Study Guide, Exam 1
advertisement

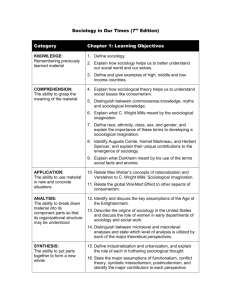
Study Guide, Exam 1, SOCY1001 Spring Semester 2013 Prof. Hunter ****note that Exam 1 will contain questions from the Witt textbook, recitation readings/discussion and lecture. Good luck with your studies! The Sociological Imagination What is the Sociological Imagination and how might you apply it to a particular social problem? According to C. Wright Mills, what are “issues”? “troubles”? “biography” vs. “history”? Can you link this to “macro” and “micro”? Offer examples as to how “macro” and “micro” are connected via the Sociological Imagination? Why is the Sociological Imagination both a blessing and a curse? What does Berger mean when he says “things are not what they seem?” What is Sociology and what do Sociologists study? What does Witt aim to illustrate with the example of a hamburger? Can you give other examples of this concept? What are the key components of Sociology? Can you give examples of each? Why is Sociology more than common sense? In Sociological terms, what is “agency”? Can you give examples? How can you position “agency” visà-vis the Sociological Imagination? What is social inequality and how does it relate to Sociological resaerch? Is Sociology a science? If so, why? How is it distinct from natural sciences? How is it similar? What’s a theory? A sociological theory? Can you give examples? How are they applied/tested? What are theories used for anyway? Can you describe Durkheim’s study of suicide? Why was it sociological? How did Sociology develop? Can you describe the primary contributions of the early Sociologists outlined in your textbook? These include Durkheim’s study of suicide, Marx’s critique of capitalism, and DuBois’ exploring of the meaning of being black in America. What are the three core perspectives? Can you apply them to particular issues? Why study Sociology? What’s the difference between applied, academic and clinical sociology? Why is globalization of Sociological interest? What is Sociology’s primary professional organization and what’s its purpose? How is the Sociological Imagination helpful in considering Hernando Washington’s story? In what ways does considering violence in muscial lyrics relate to the Sociological Imagination and Hernando Washington’s “biography”? Chapter 2: Sociological Research What are the steps in the research process? Can you give examples of each step? An analysis of violence in music lyrics represents what form of research design? Can you given other examples of this form of research design? What is an operational definition? Can you give examples? What is a hypothesis? Can you give examples? o Variables? Independent variable? Dependent variable? Control variable? Examples? o Causal logic? Examples? o Correlations? Examples? o What’s a sample? A random sample? Why is it important to carefully consider sampling? o Validity? Reliability? Overall – what’s a research design? Why is it important to consider this design carefully? What types of data collection procedures are available to Sociologists? Can you give examples? Can you distinguish between quantitative and qualitiative research? Give examples? Can you explain social experiments? Examples? Control/experimental groups? The Hawthorne effect? What’s secondary analysis? Can you give examples? What type of research is represented by the box outlining “White Privilege in Job seeking” ? What’s content analysis? Can you give examples? Is it a valid form of social research? Why are reseach ethics important to consider within Sociological Research? What’s the ASA? The Code of Ethics? Can you list its components? Why is confidentiality an issue? What about research funding as related to ethics? What is objectivity and value neutrality and why are these important for Sociologists? What motivates choice of a research topic? Why does this chapter include mention of feminist methodology? Can you describe it? What is a correlation and why are some spurious? Control variables? Can you give examples? Why are some data collection techniques not scientific (e.g., Glamour online surveys? “person on the street” interviews)? How do Adler and Adler (in the recitation reading) describe ethnography? o What are its strengths and weaknesses? What did the video clip of the Milgram shock experiment revisited reveal about social structure and social interaction? What lessons did it offer with regard to the ethics of social research? Chapter 3 Culture Can you define culture? society? How are these related? Can you give examples? What’s with the hug example? Why do humans need culture? Can you identify material elements of culture? non-material elements? Can you distinguish amon types of non-material elements? Can you identify areas in which material and non-material are intertwined? What have been identified as core American values? What are cultural universals? Can you give examples? What is sociobiology and how does it differ from sociology? What is innovation? Discovery? Invention? Diffusion? What do these concepts have to do with culture? Can you give examples? Can you give examples of how geographic and historical forces shape culture? Why did Witt include the superhero image on page 50? In Sociological terms, what’s language? What does it have to do with culture? Can you describe the Sapir- Whorf hypothesis? Give examples? What is culture lag? Can you give examples? Does it have to do with material, non-material culture or both? Describe. Can you describe values? American values? Changes in American values? What about norms (formal, informal and other types)? How are values and norms related? Why does Witt include a question about cheating in the hot pepper on page 54? What does this have to do with culture, norms and other topics in this chapter? What are sanctions? Can you name the various kinds and give examples? What is dominant ideology and why is this concept included in the chapter on culture? What about subcultures? Counter cultures? What characteristics distinguish these two categories of cultural variation? What’s argot? Can you offer examples? What is ethnocentrism? Culture shock? What is the association between these? What about reverse ethnocentrism? Reverse culture shock? What about cultural relativism? Should we ALWAYS be tolerant of cultural differences or might there be exceptions? What are the primary lessons to be learned from your recitation reading and discussions of this week? How did the Facebook example in recitation illustrate how technology has changed norms regarding social interaction?