The Grapes of Wrath
advertisement
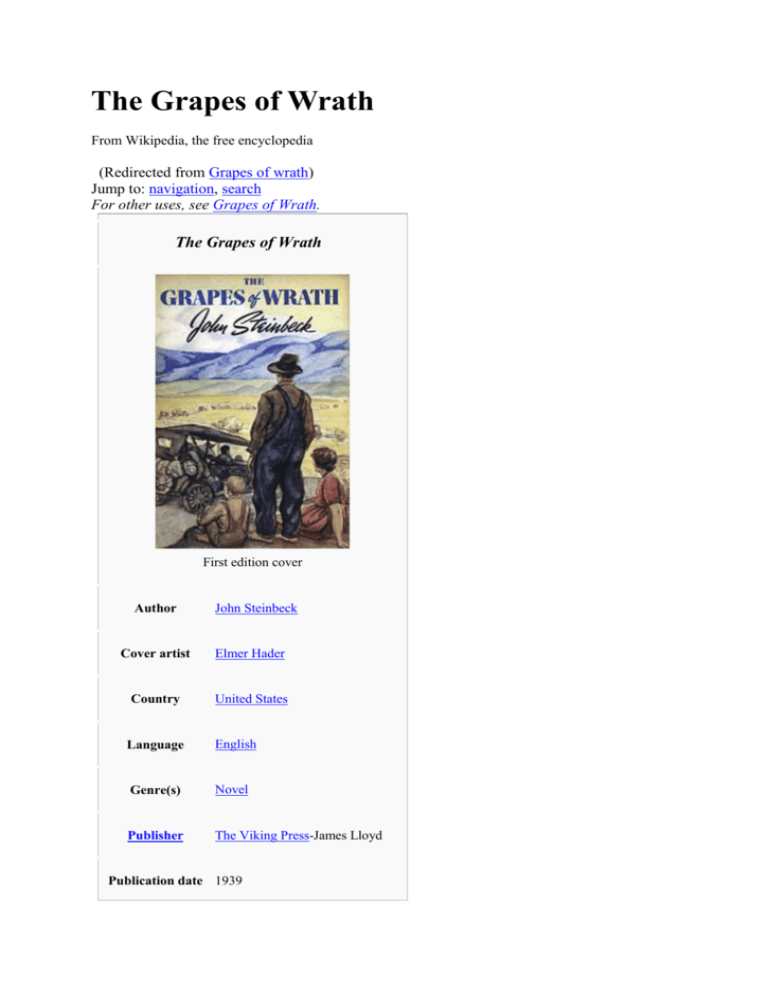
The Grapes of Wrath From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia (Redirected from Grapes of wrath) Jump to: navigation, search For other uses, see Grapes of Wrath. The Grapes of Wrath First edition cover Author John Steinbeck Cover artist Elmer Hader Country United States Language English Genre(s) Novel Publisher The Viking Press-James Lloyd Publication date 1939 Media type Print (Hardcover and Paperback) Pages 535 OCLC 289946 The Grapes of Wrath is a novel published in 1939 and written by John Steinbeck, who was awarded the Pulitzer Prize and the Nobel Prize for Literature. It is frequently read in American high school and college literature classes. A celebrated Hollywood film version, starring Henry Fonda and directed by John Ford, was made in 1940; however, the endings of the book and the movie differ greatly. Steinbeck wrote The Grapes of Wrath at his home, 16250 Greenwood Lane, in what is now Monte Sereno, California. Set during the Great Depression, the novel focuses on a poor family of sharecroppers, the Joads, driven from their home by drought, economic hardship, and changes in the agriculture industry. In a nearly hopeless situation, they set out for California's Central Valley along with thousands of other "Okies" in search of land, jobs, and dignity. Contents [hide] 1 Plot 2 Characters 3 Development o 3.1 Title 4 In popular culture o 4.1 Adaptations o 4.2 Literature o 4.3 Music o 4.4 Television 5 Critical reception 6 References o 6.1 Notes o 6.2 Bibliography 7 External links [edit] Plot The narrative begins from Tom Joad's point of view just after he is paroled from prison for homicide. On his journey home, he meets a now-former preacher, Jim Casy, whom he remembers from his childhood, and the two travel together. When they arrive at his childhood farm home, they find it deserted. Disconcerted and confused, he and Casy go to his Uncle John's home nearby where he finds his family loading a converted Hudson truck with what remains of their possessions; the crops were destroyed in the Dust Bowl and as a result, the family had to default on their loans. With their farm repossessed, the Joads seek solace in hope; hope inscribed on the handbills which are distributed everywhere in Oklahoma, describing the beautiful and fruitful country of California and high pay to be had in that state. The Joads, along with Jim Casy, are seduced by this advertising and invest everything they have into the journey. Although leaving Oklahoma would be breaking parole, Tom decides that it is a risk, albeit minimal, that he has to take. While en route, they discover that all of the roads and the highways are saturated with other families who are also making the same trek, ensnared by the same promise. As the Joads continue on their journey and hear many stories from others, some coming from California, they are forced to confront the possibility that their prospects may not be what they hoped. This realization, supported by the deaths of Grandpa and Grandma and the departure of Noah (the eldest Joad son) and Connie (the husband of the pregnant Joad daughter, Rose of Sharon), is forced from their thoughts: they must go on because they have no choice--there is nothing remaining for them in Oklahoma. Upon arrival, they find little hope of finding a decent wage, as there is an oversupply of labor and a lack of rights, and the big corporate farmers are in collusion. The tragedy lies in the simplicity and impossibility of their dream: a house, a family, and a steady job. A gleam of hope is presented at Weedpatch, in one of the clean, utility-supplied camps operated by the Resettlement Administration, a New Deal agency that tried to help the migrants, but there is not enough money and space to care for all of the needy. In response to the exploitation of laborers, the workers begin to join unions. The surviving members of the family unknowingly work as strikebreakers on an orchard involved in a strike that eventually turns violent, killing the preacher Casy and forcing Tom Joad to kill again and become a fugitive. He bids farewell to his mother, promising that no matter where he runs, he will be a tireless advocate for the oppressed. Rose of Sharon's baby is stillborn; however, Ma Joad remains steadfast and forces the family through the bereavement. In the end, Rose of Sharon commits the only act in the book that is not futile: she breast feeds a starving man, still trying to show hope in humanity after her own negative experience. This final act is said to illustrate the spontaneous mutual sharing that will lead to a new awareness of collective values. [edit] Characters Tom Joad — Protagonist of the story; the Joad family's second son, named for his father. Ma Joad — matriarch. Practical and warm-spirited, she tries to hold the family together. Her given name is never learned; it is suggested that her maiden name was Hazlett. Pa Joad — patriarch, also named Tom. Hardworking sharecropper and family man. Uncle John — Older brother of Pa Joad, feels responsible for the death of his young wife years before when he ignored her pleas for a doctor because he thought she just had a stomachache. He tries to repress "sins" such as drinking, then fulfills them with gross excesses like binge drinking. Jim Casy — A preacher who loses his faith after committing fornication with willing members of his church numerous times, and from his perception that religion has no solace or answer for the difficulties the people are experiencing. Al Joad — The second youngest son who cares mainly for cars and girls; looks up to Tom, but begins to find his own way. Over the book's course he gradually matures and learns responsibility. Rose of Sharon Rivers ("Rosasharn") — Childish and dreamy teenage daughter who develops as the novel progresses to become a mature woman. She symbolizes regrowth when she helps the starving stranger (see also Roman Charity, works of art based on the legend of a daughter as wet nurse to a dying father). Pregnant in the beginning of the novel, she delivers a stillborn baby, probably as a result of malnutrition. Connie Rivers — Rose of Sharon's husband. Young and naive, he is overwhelmed by the responsibilities of marriage and impending fatherhood, and abandons her shortly after arriving in California. Noah Joad — The oldest son who is the first to willingly leave the family, choosing to stay by an idyllic river and survive by fishing. Injured at birth, described as "strange", he may have slight learning difficulties or autistic spectrum disorder. Grandpa (William) Joad — Tom's grandfather who expresses his strong desire to stay in Oklahoma. He is drugged to make him leave but dies shortly after of a stroke. Symbolically, it is due to his spirit staying at the farm. Grandma Joad — The religious wife of Grandpa Joad, she seems to lose will to live (and consequently dies while crossing the desert) after her husband's death. Ruthie Joad — One of the younger children. Winfield Joad — A child. The youngest male in the family. He and Ruthie are close. Ivy and Sairey Wilson — Kansas folks in a similar predicament, who help attend the death of Grandpa and subsequently share the travelling with the Joads as far as the California state line. Mr. Wainwright — The father of Aggie Wainwright and husband of Mrs. Wainwright. Worries over his daughter who is sixteen and in his words "growed up". Mrs. Wainwright — Mother to Aggie Wainwright and wife to Mr. Wainwright. She helps deliver Rose of Sharon's stillborn baby with Ma. Aggie Wainwright — Sixteen years of age. Daughter to Mr. and Mrs. Wainwright. Intends on marrying Al. She has limited interactions with the other characters, but does speak with Ruthie and Winfield when Rose of Sharon goes into labor. [edit] Development [edit] Title Steinbeck had unusual difficulty devising a title for his novel. "The Grapes of Wrath", suggested by his wife, Carol Steinbeck, was deemed more suitable than anything the author could come up with. The title is a reference to some lyrics from "The Battle Hymn of the Republic", by Julia Ward Howe: Mine eyes have seen the glory of the coming of the Lord: He is trampling out the vintage where the grapes of wrath are stored; He hath loosed the fateful lightning of His terrible swift sword: His truth is marching on. These lyrics refer, in turn, to the biblical passage Revelation 14:19-20, an apocalyptic appeal to divine justice and deliverance from oppression in the final judgment. And the angel thrust in his sickle into the earth, and gathered the vine of the earth, and cast it into the great winepress of the wrath of God. And the winepress was trodden without the city, and blood came out of the winepress, even unto the horse bridles, by the space of a thousand and six hundred furlongs. As might be expected, the image invoked by the title serves as a crucial symbol in the development of both the plot and the novel's greater thematic concerns: From the terrible winepress of Dust Bowl oppression will come terrible wrath but also the deliverance of workers through their cooperation. [edit] In popular culture Lists of miscellaneous information should be avoided. Please relocate any relevant information into appropriate sections or articles. (December 2008) [edit] Adaptations 1940 film adaptation of The Grapes of Wrath A film version was produced by Darryl F. Zanuck in 1940 and directed by John Ford. Ford won the Academy Award for Directing and Jane Darwell won the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actress. The film was also nominated for several other awards: Academy Award for Best Picture, Henry Fonda for Best Actor, Robert L. Simpson for Best Film Editing, Edmund H. Hansen for Best Sound Recording, and Nunnally Johnson for Best Screenplay Writing. It has been selected for preservation in the United States National Film Registry. The Steppenwolf Theatre Company produced a stage version of the book, adapted by Frank Galati. Gary Sinise played Tom Joad for its entire run of 188 performances on Broadway in 1990,[1] and was shown on PBS the following year.[2] An opera based on the novel was co-produced by the Minnesota Opera and Utah Symphony and Opera, with music by Ricky Ian Gordon and libretto by Michael Korie. The world premiere performance of the opera was given in February 2007, to favorable local reviews.[3] [edit] Literature Tom Joad appears as a background figure in the short story "Tom Joad" by Kim Newman and Eugene Byrne, in part of the short story collection Back in the USSA. [edit] Music In 1940, Woody Guthrie recorded a ballad called "Tom Joad". This ballad, set to the tune of "John Hardy", summarizes the plot of the book and movie. It was so long that it had to be recorded in two parts. Woody wrote the song after seeing the movie, which he described as the "best cussed pitcher I ever seen". 'The Grapes of Wrath' was a popular Canadian alternative rock band from 1984 to 1994. The English progressive rock band Camel recorded an album Dust and Dreams (1991) inspired by The Grapes of Wrath. On Pink Floyd's 1987 album A Momentary Lapse of Reason, the opening lines for the song "Sorrow" are paraphrased from the beginning of a chapter in The Grapes of Wrath: "Sweet smell of a great sorrow lies over the land." Kris Kristofferson's 1981 single "Here Comes That Rainbow Again" is based on a scene from the book. The Massachusetts metalcore band Killswitch Engage's 2004 album "The End of Heartache" consisted of the track, "Rose of Sharyn." In 1995, Bruce Springsteen recorded his song "The Ghost of Tom Joad" on the album of the same name. The lyric is set in contemporary times, but the third verse quotes Tom's famous "wherever there's a ..." lines. The song was later recorded by Rage Against The Machine, José González's band Junip, and others. Springsteen has stated that he was first inspired by the John Ford film. [edit] Television In the Boy Meets World episode "Me and Mr. Joad", Cory Matthews and Shawn Hunter lead their 7th grade class in a "strike" and class walkout inspired by the strike the workers did in the book.[4] An episode of television show South Park, entitled Over Logging parodied the novel, substituting a shortage of Internet access for a shortage of employment. [edit] Critical reception At the time of publication, Steinbeck's novel "was a phenomenon on the scale of a national event. It was publicly banned and burned by citizens, it was debated on national radio hookups; but above all, it was read." [5] Steinbeck scholar John Timmerman sums up the book's impact: "The Grapes of Wrath may well be the most thoroughly discussed novel - in criticism, reviews, and college classrooms - of twentieth century American literature." Part of its impact stemmed from its passionate depiction of the plight of the poor, and in fact, many of Steinbeck's contemporaries attacked his social and political views. Bryan Cordyack writes, "Steinbeck was attacked as a propagandist and a socialist from both the left and the right of the political spectrum. The most fervent of these attacks came from the Associated Farmers of California; they were displeased with the book's depiction of California farmers' attitudes and conduct toward the migrants. They denounced the book as a 'pack of lies' and labeled it 'communist propaganda'."[6] However, although Steinbeck was accused of exaggeration of the camp conditions to make a political point, in fact he had done the opposite, underplaying the conditions that he well knew were worse than the novel describes[7] because he felt exact description would have gotten in the way of his story. Furthermore, there are several references to socialist politics and questions which appear in the John Ford film of 1940 which do not appear in the novel, which is less political in its terminology and interests. Franklin D. Roosevelt was an early advocate for addressing the plight of those featured in the book. In 1962, the Nobel Prize committee cited Grapes of Wrath as a "great work" and as one of the committee's main reasons for granting Steinbeck the Nobel Prize for Literature.[8] Time Magazine included the novel in its TIME 100 Best English-language Novels from 1923 to 2005.[9] [edit] References [edit] Notes 1. ^ Internet Broadway Database: The Grapes of Wrath Production Credits 2. ^ The Grapes of Wrath (1991) (TV) 3. ^ Michael Anthony, "'Grapes' is a sweet, juicy production," Minneapolis Star Tribune, 2/12/2007 4. ^ Internet Movie Database: "Boy Meets World" Me and Mr. Joad Episode Overview 5. ^ Peter Lisca, The Wide World of John Steinbeck 6. ^ Cordyack, Brian. "20th-Century American Bestsellers: John Steinbeck, The Grapes of Wrath". Graduate School of Library and Information Science, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign. Retrieved on 2007-02-18. 7. ^ Shillinglaw, Susan; Benson, Jackson J (2002), Of Men and Their Making: The NonFiction Of John Steinbeck, Penguin, http://books.guardian.co.uk/extracts/story/0,6761,643450,00.html, retrieved on 17 December 2008 8. ^ Osterling, Anders. "Nobel Prize in Literature 1962 - Presentation Speech". Retrieved on 2007-02-18. 9. ^ http://www.time.com/time/2005/100books/ [edit] Bibliography Gregory, James N. "Dust Bowl Legacies: the Okie Impact on California, 1939-1989." California History 1989 68(3): 74-85. Issn: 0162-2897 Saxton, Alexander. "In Dubious Battle: Looking Backward." Pacific Historical Review 2004 73(2): 249-262. Issn: 0030-8684 Fulltext: online at Swetswise, Ingenta, Ebsco Sobchack, Vivian C. "The Grapes of Wrath (1940): Thematic Emphasis Through Visual Style." American Quarterly 1979 31(5): 596-615. Issn: 0003-0678 Fulltext: in Jstor. Discusses the visual style of John Ford's cinematic adaptation of the novel. Usually the movie is examined in terms of its literary roots or its social protest. But the imagery of the film reveals the important theme of the Joad family's coherence. The movie shows the family in closeups, cramped in small spaces on a cluttered screen, isolated from the land and their surroundings. Dim lighting helps abstract the Joad family from the reality of Dust Bowl migrants. The film's emotional and aesthetic power comes from its generalized quality attained through this visual style. Windschuttle, Keith. "Steinbeck's Myth of the Okies". The New Criterion, Vol. 20, No. 10, June 2002. Zirakzadeh, Cyrus Ernesto. "John Steinbeck on the Political Capacities of Everyday Folk: Moms, Reds, and Ma Joad's Revolt." Polity 2004 36(4): 595-618. Issn: 0032-3497 [edit] External links Wikiquote has a collection of quotations related to: The Grapes of Wrath The Grapes of Wrath: a Study Guide Study of "The Grapes of Wrath" on Sparknotes Death in the Dust: John Steinbeck's first-person account of the conditions he observed at a California squatter's camp. Woody Guthrie's Tom Joad Photos of the first edition of The Grapes of Wrath A Review Of John Steinbeck's 1939 novel "The Grapes Of Wrath" Study resource for Grapes of Wrath Awards and achievements Preceded by The Yearling by Marjorie Kinnan Rawlings Pulitzer Prize for the Novel 1940 Succeeded by 1941: no award given 1942:In This Our Life by Ellen Glasgow [hide] v•d•e Works by John Steinbeck Novels Non-fiction Short stories Cup of Gold · To a God Unknown · Tortilla Flat · In Dubious Battle · Of Mice and Men · The Grapes of Wrath · The Moon Is Down · Cannery Row · The Pearl · The Wayward Bus · Burning Bright · East of Eden · Sweet Thursday · The Short Reign of Pippin IV · The Winter of Our Discontent · The Acts of King Arthur and His Noble Knights The Log from the Sea of Cortez · Bombs Away: The Story of a Bomber Team · A Russian Journal · Once There Was a War · Travels with Charley · Journal of a Novel: The East of Eden Letters · America and Americans "The Chrysanthemums" · "The White Quail" · "Flight" · "The Snake" · "Breakfast" · "The Raid" · "The Harness" · "The Vigilante" · "Johnny Bear" · "Red Pony" · "The Murder" · "Saint Katy the Virgin" Short story collections The Pastures of Heaven · The Long Valley Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Grapes_of_Wrath" Categories: 1939 novels | Novels by John Steinbeck | Great Depression fiction | Pulitzer Prize for the Novel | American novels | Culture of Bakersfield, California Hidden category: Articles with trivia sections from December 2008