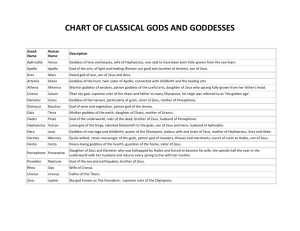
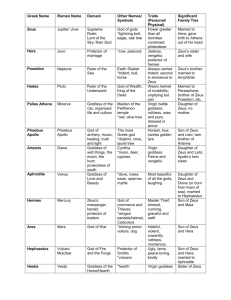
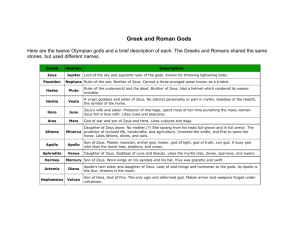
greekgodinfo - Kent City School District
advertisement

Aphrodite was th e Greek goddess of Love, Beauty and Eternal Youth A ph r od it e m e a n s " a r is e n f ro m t he fo a m" i n a nc i en t G r ee k B i r t h a nd F a m i l y o f A phr o d it e T he R o l e o f A p hr o di te a s a G o d d e s s T he P e r s o na l it y o f A p hr o d it e A p p e a r a nc e o f A p hr odi t e S y m b o l s o f A p hr od it e B ir th a n d F am i l y o f A p hr o di te Aphrodite was created from the foam of the crystal waters of Paphos in the fragrant island of Cyprus, when the Titan Cronos slew his father, the major Titan Ouranos. Aphrodite was married to the lame smith Hephaestus, who was the Olympian God of the Iron, but her heart was devoted to Ares, the God of War, with whom Aphrodite was having a passionate, but secret love affair. According to a myth, Aphrodite gave birth to Eros (a.k.a. Cupid), the winged cupid of love and was often accompanied by him. Other children of Aphrodite were Hemeros, Pothos(desire), Phobos(fear), Demos, Harmonia and Rhodes [1]. T h e Ro l e o f Ap h ro di te a s a Go dd e s s Aphrodite was the most attractive goddess of Mount Olympus. She was the goddess of Love, Beauty and Eternal Youth, arousing desire to gods and humans as well as birds and beasts. In addition, she was connected with the death/rebirth of nature and human beings. T h e Pe r s on a l it y o f Ap h ro d it e Aphrodite may have been the most attractive goddess, but according to the Iliad(the famous poem by Homer), she was a rather weak, frightful goddess. A pp e a r an ce of A p hr o di te Aphrodite was a highly attractive young woman who dressed elegantly and loved to wear jewellery. Her eyelashes were curled and she had a constant smile on her lovely face, since she was a lover of smiles. Aphrodite had a tender neck, tender breasts [2] and beautiful buttocks [3]. Sy mb o ls of A ph r o di te Aphrodite's symbols were the girdle(which she was using to compel love), the seashell and the mirror. Her sacred animal was the dove. Aphrodite's Appearance: Aphrodite is a gorgeous, perfect, eternally young woman with a beautiful body. Aphrodite's Symbol or Attribute: Her Girdle, which has magical powers to compel love. Strengths: Potent attractiveness, dazzling beauty. Weaknesses: A bit stuck on herself, but with a perfect face and body, who can blame her? Aphrodite's Parents:One genealogy gives her parents as Zeus, King of the Gods, andDione, an early earth/mother goddess. More commonly, she was believed to be born of the foam in the sea which bubbled around the severed member of Ouranos when Kronos slew him. Aphrodite's Birthplace: Rising from the foam off of the islands of Cyprus or Kythira. Milos, where the famed Venus de Milo was found, is also associated with her in modern times. Aprhodite's Husband: Hephaestus, the lame smith-god. Also associated with Ares, god of War. Children: Eros, a Cupid-like figure. Some Major Temple Sites of Aphrodite: Kythira, an island she visited; Cyprus. Basic Story: Aphrodite rises from the foam of the waves of the sea, enchanting anyone who sees her and inciting feelings of love and lust wherever she goes. She is a contender in the story of the Golden Apples, when Paris chooses her as the fairest of the three goddesses (the others were Hera and Athena) and Aphrodite decides to "reward" him for giving her the Golden Apple (the prototype of most modern awards) by giving him the love of Helen of Troy, something of a mixed blessing that led to the Trojan War. Interesting Fact: The island of Cyprus has many places believed to have been enjoyed by Aphrodite when she was on earth. Recently, the Cypriots have revived a tourist-friendly version of some of Aphrodite's festivals at the town of Paphos. In 2010, the still-potent image of Aphrodite hit the news, as the island nation of Cyprus released a new passport with a nearlynaked image of Aphrodite on it; some in the government were scandalized that this image was now so official and worried that it would cause problems for travelers to conservative Muslim nations. Ares was the Olympian God of War and the figure behind all kind of violence A r e s , t he G o d o f W a r R e p ut a ti o n o f A r e s A r e s ' W a y o f L i fe Int e r e s ti ng F a c t s a b o ut A r e s Symbols of Ares A re s , t he Go d o f W a r Ares, the Greek god of War, was the son of Zeus and Hera. The half-sister of Ares was Athena, the goddess of Wisdom and Skill. Athena also was a goddess of War but approached war solely for the purposes of justice. Re p ut at io n o f A re s Just like his mother Hera, Ares had a very difficult character to deal with and was therefore rather unpopular among the other deities and mankind. For this reason, no Greek city wanted to have him as its patron. He often had conflicts and fights with Artemis, the goddess of the Hunt and also with his sister Athena, especially during the Trojan War. A re s' W a y o f L i fe Ares had his residence up on Mount Olympus and his throne was upholstered with human skin. Usually he was accompanied by Eris, the goddess of discord. Ares' secret mistress was Aphrodite, the goddess of Love and Beauty; their union resulted to the birth of Armonia (Harmony), which was seen as a blend of two opposing powers. Sy mb o ls of A r es The symbol of Ares was the spear and his sacred animal was the dog Profile of Ares Ares is a war god and god of violence in Greek mythology. He was not well-liked or trusted by the ancient Greeks and there are few tales in which he plays a major role. Cults of Ares are found mainly in Crete and the Peloponnese where the militaristic Spartans honored him. Athena is also a war goddess, but was well-respected, as a polis protector and goddess of strategy instead of Ares' forte, mayhem and destruction. Ares appears in what one might call bit parts, overshadowed by heroes or other gods, and in many battle scenes in Greek mythology. In the Iliad, Ares is wounded, treated, and returns to the fray. See Iliad V Summary. Family of Ares: Thracian-born Ares is usually counted the son of Zeus and Hera, although Ovid has Hera produce him parthenogenically (like Hephaestus). Harmonia (whose necklace turns up in stories ofCadmus and the founding of Thebes), the goddess of harmony, and the AmazonsPenthesilea and Hippolyte were daughters of Ares. Through Cadmus' marriage to Harmonia and the dragon Ares sired that produced the sown men (Spartoi), Ares is the mythological ancestor of the Thebans. Mates and Children of Ares Roman Equivalent: Ares was called Mars by the Romans, although the Roman god Mars was much more important to the Romans than Ares was to the Greeks. Attributes: Ares has no unique attributes, but is described as strong, harnessed in bronze, and golden helmeted. He rides a war chariot. The serpent, owls, vultures, and woodpecker are sacred to him. Ares had unsavory companions like Phobos ("Fear") and Deimos ("Terror"), Eris("Strife") and Enyo ("Horror"). Early depictions show him as a mature, bearded man. Later representations show him as a youth or ephebe (like Apollo). Photo of an Ares Statue Powers: Ares is a god of warfare and murder. Some Myths Involving Ares: Adonis Ares rather than Artemis is sometimes said to have been responsible for the death of Adonis. He either sent a boar or was himself one. [Source: Carlos Parada] Aphrodite and Ares One of the most famous stories involving Ares is his being caught in flagrante delicto with Aphrodite. Although the lovers were caught in a net in a compromising position, the gods watching envied Ares. Read: Mars and Venus Caught in a Net Ares and the Giants Ephialtes and Otos, sons of the Giant Aloeus, put Ares in chains and into a cauldron where he was stuck until Hermes rescued him. (See the Story according to Homer, inIliad 5). In the war against the giants, Ares slew the giant Mimas (Apollonius Rhodius,Argonautica 3. 1227 ff) Cadmus and the founding of Thebes Cadmus slew the dragon of Ares and, on the advice of Athena, planted its teeth. From the sown teeth armed men sprang up ready to fight. All were killed but five who were known as the sown men or Spartoi. Apollodorus says Cadmus served as a laborer for Ares for a "year" as atonement for the killing. Artemis was the Greek goddess of the Hunt and th e Moon and protector of expectant women and the young. F a m i l y o f A r t e mi s A r t e m i s , t he V i r g i n H unt r e s s O d d t hi ng s a bo ut A r t em i s T he A p p e a r a nc e o f A r te m i s S y m b o l s a nd s a c r e d Ani m a l s o f A r t e mi s F am i ly of A rt em i s Greek goddess Artemis was born in Mount Cynthus at the island of Delos in Greece as a daughter of Zeus, the Ruler of the Greek gods and the mortal Leto. Artemis' twin brother was Apollo, the god of the Sun, whereas Artemis' cult was connected with the Moon. She had been born before Apollo and had helped her mother Leto to give birth to her little brother. A rt em i s, t h e Vi r g i n H u nt r e ss As a child, Artemis had asked from her father Zeus to remain an eternal virgin and therefore became one of the three Virgin Goddesses in Greek mythology. Artemis had absolute sovereignty over nature and was said to bring fertility to all places that worshipped her. Usually accompanied by Nymphs and Oceanids, Artemis loved to hunt with arrows dipped in poison. O dd th i ng s a bo ut A rt em i s Oddly enough, Artemis was both a killer of wild animals and their protector. T h e A p pe a r a nc e o f A rt em i s Artemis was usually armed with bow and arrows and was wearing a knee-high chiton (a sort of tunic). Sy mb o ls a n d s ac r e d A n i m al s o f A rt e mi s The symbols of Artemis were the bow and the pike. Her tree was the cedar and her sacred animals were the snake, the bear and the deer. Artemis' Appearance: Usually, an eternally young woman, beautiful and vigorous, wearing a short costume which leaves her legs free. At Ephesus, Artemis wears a controversial costume which may represent many breasts, fruits, honeycombs, or parts of sacrificed animals. Scholars are undecided on how to interpret her outfit. Artemis' Symbol or Attribute: Her bow, which she uses to hunt, and her hounds. She often wears the lunar crescent on her brow. Strengths/Talents:Physically strong, able to defend herself, defender and guardian of women in childbirth and of wildlife in general. Weaknesses/Flaws/Quirks: Dislikes men, whom she sometimes orders torn apart if they see her bathing. Opposes the institution of marriage and the subsequent loss of freedom it entails for women. Parents of Artemis: Zeus and Leto Birthplace of Artemis: The island of Delos, where she was born under a palm tree along with her twin brother Apollo. Spouse: None. She runs with her maidens in the forests. Children: None Some Major Temple Sites: Brauron (also called Vravrona), outside of Athens. Ephesus in Turkey. Basic Story: Artemis is a freedom-loving young woman who likes to roam the forests with her female companions. She doesn't care for city life and keeps to the natural, wild environment. Interesting Facts: Though Artemis didn't care much for men, young boys were welcome to study at her sanctuary at Brauron. Statues of both young boys and girls have survived and can be seen at the Brauron Museum. Some scholars assert that the Artemis of Ephesus was actually a completely different goddess than the Greek Artemis. Common Athena was the Greek goddess of Wisdom, Skill and War A t he na ' s e xt r a o r di na ry Bi r t h A t he na ' s p r e c io us S ki l l s A t he na a nd t he C i t y o f A t he ns A p p e a r a nc e o f A t he na S y m b o l s o f A t he na At h en a' s ex t r ao r d i n ar y Bi r th Athena was a child of Zeus and Metis, Zeus' first wife, who was keeping inside herself all the world's wisdom. She was born during the battle of the Giants, when she suddenly sprang out of the head of Zeus fully grown.[Read the story...] At h en a' s pr ec i o us Sk il l s Athena was the goddess who taught mankind various skills such as weaving and sewing to the women and agriculture and metallurgy to men. She was always giving precious advice and stood by on any danger. At h en a a n d th e Ci t y of A th e n s After competing against the Greek god Poseidon, Athena officially became the patron deity of the city of ancient Athens and the Parthenon was built in her honour. She was known as "Athena Nike" (Athena the victorious), as she was believed to have given the Athenians the victory during the Persian War. A pp e a r an ce of A th en a A tall, slim woman with glaucous eyes trickling light, wearing a suit of armour and a golden helmet [1] Sy mb o ls of At h e n a Athena's symbols were the spear, the distaff and the aegis (a goat-like shield, to which the head of theGorgon Medusa was fastened in order to terrify the opponents). Athena's tree was the olive tree and her sacred animal was the owl, the symbol of wisdom. Athena's Appearance: A young woman wearing a helmet and holding a shield, often accompanied by a small owl. A huge statue of Athena depicted this way once stood in the Parthenon. Athena's Symbol or Attribute:The Owl, signifying watchfulness and wisdom; the aegis (small shield) showing the snaky head ofMedusa. Athena's Strengths: Rational, intelligent, a powerful defender in war but also a potent peacemaker. Athena's Weaknesses:Reason rules her; she is not usually emotional or compassionate but she does have her favorites, such as the beleaguered heroes Odysseus and Perseus. Birthplace of Athena: From the forehead of her father Zeus. Athena's Spouse: None. She was very fond of Odysseus and helped him whenever she could on his long journey home. Athena's Children: None. Some Major Temple Sites for Athena:The city of Athens, which is named after her. The Parthenonis her best-known, and bestpreserved, temple. Basic Story for Athena: Athena was born fully-armed from the forehead of her father Zeus - according to one story, this is because he swallowed her mother, Metis, while she was pregnant with Athena. Although Zeus's daughter, she could also oppose his plans and conspire against him. Athena and her uncle, the sea god Poseidon, competed for the affections of the Greeks, each providing one gift to the nation. Poseidon provided either a wonderful horse or a salt-water spring rising from the slopes of the Acropolis, but Athena provided the olive tree, giving shade, oil, and olives. The Greeks preferred her gift and named the city after her and built the Parthenon on the Acropolis where Athena is believed to have produced the first olive tree. Interesting Fact about Athena: One of her epithets (titles) is "Grey-eyed". Her gift to the Greeks was the useful olive tree. The underside of the olive tree's leaf is grey, and when the wind lifts the leaves, it shows Athena's many "eyes". Demeter was the Greek goddess of agricultur e and vegetation F a m i l y o f D e me te r D e m et e r ' s P e r so na l it y a nd he r R o l e a s a G o d d e s s A p p e a r a nc e a nd S a c r ed S ym b o l s S y m b o l s o f D em et e r F am i ly of De me te r Demeter was the second daughter of the major Titans Rhea and Cronus, after Hestia, the goddess of the hearth. De me te r' s P e rs o n a l it y a n d h e r R ol e a s a G o dd e ss Demeter was a peace-loving deity and the source of all growth and life; she was the goddess who provided all nutrition on the earth and taught mortals how to cultivate the earth and ease life. Demeter was most appreciated for introducing wheat to mankind, making man different from animals. A pp e a r an ce a n d S ac r ed Sy mb o l s A rich haired woman with golden tresses and slender feet, usually wearing a dark cloak [1]. Sy mb o ls of De me t er The symbols of Demeter were the ear of wheat and the grains. Demeter's Appearance: Pleasant-looking mature woman, generally with a veil over her head though her face is visible. Often carrying wheat or her Horn. Demeter's Symbols and Attributes: An ear of wheat and the Horn of Plenty (Cornucopia). Major Temple Site to Visit: Demeter was revered at Eleusis, where initiatory rites called the Eleusinian Mysteries were performed for select participants. These were secret; apparently, no one ever broke their vows and described the details and the content of the rites is still debated even today. Eleusis is near Athens and can still be visited though it is regrettably surrounded by heavy industry. Demeter's Strengths:Demeter controls the fertility of the earth as goddess of Agriculture; also gives life after death to those who learn her Mysteries. Demeter's Weaknesses: Not one to cross lightly. After the kidnapping of her daughter Persephone, Demeter blights the earth and won't let the plants grow. But who can blame her? Zeus gaveHades permission to "marry" Persephone but whoops! didn't mention it to her or her Mom. Demeter's Birthplace: Not known Demeter's Spouse: Not married; had affair with Iason. Demeter's Children: Persephone, also known as Kore, the Maiden. Zeus is generally said to be her father, but at other times, it seems as if Demeter managed without anyone else involved. Demeter's Basic Story: Persephone is snatched by Hades; Demeter searches for her but can't find her, and finally stops all life from growing on the earth. Pan spots Demeter in the wilderness and reports her position to Zeus, who then starts negotiations. Ultimately, Demeter gets her daughter for a third of the year, Hades gets her for a third, and Zeus has her services as a handmaiden the rest of the time. Sometimes this is a simpler split, with Mom getting six months and Hubby getting the other six. Interesting Demeter Facts: Some scholars believe that the mystery rites of Demeter derived from those of the Egyptian goddess Isis. In Graeco-Roman times, they were sometimes considered to be the same or at least strongly similar goddesses. Ancient Greeks might also dedicate sneezes to Demeter, similar to someone saying "God bless you!" An unexpected or timely sneeze could be thought to have oracular meaning as a message from Demeter, perhaps to abandon the idea under discussion. This may be the origin of the phrase "not to be sneezed at", not to be discounted or taken lightly. Dionysus was th e Greek God of Wine, Joy and Theatre and a Lover of Peace F a m i l y o f D io nys us P e r s o na li t y a nd S t yl e o f D i o nys us A p p e a r a nc e o f Di o nys us S y m b o l s o f Di o nys us F am i ly of Di o ny s u s Dionysus was born in Thebes as the son of Zeus, the King of the Gods and the beautiful princess Semele. Because of his mortal mother, his birthplace Thebes refused to acknowledge him as an immortal at first. Pe r so n a l ity a n d St yl e o f D i on y su s Dionysus was a god known for his lightheartness and always offered his help to anyone in need. He was therefore very popular among gods and mortals and many festivals were being held every year in his honor. Nevertheless, Dionysus was many times misunderstood. Dionysus was one of the Olympian gods who actually did not live in Mount Olympus but was constantly travelling around the world together with Satyrs and Maenads in order to discover the secrets of winemaking. A pp e a r an ce of Di o ny s u s Dionysus was a handsome young man with impressive hair (usually tresses falling below his shoulders) and a wreath of ivy on his head. In his hand he was holding a "thyrsos", which was a light staff wrapped with leaves of ivy and a pine cone on its top. Sy mb o ls of Di o ny s us The symbols of Dionysus were the thyrsos, a wooden stick wrapped with ivy leaves and vines, the flute and the wine barrels. his sacred animals were the panther and the tiger. Appearance: Dionysus is usually depicted as a dark haired, bearded young man but he can be shown beardless as well. Dionysus' Symbol or Attribute: Grapes, winecups, and wineskins; the staff formed of a pinecone on a stick called a thyrsus. Strengths: Dionysus is the creator of wine. He also shakes things up when it gets dull. Weaknesses: God of intoxication and drunkenness, states he pursues frequently. Parents: Son of Zeus and Semele, who unwisely asked to see her lover Zeus in his real form; he appeared and thunder and lightning and Semele was consumed; Zeus saved their child from the ashes of her body. Spouse: Best known is Ariadne, Cretan princess/priestess who assisted Theseus defeat the Minotaur only to be abandoned by him on the shores of Naxos, one of the islands favored by Dionysos. Fortunately, Dionysus liked beachcombing and quickly found and comforted the abandoned princess with an offer of marriage. Children:Several children by Ariadne, including Oenopion and Staphylos, both associated with grapes and winemaking. Some Major Temple Sites: Dionysus was reverenced at Naxos and generally wherever grapes were grown and wine was produced. In modern times, the so-called "Dirty Monday" rites at Tyrnavos in the Thessaly region of Greece are believed to retain traditions dating back to when he was openly worshiped. Basic Story: Other than the story of his birth, Dionysus is relatively myth-free, yet he was very widespread in later Greek belief. He was not considered to be one of the Olympians, and since Homer skips him, it is suspected that his worship came late to the Greeks, possibly from Anatolia. He was later "adopted" by the Romans under the name of Bacchus, god of the grape, but the Greek worship of Dionysus was more ecstatic and may have preserved some early shamanic practices related to the intoxication provided by wine. Some see in him a survival of the young, vigorous "Cretan-born" Zeus. Interesting Fact:Otherwise proper and repressed Greek matrons devoted to Dionysus would become wild maenads for a night and run the slopes of the mountains, looking for prey to catch and tear apart with their bare hands. Hades was the G od and Ruler of the Underworld H a de s me a n s " in v i s ib l e" in a nc i en t G re ek Family of Hades H a d e s , t he R ul e r o f t he U nd e r w o rl d Int e r e s ti ng F a c t s a b o ut H a d e s A p p e a r a nc e a nd S a c r e d S ym b o l s F am i ly of H a de s Greek god Hades was a son of the titans Cronus and Rhea. Hades' wife was Persephone, whom he abducted from her divine mother Demeter and took with him down to the Underworld. H a de s , th e R u l er o f th e U nd e r wo r ld Hades was the Greek god of the Dead and, according to Plato, [1] he should be considered as one of the Olympian gods.Hades was the supreme ruler of the Underworld. Almost never did he leave his gloomy kingdom but was residing there instead, surrounded by darkness and silence... Hades' helper was Charos, the angel of dead. Charos had the duty to transfer the dead people 's souls with a boat over the River Acheron from the world of the living to the world of the dead. Furthermore, Hades had a dog with three heads which was named Cerberus. A pp e a r an ce a n d S ac r ed Sy mb o l s Hades had gloomy features. He had a beard and dark hair falling over his brow helmet, which helped him stay invisible. [2]. His sacred symbol was the Hades'Appearance: Like Zeus, Hades is usually represented as a vigorous bearded man. Symbol or Attribute:Scepter or horn of plenty. Strengths: Rich with the wealth of the earth, especially precious metals. Persistent and determined. Hades' Weaknesses: Passionate over Persephone, the daughter of Demeter, whom Zeus promised to Hades as his bride. (Unfortunately, Zeus apparently neglected to mention it to either Demeter or Persephone.) Impulsive, favoring sudden, decisive actions. Can also be deceptive. Birthplace of Hades: The most common story is that Hades was born to the Great Mother goddess Rhea and Kronos (Father Time) on the island of Crete, along with his brothers Zeus and Poseidon. Spouse of Hades: Persephone, who must stay with him part of each year because she ate a few pomegranate seeds in the Underworld. Pets: Cerberus, a three-headed dog (In "Harry Potter", this beast has been recently renamed "Fluffy".); black horses; various other hounds. Some Major Temple Sites: The spookyNekromanteion on the River Styx along the west coast of mainland Greece, still visitable today. Basic Myth: Hades springs out of the earth and captures Persephone, dragging her off to be his queen in the Underworld. Her mother Demeter searches for her and stops all foods from growing until Persephone is returned. Finally, a deal is worked out where Persephone stays one-third of the year with Hades, one-third of the year serving as a handmaiden to Zeus at Mount Olympus, and one-third with her mother; other stories skip Zeus's portion and divide Persephone's time between Hades and her Mom. Interesting Fact: Hades originally may have been all of the dark and underworld aspects of Zeus, eventually considered to be a separate deity. He is sometimes called "Zeus of the Departed". His name originally probably meant "invisible" or "unseen", as the dead go away and are seen no more. Hephaestus was the Greek God of Metallurgy and the Smith of the Olympian Gods. F a m i l y T r e e o f H e p ha es t us T he D i s a b il it y o f H e p ha e s t us T he W o r ks ho p o f H e p ha e s t us S y m b o l s o f H e p ha e st us F am i ly T r ee of H e ph a e st u s Hephaestus was the son of Zeus and Hera , although it was considered by some that he had been conceived prenuptially. Hephaestus was married to Aphrodite, the Greek goddess of Beauty, but unfortunately Aphrodite never devoted herself entirely to Hephaestus. T h e D is a b i l ity of H ep h a es tu s Hephaestus was a very kind and loveable god, but was the only deity who was physically ugly and lame. When his mother Hera saw him for the first time, she was so frustrated that she took her son and threw him from Mount Olympus to the depths of the seas, causing a deformation to his leg. Hephaestus was finally rescued by two Nereids, Thetis and Eurynome, who raised him for nine years inside a cave, far away and hidden from his cruel mother. T h e Wo rk s ho p o f H ep h a e st us Hephaestus had his working lay beneath the crater of the volcano of Aetna in Italy. There, he was working together closely with the one-eyed Cyclopes to create strong thunderbolts for his master Zeus. Hephaestus was also famous for having created the first woman of the ancient world, Pandora. Sy mb o ls of H e ph a es tu s The symbols of Hephaestus were the Fire, the axe, the pincers and the hammer The Roman name of Hephaestus is "Vulcan" Hephaestus' Appearance: A dark haired man who has difficulty walking due to misformed feet. Some accounts make him small in stature. Symbol or Attribute of Hephaestus: The forge and fire. Strengths: Hephaestus is creative, cunning, and an able metal worker Weaknesses:Can't handle his liquor; can be crafty and vindictive. Parents: Usually said to be Zeus and Hera; some say Hera bore him without the help of a father. Hera is also said to have thrown him into the sea, where he was rescued by Thetis and her sisters. Spouse: Aphrodite. The blacksmith-god married well. Other tales give him as wife the youngest of the Graces, Aglaia. Children: He created Pandora of the famous box; some tales give him as the father of Eros, though most ascribe this love-god to the union of Ares and Aphrodite. Some divine genealogies have him as the father or grandfather of Radamanthys who ruled at Phaestos on the island of Crete, though Radamanthys is usually considered to be the son of Io and Zeus. Some Major Temple Sites: The Hephaestaion near the Acropolis in Athens, which is the best-preserved Doric-style temple in Greece, built in 449 B.C.E. He was also associated with the islands of Naxos and Lemnos. Basic Story: Feeling rejected by his mother Hera, Hephaestus made a lovely throne for her and sent it to Olympus. She sat in it and discovered she could not get up again. Then the chair levitated. The other Olympian gods tried to reason with Hephaestus, but even Ares was driven off with his flames. He finally was given wine by Dionysus and, drunk, was brought to Olmypus. Drunk or not, he still refused to free Hera unless he could have either Aphrodite or Athene as wife. He ended up with Aphrodite, who in this instance was not a quick learner. When she lay with his brother Ares in the bed Hephaestus had made, chains emerged and they could not leave the bed, exposing them to the laughter of the rest of the Olympians when Hephaestus called them all together to witness his adulterous wife and brother. Interesting Fact:Hephaestus could sometimes be called Daidalos, connecting him to the famous Cretan craftsman who was the first to fly. Hera was the goddess of Marriage an d Family and protector of mar ried women. T he F a m i l y o f H e r a H e r a ' s t r o ubl e d m a r ria g e w i t h Z e us F un F a c t s a b o ut H e r a A p p e a r a nc e o f H e r a Symbols of Hera T h e F am i l y o f H e r a Hera was born by the Titans Cronus and Rhea and was one of the three sisters of Zeus and later on became his wife as well. The royal wedding of Zeus and Hera was celebrated with exceptional splendour and the couple gave birth to four children; Eilithyia, the goddess who was protecting the childbirth, Ares, the Olympian god of war, Hebe, the goddess of youth and Hephaestus, the Olympian god of metallurgy. According to some beliefs, Hephaestus was born without the intervention of Zeus. H e r a' s t r ou b l ed m a r ri a g e w i th Z eu s Although Hera was one of the fairest goddesses in Mount Olympus, Zeus was giving Hera plenty of reason to be suspicious and jealous; Hera therefore used to stay in high places in order to keep an eye on her husband's doings. There were times she would also interfering, causing harm to Zeus' mistresses, since Zeus himself was invincible. A pp e a r an ce of H e r a Hera was a beautiful(but not really desirable), mature woman with big eyes and pierced lobes. She was wearing an ornate crown on her head, elegant clothes tightened with a belt and woven by goddess Athenaand golden sandals were hugging her feet. Hera loved to wear jewelery and pamper her body with divine cosmetics. Sy mb o ls of H e r a Hera's symbol were the diadem, the scepter and the pomegranate, a symbol of fertility. Her flower was the lily and her sacred animals were the peacock and the cow. Hera's Appearance: A young beautiful woman, said to be the most beautiful of all goddesses, even beating out Aphrodite. Hera's Symbol or Attribute:The peacock. Hera's Strengths: Determined defender of the sanctity of marriage and monogamy. Hera's Weaknesses:Determined defender of the sanctity of marriage and monogamy - but married Zeus. Some Major Temple Sites: The island of Samos was said to be where Zeus and Hera spent the first secret three hundred years of their marriage, making this the longest honeymoon on record. Basic Story:Zeus was the brother of Hera, who fell in love with him from the first moment she saw him, and eventually got a love charm from Aphrodite to seal the deal. She is very relationship-oriented and spends much of her time driving off Zeus's innumerable mistresses. She also sometimes torments the offspring of those unions, especially Hercules. To her credit, she's gorgeous and kept Zeus busy on his honeymoon for three hundred years, so she rightfully wonders why on earth he needs to go anywhere else. When she's really fed up, she wanders off by herself, always hoping Zeus will miss her and seek her, usually eventually relenting and returning without being so sought. Interesting Fact:Hera is said to restore her virginity each year by bathing in Kanathos, a sacred spring. One tale suggests Hera used magic to force Zeus into marrying her in a secret ceremony. Given some of Zeus's later behavior, perhaps it was a secret even from him. Other tales have Zeus seducing her, in the form of a damp cuckoo bird seeking refuge in her lap during a storm. Hermes was the Greek God of the Trade, the god of eloquence and a luck bringing Messenger of the Gods. Birth of Hermes T he R o l e o f H e r m e s i n G r e e k M yt ho l og y H e r m e s , t he G o d o f t he T hi e ve s H e r m e s ' s p e ci a l R el a tio n t o Z e us A p p e a r a nc e a nd s a c r ed S ym b o l s B ir th of H e rm e s Hermes was born inside a cave on Mount Cyllene in Arcadia (Peloponnes) as the son Zeus, the King of the Gods, and the mountain Nymph Maea, who was a daughter of the Titan Atlas. T h e Ro l e o f H e r me s i n G re ek M yt ho l o gy Hermes was wearing wings on his sandals and therefore was the speediest of all Greek gods. Because of his speed, Hermes received the role of the messenger and conductor of souls to the Underworld. Hermes was the only Olympian god who was authorized to visit Heaven, Earth and also the Underworld and enjoyed this way popularity among all the Greek gods and spirits. H e rm e s, t he G od o f th e T h ie ve s It is well known that Ancient Greeks endowed their gods with human weaknesses. Hermes, for instance, felt an irresistible impulse of stealing ever since his infancy and quickly developed as the god of the cheaters and the thieves. H e rm e s' s pe c i al R el a t io n t o Z e u s Hermes was a messenger of all gods, but mostly he was known for performing duties for his father Zeus with great pleasure. Zeus appreciated Hermes' wits highly and always asked for Hermes' assistance throughout his decisions, especially when it came to cheating on his wife Hera. A pp e a r an ce a n d s ac r ed Sy mb o l s Hermes was a young man, wearing traveling clothes, a flat hat known as "petasus" and winged sandals on his feet. Oftentimes he was also considered to have wings attached to his shoulders and hat. Hermes usually held a winged staff with snakes wrapped around it in his hands in order to gain access everywhere. Hermes' Appearance: A handsome young man with a winged hat, winged sandals, and a golden staff twined with serpents. Hermes' Symbol or Attribute:His staff, called kerykerion in Greek, caduceus in Latin. This is the symbol used by doctors, though Hermes' connection with healing is faint. He is, however, the god of merchants. Hermes' Strengths: Clever, bold, determined, athletic, a powerful magician. Can charm monsters with his flute or lyre music. Hermes' Weaknesses: No major weakness unless you count seldom staying still for long. Hermes has it together. Birthplace of Hermes: Born in a cave on Mount Cylene in Arcadia to Maia, who had just slept with his father Zeus the night before. Talk about quick consequences! Spouse: Hasn't settled down yet. Children of Hermes:By his affair with Dryope, Pan, lusty god of the wild; by the Goddess of Love Aphrodite, Hermaphroditus, a halfman, half-woman deity; Abderus (mother unknown). Some Major Temple Sites of Hermes: Generally, Hermes did not have temples. His statue was placed everywhere, and square blocks of marble showing a head and the male genitalia were called "Herms" and set up in many places. On these statues, Hermes is generally shown with a beard. Basic Myth: Hermes is the herald of the gods and also leads human souls into and occasionally out of the underworld. Zeus used him as a troubleshooter and secret-agent type, dispatching him to take care of assorted problems - he put Argos to sleep so Io could escape from Zeus's outraged wife Hera. Hermes also arranged for Odysseus to slip away from Callisto, among many other tasks. Interesting Fact: Hermes shows up in the Roman pantheon under the name Mercury. He also is said to have invented the lyre from a turtle shell. Hestia was the goddess of the hearth, home and family. F a m i l y o f H e s ti a H e s t i a , t he V i rg i n G o dd e s s W o r s hi p o f H e s ti a A p p e a r a nc e a nd S a c r ed S ym b o l s F am i ly of H e st i a Greek goddess Hestia was the eldest daughter of the titans Cronus and Rhea and a senior goddess among the mortals. [1]. She was the first to be swallowed by her father, but the last to be disgorged. H e st i a, t h e V i r gi n Go d de s s Hestia was one of the three virgin goddesses, next to Athena and Hera. Both Poseidon and Apollo had wished to marry her; however Hestia had given the oath to Zeus to never enter into a union with a male and to remain forever pure and undefiled. W o rs h i p of H e st i a Hestia personified the fire hat was burning in the hearth of every home. All families were pouring sweet wine in her name and dedicated her the richest portion. The hearth fire was not allowed to go out by any family unless it was ritually extinguished. Hestia herself was never leaving her residence, the sacred mountain ofOlympus. Hestia may not have had a public cult, but she was always worshipped in any temple, regardless of the god it was dedicated to. All Olympian deities respected and loved Hestia because of her kind, forgiving soul and her discrete character, since Hestia never participated in any disputes or wars. A pp e a r an ce a n d S ac r ed Sy mb o l s A bashful woman, usually seated Origin of Hestia: Cronus the Titan was told that one day, his son would overthrow him. In fear, he swallowed his children right after his wife Rhea gave birth. The five children were Hades, Poseidon,Demeter, Hera and Hestia. Their younger brother, Zeus then rescued them from their father and they proceeded to take over the Titans and imprison them in the Underworld The honored, first born of the Olympian gods, Greek goddess Hestia is also called the last born because her father swallowed his children and then regurgitated them in reverse order. Hestia has power over altars, hearths, town halls and states. In return for a vow of chastity, Zeus assigned honor to Hestia in human homes.Family of Origin: Hestia was the first born child of Cronos and Rhea. Her brothers were Zeus, Hades, and Poseidon. Her sisters were Demeter and Hera Poseidon was the God of the Seas, the horses an d the earthquakes. F a m i l y o f P o s ei do n T he P e r s o na l it y o f P o s e i do n a nd hi s W a y o f L i fe T he P o w e r s o f P o s e id on A p p e a r a nc e o f P o se i don S y m b o l s o f P o se i do n F am i ly of P o se i do n Poseidon, the Greek god of the Seas, was born by the major Titans Cronus and Rhea. He was an older brother of Zeus, the King of the gods. T h e Pe r s on a l it y o f P o se i do n an d hi s Wa y o f L if e Poseidon was considered to be the bad-tempered, moody and greedy god among the Olympians. Once insulted, he would revenge himself, like he did in the case of Odysseus, who brutally blinded his son, the Cyclopes Polyphemus [1]. Poseidon loved to cross the oceans and seas with his golden chariot surrounded by dolphins. T h e Po w e rs of Po s ei d on Poseidon was the Greek god responsible for natural and supernatural events, mainly the ones associated to the sea world. He possessed a trident which was so powerful that it could shake the earth. Poseidon could cause tempests and earthquakes, drown lands, shatter rocks and had the ability to finally bring back peacefulness. Poseidon possessed two palaces, the one was up in Mount Olympus and the other was located in the depths of the seas and was bejeweled with gold and precious gems. Usually Poseidon preferred to stay with his wife Amphitrite beneath the ocean. A pp e a r an ce of Po s ei d on Poseidon was imposing and strong with long, blue hair. Poseidon is a bearded, older man usually pictured with seashells and other sealife. Poseidon usually holds a trident. Sy mb o ls of Po s ei d on His symbol was the trident and his sacred animals were the dolphin and the horse. According to a tradition, he was the one who breathed life into the first horse on earth. Poseidon's Symbol or Attribute: The three-pronged trident. He is associated with horses, believed to be seen in the crashing of waves on the shore. He is also believed to be the force behind earthquakes, an odd expansion of the power of a sea god, but possibly due to the association between earthquakes and tsunamis in Greece. Some scholars believe he was first a god of the earth and earthquakes, and only later took on the role of sea god. Major Temple Sites to Visit: The Temple of Poseidon at Cape Sounion still draws huge crowds of visitors to the cliffside site overlooking the sea. Poseidon's Strengths: A creative god, designing all the creatures of the sea. Poseidon's Weaknesses: Warlike, though not so much as Ares; moody and unpredictable. Spouse: Amphitrite, a sea goddess. Parents: Kronos, god of time, and Rhea, goddess of the earth. Brother to the gods Zeusand Hades. Children: Many - second only to Zeus in the number of illicit liaisons. With his wife Amphitrite he fathered a half-fish son, Triton. Dalliances include Medusa, with whom he fathered Pegasus, the flying horse, and Demeter, his sister, with whom he fathered a horse, Arion. A Basic Story: Poseidon and Athena were in a competition for the love of the people of the area around the Acropolis. It was decided that the divinity who created the most useful object would win the right to have the city named for them. Poseidon created horses (some versions say a spring of salt water), but Athena created the incredibly useful olive tree, and so the capital of Greece is Athens, not Poseidonia. Interesting Fact: Poseidon is often compared or combined with the Roman god of the sea, Neptune. In addition to creating horses, he is also credited with the creation of the zebra, believed to be one of his early experiments in equine engineering. Zeus was the Su preme God in An cient Greece, father of the Olympian gods ruler of mankind. T he F a m i l y o f Z e us R o l e a nd R e sp o ns ib il iti e s T he P e r s o na l it y o f Z e us A p p e a r a nc e o f Z e us S ym b o l s o f Z e us T h e F am i l y o f Z e u s Zeus was the last child of the Titans Cronus and Rhea and had five older brothers and sisters. All of them had been swallowed by their jealous father; however, Zeus managed to escape the menace and flee. Later on, he would revenge on his father and set his siblings free. Zeus married his own sister Hera, the goddess of marriage and monogamy, but was giving her plenty of reasons to be jealous, since Zeus was renowned of his numerous love affairs. As a result, Zeus was the father of plenty of children. Ro l e a n d R e sp on s i bi l it i e s Zeus had his golden throne on the highest summit of Mount Olympus and was respected and awed by all Gods and mortals. He was the "Lord of Justice", punishing anyone who lied or broke an oath, but was fair and always striving to keep a balance of all things. Furthermore, Zeus was responsible for the weather and was shaping it according to his temper. When in high spirits, Zeus was blessing the world with fine weather; in case of bad mood, however, he would throw rain, winds, lightnings and thunderbolts to cause disaster to the mortals. But even Zeus' powers had their limits, for, however powerful as he was, he had neither the right nor the ability to intervene the decisions of the Fates. T h e Pe r s on a l it y o f Ze u s Zeus was carefree and loved to laugh out loud[1]. He possessed the perfect knowledge and was just, merciful and prudent. However, he was rather unpredictable, since no one could guess the decisions he would make. A pp e a r an ce of Z e u s Zeus was strong and imposing, with long, oftentimes curly hair. Sy mb o ls of Z eu s The symbols of Zeus were the scepter, the throne and the thunderbolt, which was as a gift from the Cyclopes because he liberated them. Zeus' tree was the oak tree and his sacred animal was the eagle. Appearance: Usually represented as an older, vigorous bearded man. But representations of Zeus as a powerful young man also exist. Symbol or Attribute: Thunderbolt. Strengths: Highly powerful, strong, charming, persuasive. Weaknesses: Gets in trouble over love affairs, can be moody. Birthplace: Most commonly believed to be born in a cave on Mount Ida on the island of Crete, where he took ashore Europa at the beach of Matala. Zeus's Spouse: Hera in most stories; Dione, mother of Aphrodite, at Dodona. Here is a picture of Zeus: at Dodona. On Crete, Europa is often considered to be the wife of Zeus. Children: Lots and lots of them. Hercules is one famous child. Some Major Temple Sites for Zeus:Dodona in northwestern Greece, the temple of the Olympian Zeus in Athens. Basic Story: Zeus is King of the Gods of Mount Olympus, seen here from space, fights with his wife Hera, and drops down to earth in a variety of disguises to seduce maidens who catch his fancy. Interesting Fact about Zeus: Some experts believe that not all the names of Zeus really refer to Zeus, but instead refer to similar gods popular in local areas of Greece. Zeus Kretagenes is the Zeus born on Crete. Apollo was the Olympian God of the Sun, the Light, the Music and the Prophecy F a m i l y T r e e o f A p o ll o A p o l l o , t he Go d o f M us i c A p o ll o , t he Go d o f P r op he c y A p p e a r a nc e o f A po ll o S ym b o l s o f A p ol lo F am i ly T r ee of A p ol l o Apollo was born by the King of the Gods Zeus and the mortal Leto in the divine Greek island of Delos. He was the younger twin of Artemis, the Greek goddess of the hunt. A po l lo , t he G od of M u si c Apollo was the Greek god of the Music. He invented the lute(a plucked string instrument with a body shaped like a pear), but he was more popular for playing the lyre, which was invented by Hermes, the messenger of the gods. Apollo excelled in important music contests, competing against Greek god Hermes and the Satyr Pan as well as other deities. A po l lo , t he G od of P r op h ecy In addition, Apollo owned the precious gift of prophecy, given to him by his father Zeus in his infancy. He was the patron of the ancient city of Delphi, where the first oracle of Ancient Greece was located. The district was considered to be the Navel of the World (the "Omphalus") in Ancient times. A pp e a r an ce of A p ol l o Apollo was a handsome, strong and youthful god with impressive golden hair. Sy mb o ls of A po l lo Apollo's symbols were the lyre, the tripod, the laurel tree and the navel stone. His plants were the myrtle and the laurel. Apollo's sacred animals were the wolf, the raven and the lizard. Apollo's Appearance: A young man with curly golden hair. Symbol or Attribute of Apollo: The Sun itself, the lyre (a type of musical instrument), the bow, and the chariot he drives across the sky daily, borrowed from an earlier pre-Greek Sun god,Helios. Apollo's Strengths: Creative, handsome, supportive of all the arts of civilization. Apollo's Weaknesses: Like his father Zeus, Apollo is all too happy to enjoy the charms of the occasional youth, and his conquests number in the dozens. Birthplace of Apollo: On the sunny Greek island of Delos, where he was born along with his twin sister, Artemis. Another tradition gives the islands of Lato, now called Paximadia, off the southern coast of Crete. Spouse: Apollo had many encounters, but no marriages. Flings with Cassandra, to whom he gave the gift of prophecy; Daphne, who fled from his embrace and turned into a laurel tree; and Calliope, with whom he had a child, Orpheus. Apollo's Children: The enchanting semi-divine singer Orpheus and Asklepios, god of healing, are the most famous of Apollo's offspring. Some Major Temple Sites of Apollo: The mountain town of Delphi, where a few columns from an early temple of Apollo still stand. The island of Delos is also sacred to him, but there is no temple remaining there today. Basic Story: Apollo was the son of the supreme Greek god Zeus and Leto, a nymph. Zeus's wife Hera was outraged and convinced the earth to refuse to allow Leto to give birth anywhere on its surface. But the island of Delos allowed Leto to take refuge there and give birth to Apollo and his twin sister, Artemis, goddess of the hunt and wild things. The goddess Themis assisted in raising him by feeding him ambrosia, the sacred nectar of the gods. Interesting Fact: Apollo Delphinus or Delphinius was the dolphin-form of the god and was revered at Delphi - despite its location high in the mountains. He was also believed to have destroyed an evil serpent at Delphi, and was the patron god of the oracle there .