Practice Exam #2 Fall 2007
advertisement

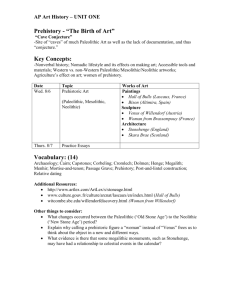
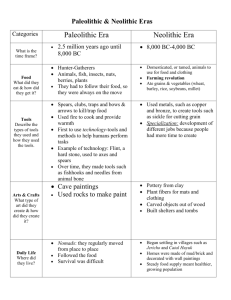
Practice Exam #2 Fall 2007 [Short answer questions will be posted separately] 1. Which of the following is not associated with the Upper Paleolithic? A. B. C. D. 2. The culture associated with the paintings at Lascaux is the A. B. C. D. E. 3. Lascaux Altamira Chauvet Cosquer The earliest known cave art in Europe dates to approximately A. B. C. D. E. 5. Solutrean Perigordian Magdalenian Aurignacian Chatelperonnian The oldest securely dated cave paintings in Europe are found at A. B. C. D. 4. domestication of plants exchange of exotic materials over large areas indirect percussion for production of stone flakes bow and arrow 40,000 38,000 32,000 22,000 17,000 years years years years years ago ago ago ago ago True or false. Representations of humans are much less common in European Upper Paleolithic cave art than are depictions of animals. A. True B. False 6. When we say that Upper Paleolithic people lived partially on unearned resources, we mean that they A. B. C. D. 7. frequently stole other peoples' food harvested wild but nutritious plants growing near their homes were adept at catching small animals such as rabbits hunted migratory animals Alexander Marshack's concept of time-factorial objects refers to A. the precise dating of Upper Paleolithic art B. artifacts such as some bone plaques that appear to have recorded the passage of time C. artifacts particularly useful in tracking the evolution of technology D. his belief that some cave paintings portray a series of related events -- that is, they tell a story 8. True or false? It does not appear that anyone actually resided in the caves of Lascaux, Chauvet and Cosquer. A. True B. False 9. Caves such as Lascaux tend to occur in areas that A. B. C. D. were remote and rarely visited had higher than normal populations in the vicinity had relatively few natural resources were situated along the Atlantic coast 10. Most archaeologists and art historians agree that Upper Paleolithic cave paintings A. B. C. D. E. are all representations of sympathetic (hunting) magic primarily depict myths probably record the passage of time were painted for a variety of purposes shared a common, but as yet unknown purpose 11. True or false? The first affluent societies were ones that replaced hunting and gathering with agriculture. A. True B. False 12. Hunter-gatherer societies are characterized by greater amounts of leisure time than agricultural and industrial societies. A. True B. False 13. The end of the Upper Paleolithic was brought about by A. high population, which required a shift from hunting-gathering to farming B. warming temperatures C. the replacement of Neanderthals by Homo sapiens D. a period of dramatically colder weather 14. True or false? The process of domestication involved human selection for plants with tough rachises. A. True B. False 15. The site of Jericho was probably attractive to the first people who settled there because of its A. B. C. D. E. defensive location closeness to pistachio and oak forests easy access to the Mediterranean permanent spring supply of high quality stone that could be traded 16. The practice of removing skulls from the deceased in places such as 'Ain Mallaha, Jericho and 'Ain Ghazal is associated with A. B. C. D. the use of skulls as bowls and cups in ceremonies cannibalism warfare ancestor veneration 17. True or false? Deformities in the skeletons of women from some Neolithic sites in the Middle East are associated with A. B. C. D. poor nutrition their work habits genetic defects an apparent increase in violence in early farming communities 18. The earliest known domesticated plant dates to approximately A. B. C. D. 14,000 B.C. 10,000 B.C. 9500 B.C. 8500 B.C. 19. The Kebaran period is characterized by A. B. C. D. intensive collection of wild cereal grains the earliest domestication of wild cereals the construction of a massive wall and tower at Jericho mobile hunting and gathering groups 20. The Younger Dryas period is associated with A. the expansion of cereal plants, oaks and pistachios into environments that could not support them during the Upper Paleolithic period B. a contraction of the geographic range of cereal plants, oaks and pistachios C. a significant increase in the number of human settlements and overall population in the Middle East D. the beginning of the Mesolithic in the Middle East 21. Abu Hureyra is best known for A. its remarkable plaster figurines that may have represented important ancestors B. the earliest domesticated sheep C. its surprisingly large population for a village relying on intensive collection of wild cereals D. the earliest domesticated rye 22. 'Ain Mallaha provides evidence for A. the high productivity achieved by early farmers in the area B. a surprising degree of sedentism for a community based on hunting and gathering C. how easily early farmers depleted the nutrients in the soils D. the role of long distance trade in the development of economic specialization and social ranking 23. In comparing the Kebaran and Natufian periods, we see evidence for A. B. C. D. E. increased hunting in the Natufian a decrease in storage pits in the Natufian increased reliance on wild cereal plants in the Natufian increased reliance on domesticated cereal plants in the Kebaran B and D 24. True or false. The high incidence of tooth decay in the teeth of people buried at 'Ain Mallaha helps to prove that its residents had domesticated cereal plants and were practicing farming. A. True B. False 25. True or false. Sites that contain permanent, substantial dwellings, storage pits, and abundant ground stone grinding tools can safely be placed in the early to middle Neolithic. A. True B. False 26. The early Neolithic site of Hallam Cemi in eastern Turkey provides us with A. the earliest known domesticated wheat B. some of the earliest domesticated “farm” animals, around 9000 B.C. C. the largest village of its day, with 2000-3000 people D. a clear indication that pigs were domesticated prior to cereal plants 27. Lactational amenorrhea has been cited as a factor related to A. low birth rates in hunter-gatherer societies B. an increase in infant mortality in early villages C. a decline in the health of women associated with the stress of life in early farming communities D. use of animal milk to feed infants 28. True or false? A Neolithic tomb with a roof is called a menhir. A. True B. False 29. An economic recession that occurred in Wessex at around 3,000 B.C. appears to have been primarily the result of A. deforestation and resulting erosion from building of henges and large settlements B. increased warfare C. a decline in temperature and rainfall that began at that time D. the effects of population growth and early agricultural practices 30. The alignment between the center of Stonehenge and the Heel Stone A. B. C. D. is associated with is associated with points directly to appears to have no the sunrise on the summer solstice the sunrise on the winter solstice the burial mound of the chief of the region celestial significance 31. The large sarsen structures at Stonehenge are properly referred to as A. B. C. D. E. trilithons menhirs dolmens bilithons long barrows 32. The bodies found in many megalithic tombs suggest the practice of A. B. C. D. cannibalism excarnation mummification reincarnation 33. The first farmers began to spread across Britain at about A. B. C. D. E. 6500 5200 4200 3000 2500 B.C. B.C. B.C. B.C. B.C. 34. Refuse obtained from Durrington Walls suggests that the site was A. a large Neolithic village in Wessex B. largely devote to ceremonial as well as ordinary, everyday activities C. considerably earlier in time than the long barrows in the vicinity and hence, had no direct connection with them D. the site of feasting and ceremonial activities involving large groups of people E. attacked and burned during the economic recession 35. The Bronze Age in Britain was characterized by A. B. C. D. E. long distance trade of valuable materials burials of elite individuals construction of monumental structures all of the above B and C only 36. Originally the Aubrey Holes at Stonehenge A. B. C. D. contained small, upright bluestones that were later removed oriented the inner horseshoe to the southeast formed a circle whose purpose is unknown held 56 cremations arranged in a circular pattern 37. In Wessex, a large pig population after about 3000 B.C. is thought to have been responsible for A. B. C. D. destruction of agricultural land reclamation of farmland disease that appears to have reduced the population the construction of circular bank/ditch enclosures which served as pens E. A and C 38. A connection between the builders of Stonehenge and Wales is suggested by the A. B. C. D. similar design of monuments in both areas sarsens bluestones presence of similar high-status artifacts in both regions 39. Construction of Stonehenge took place over approximately A. B. C. D. 400 years 800 years 1200 years 1500 years 40. Which one of the following types of evidence was NOT used in the past to argue for Mycenaean influence on the design and construction of Stonehenge? A. B. C. D. E. the design and quality of construction a depiction of a dagger that was pecked into one of the stones finely crafted artifacts of gold and amber faience beads none of the above -- all were used to argue for Mycenaean influence