increases? E. Electrical Power 1. Two resistors in series are connected across a battery. Which expression are you going to use to calculate the power consumption in one of the resistor? 2. A voltage ΔV is applied to two identical resistors in series. By what factor does the power consumption increase if you reconnect the resistors in parallel? 3. How much does it cost to use 1 000-W drier for 30 minutes if the cost of the electricity is $0.1/kWh? February 12, 2009 PHY 2054 Discussion – Spring ‘08 Practice Exam Problems (Chapter 17) 1. The current in an electron beam in a cathode-ray tube is measured to be 70 µA. How many electrons hit the screen in 5.0 s? (e = 1.6 1019 C) (Electric Current) electrons c.. 2.2 1015 electrons a. . 2.2 1011 electrons b. 8.8 1013 d. 8.8 1018 electrons 2. Wire A and Wire B are each carrying the same current. If the diameter of Wire A is twice that of Wire B, how does the drift velocity vdA in Wire A compare to that in in Wire B? (Drift Speed) a. vdA = vdB = 2 vdB c. vdA = vdB /2 d. vdA = b. vdA vdB /4 3. You measure a 25.0-V potential difference across a 5.00- resistor. What is the current flowing through it? (Ohm’s Law) a. 125 A b. 5.00 A c. 4.00 A d. 1.00 A 4. How long is a wire made from 100 cm3 of copper if its resistance is 8.5 ohms? The resistivity of copper is 1.7 × 10-5 ·m. (Resistivity) a. 7.1 m b. 1.7 × 102 m c. 2.2 × 102 m d. 3.0 × 103 m 5. A resistor is made of a material that has a resistivity that is proportional to the current going through it. If the voltage across the resistor is doubled, what happens to the current through it? (Nonohmic Material) a. It doubles. b. It quadruples. c. It increases by a factor of 23/2 d. It increases by a factor of 21/2 6. Carbon has a negative temperature coefficient of resistance of –0.5 × 10-3 (C)1. What temperature increase would result in a resistance decrease of 1% for a carbon resistor? (Temperature Variation of Resistance) a. 2C b. 20C c. 50C d. 100C 7. If electrical energy costs 5.5 cents per kWh, what does it cost to heat 200 kg water from 15C to 80C? (The specific heat of water = 103 cal/kgC and 1.0 cal = 4.186 J.) cents c. 16 cents potential across it? (Power) 2-d b. 83 d. 80 cents 8. An 8.00-Ω resistor is dissipating 100 watts. Answers: 1-c (Electrical Energy) a. 48 cents 3-b What are the current through it, and the difference of a. 12.5 A, 28.3 V b. 3.54 A, 12.5 V c. 3.54 A, 28.3 V d. 28.3 A, 3.54 V 4-a 5-d 6-b 7-b 8-c