CS 366: Using a 2-way Associative Write
advertisement

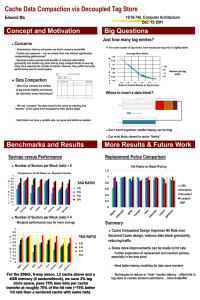
CS 366: Using a 2-way Associative Write-through Cache (Excerpted from Mano, pp. 628-631) CPU Address to use is: $ 0F3F 4024. Instruction has a 15-bit tag, 13-bit Index, 2-bit word select, 2-bit byte select 0 F 3 F 4 0 2 4 In Binary: 0000 1111 0011 1111 0100 0000 0010 0100 Regrouping to match instruction format [Fig 12-9a] _______Tag______ ______Index____ Word Byte 0000 1111 0011 111 1 0100 0000 0010 01 00 Regrouping Tag: _000 0111 1001 1111 And in Hex: $0 7 9 F $1 4 0 2 $1 3 Cases we will look at: 1. Read Hit a) The index value $1402 references the two tags at that address in the cache. b) Those tags are passed through the Match Logic. Assume tag 0 matches, which sets Match 0. c) Match 0 is ANDed together with the valid 0 bit for index $1402, along with the Read control line. Output of this enables three-state buffer 0. d) Concurrently with step 3, the 2 word_select bits ($1 in this case) causes word 1 to be selected from the 4 possibilities for both data memories. These two words are sent to their respective three-state buffers. e) The hit/miss line is set, indicating a hit. The CPU can internally then use the 2 byte-select bits to pull out one of the 4 bytes from the 32-bit word that has been retrieved. 2. Read Miss a) The index value $1402 references the two tags at that address in the cache. Again they pass through the match logic, only this time there is no match, so the hit/miss line is set to 0, indicating a miss. This indicates the word must be fetched from Main Memory. b) The cache control selects the cache entry to be replaced (some algorithm?). Four 32-bit words (tot. 128 bits) read from memory are applied simultaneously to the cache inputs. While this is happening, the 4-to-1 Mux selects the desired word out of the 4 and sends it to the CPU data bus using three-state buffer 3. 3. Write a) The 32-bit word write from the CPU (through three-state buffer 2) is fanned out into 4 words (128 bits), since we don’t know to which of the 4 entries in the cache line it corresponds. b) The CPU address (e.g. index $1402) is used to write back only the selected word to memory. If there is a cache hit, it is written to the cache as well. (Match logic for write enabling correct data bank is not shown.)