Decimal Place Value Bars
advertisement

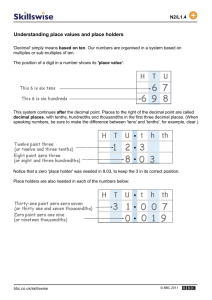
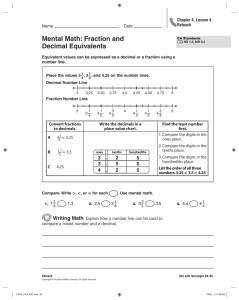
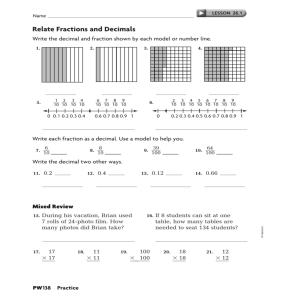
Building Decimals Workmat Reproducible Decimal Place Value Bars This Really Good Stuff® product includes: • Decimal Place Value Bars • This Really Good Stuff® Activity Guide students an opportunity to practice reading the values on each Bar. Congratulations on your purchase of the Really Good Stuff® Decimal Place Value Bars—helpful tools to foster students’ understanding of decimal place value. Meeting Common Core State Standards The Really Good Stuff® Decimal Place Value Bars are aligned with the following Common Core State Standards for Mathematics: Number and Operations in Base Ten 5.Overview • Understand the place value system. • Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to hundredths. Number and Operations—Fractions 4.Overview • Understand decimal notation for fractions, and compare decimal fractions. Displaying and Preparing the Decimal Place Value Bars Before introducing the Decimal Place Value Bars, make copies of this Really Good Stuff® Activity Guide, and file them for future use. Or, download another copy of it from our Web site at www.reallygoodstuff.com. Divide the Bars into sets for each student or group. Introducing the Decimal Place Value Bars Indicate to students that the Decimal Place Value Bars will help them think about the parts of numbers that are written as decimals. Show students a sample of each Bar. Arrange the Bars in order from smallest in size to largest in size with the .1 Bar at the top and the .001 Bar at the bottom. Ask students to notice that each Bar is a different color; that each Bar has a different value; that the size of the Bar increases as the decimal value gets smaller; and that there is an additional zero between the decimal point and the one. Make connections to the fraction values and the number of zeros after the decimal point that each Bar represents (.1 = 1/10, .01 = 1/100, .001 = 1/1,000). Help students understand that even though the values look large, they are working with very small numbers between the numbers 0 and 1. Give Building Decimal Numbers Copy and distribute the Building Decimals Workmat Reproducible. Explain to students that they are to use the Decimal Place Value Bars to show different numbers. Model building the number 0.32 by counting 3 tenths (0.1, 0.2, 0.3) and 2 hundredths (0.01, 0.02,). Explain that the 3 in the tenths place told you how many tenths you needed and the 2 in the hundredths place told you how many hundredths you needed. Write in expanded form as 0.3 + 0.02. Allow students to build several decimal numbers, such as 0.43 and 0.65. Encourage students to count up to the given number as they move the Decimal Place Value Bars and to write the number in expanded form. Model building the number .245 by counting 2 tenths (0.1, 0.2), 4 hundredths (0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04), and 5 thousandths (0.001, 0.002, 0.003, 0.004, 0.005). Explain that the 2 in the tenths place told you how many tenths you needed, the 4 in the hundredths place told you how many hundredths you needed, and the 5 in the thousandths place told you how many thousandths you needed. Remind students that looking at the place value of each number helped you to figure out how many of each of the Decimal Place Value Bars you needed. Allow students to write the number in expanded form, for example: 0.2 + 0.04 + 0.005 or 0.200 + 0.040 + 0.005. Allow students to build several numbers, such as 0.254 and 0.642. Give students an opportunity to build additional numbers on the reproducible. Instruct them to manipulate the Decimal Place Value Bars in the place value chart at the top, and then write the number in expanded form in the number sentence below. Remind students to place a comma between the digit in the hundredths and the thousandths place in their answers. Variation: Have students write the decimal numbers as fractions. For example, show students that they can write 0.2 + 0.04 + 0.005 = 0.245 as 2/10 + 4/100 + 5/1,000 = 245/1,000. All activity guides can be found online. Helping Teachers Make A Difference® © 2014 Really Good Stuff 1-800-366-1920 www.reallygoodstuff.com Made in China #162278 ® Helping Teachers Make A Difference® © 2014 Really Good Stuff 1-800-366-1920 www.reallygoodstuff.com Made in China #162278 ® Decimal Place Value Bars Reproducible Decimal Place Value Bars Exploring the Decimal Place Value Bars Separate the Decimal Place Value Bars into piles of each value. Review together how the Decimal Place Value Bars will help students see how each place value is connected. Count the thousandths as you move them into the thousandths column of a place value chart. Explain that when students get to 10, when counting, they can trade the 10 thousandths in for 1 hundredth. Model this trade, removing the 10 thousandths and replacing with 1 hundredth in the hundredth column. Move hundredths into the hundredths column until you get to 10 hundredths. Ask students what you should do now that you have 10 hundredths. Model this trade. Encourage students to notice that each place value is 10 times greater than the place to the right. Make connections to what students know about whole numbers. Write a multiplication expression for each place value: Hundredths 0.001 x 10 = 0.01 Tenths 0.01 x 10 = 0.1 Ones 0.1 x 10 = 1 Tens 1 x 10 = 10 Hundreds 10 x 10 = 100 combinations. Model combinations as addition sentences, such as: • If I have 2 tenths, how many more tenths do I need to get to the number 1? (0.2 + 0.8 = 1) • If I have 4 hundredths, how many more do I need to get to the number 0.1? (0.04 + 0.06 = 0.1) Explain that when they use the Decimal Place Value Bars, they may have to trade 10 Bars for another Bar of equal value. Comparing Decimals Encourage students to use the Decimal Place Value Bars to compare decimal numbers and tell which number is greater. Display the number sentence 0.23 _______ 0.35 and model building each decimal number: There are 2 tenths in 0.23 and 3 tenths in 0.35, so I can know that 0.23 is less than 0.35. Ask students to complete the number sentence 0.23 < 0.35. Copy and distribute the Decimal Place Value Bars Reproducible for students to practice comparing numbers, and to keep in their math folders for later use. Display the problem 0.45 − 0.16. Remind students that when they subtract, they are taking numbers away from each other. Model building 0.45 with 4 tenths and 5 hundredths. Emphasize that you are not building 0.16 because this needs to come from the 0.45. Think aloud as you trade the Decimal Place Value Bars, and model the problem on a place value chart. Answers (Comparing Decimals): 1) <, 2) <, 3) >, 4) <, 5) >, 6) <, 7) =, 8) > Recognizing Combinations of 10 in Decimal Numbers Remind students how they used combinations of the number 10 in addition. (If they have 3, they will need 7 more to make 10.) Ask them to identify other combinations of 10. Show students how to apply complements of 10 to decimals with combinations, such as 0.4 + 0.6 = 1, which is the same as 4 tenths plus 6 tenths. Encourage students to think about the number of Decimal Place Value Bars as they consider the Helping Teachers Make A Difference® © 2014 Really Good Stuff® 1-800-366-1920 www.reallygoodstuff.com Made in China #162278 Helping Teachers Make A Difference® Adding and Subtracting Decimal Numbers Explain to students that they can use Decimal Place Value Bars to model addition and subtraction of decimal numbers <1.0. Display the problem 0.34 + 0.27. Model building 0.34 and 0.27. Remind students that when they add, they are putting numbers together. Combine the tenths in one area and the hundredths in another area. Show students how to count to find the total. Tell students that the total is 5 tenths and 11 hundredths. Model physically trading 10 of the hundredths in for 1 tenth, so the answer is 6 tenths and 1 hundredth or 0.61. Display the problem 0.56 − 0.324. Model building 0.56 with 5 tenths and 6 hundredths. In this problem, explain that you need to take away 4 thousandths, but no thousandth are shown in 0.56. Model trading 1 hundredth for 10 thousandths with the Decimal Place Value Bars, and record on a place value chart. Ask students to practice both addition and subtraction problems on their Decimal Place Value Bars Repoducible. Encourage them to consider whether their answers are reasonable by estimating the answer to a problem. Answers (Adding and Subtracting Decimals): 1) 0.72, 2) 0.424, 3) 0.933, 4) 0.816, 5) 0.819, 6) 1.049, 7) 0.03, 8) 0.44, 9) 0.23, 10) 0.074, 11) 0.127, 12) 0.438 © 2014 Really Good Stuff® 1-800-366-1920 www.reallygoodstuff.com Made in China #162278 Building Decimals Workmat Reproducible Decimal Place Value Bars This Really Good Stuff® product includes: • Decimal Place Value Bars • This Really Good Stuff® Activity Guide students an opportunity to practice reading the values on each Bar. Congratulations on your purchase of the Really Good Stuff® Decimal Place Value Bars—helpful tools to foster students’ understanding of decimal place value. Meeting Common Core State Standards The Really Good Stuff® Decimal Place Value Bars are aligned with the following Common Core State Standards for Mathematics: Number and Operations in Base Ten 5.Overview • Understand the place value system. • Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to hundredths. Number and Operations—Fractions 4.Overview • Understand decimal notation for fractions, and compare decimal fractions. Displaying and Preparing the Decimal Place Value Bars Before introducing the Decimal Place Value Bars, make copies of this Really Good Stuff® Activity Guide, and file them for future use. Or, download another copy of it from our Web site at www.reallygoodstuff.com. Divide the Bars into sets for each student or group. Introducing the Decimal Place Value Bars Indicate to students that the Decimal Place Value Bars will help them think about the parts of numbers that are written as decimals. Show students a sample of each Bar. Arrange the Bars in order from smallest in size to largest in size with the .1 Bar at the top and the .001 Bar at the bottom. Ask students to notice that each Bar is a different color; that each Bar has a different value; that the size of the Bar increases as the decimal value gets smaller; and that there is an additional zero between the decimal point and the one. Make connections to the fraction values and the number of zeros after the decimal point that each Bar represents (.1 = 1/10, .01 = 1/100, .001 = 1/1,000). Help students understand that even though the values look large, they are working with very small numbers between the numbers 0 and 1. Give Building Decimal Numbers Copy and distribute the Building Decimals Workmat Reproducible. Explain to students that they are to use the Decimal Place Value Bars to show different numbers. Model building the number 0.32 by counting 3 tenths (0.1, 0.2, 0.3) and 2 hundredths (0.01, 0.02,). Explain that the 3 in the tenths place told you how many tenths you needed and the 2 in the hundredths place told you how many hundredths you needed. Write in expanded form as 0.3 + 0.02. Allow students to build several decimal numbers, such as 0.43 and 0.65. Encourage students to count up to the given number as they move the Decimal Place Value Bars and to write the number in expanded form. Model building the number .245 by counting 2 tenths (0.1, 0.2), 4 hundredths (0.01, 0.02, 0.03, 0.04), and 5 thousandths (0.001, 0.002, 0.003, 0.004, 0.005). Explain that the 2 in the tenths place told you how many tenths you needed, the 4 in the hundredths place told you how many hundredths you needed, and the 5 in the thousandths place told you how many thousandths you needed. Remind students that looking at the place value of each number helped you to figure out how many of each of the Decimal Place Value Bars you needed. Allow students to write the number in expanded form, for example: 0.2 + 0.04 + 0.005 or 0.200 + 0.040 + 0.005. Allow students to build several numbers, such as 0.254 and 0.642. Give students an opportunity to build additional numbers on the reproducible. Instruct them to manipulate the Decimal Place Value Bars in the place value chart at the top, and then write the number in expanded form in the number sentence below. Remind students to place a comma between the digit in the hundredths and the thousandths place in their answers. Variation: Have students write the decimal numbers as fractions. For example, show students that they can write 0.2 + 0.04 + 0.005 = 0.245 as 2/10 + 4/100 + 5/1,000 = 245/1,000. All activity guides can be found online. Helping Teachers Make A Difference® © 2014 Really Good Stuff 1-800-366-1920 www.reallygoodstuff.com Made in China #162278 ® Helping Teachers Make A Difference® © 2014 Really Good Stuff 1-800-366-1920 www.reallygoodstuff.com Made in China #162278 ® Decimal Place Value Bars Reproducible Decimal Place Value Bars Exploring the Decimal Place Value Bars Separate the Decimal Place Value Bars into piles of each value. Review together how the Decimal Place Value Bars will help students see how each place value is connected. Count the thousandths as you move them into the thousandths column of a place value chart. Explain that when students get to 10, when counting, they can trade the 10 thousandths in for 1 hundredth. Model this trade, removing the 10 thousandths and replacing with 1 hundredth in the hundredth column. Move hundredths into the hundredths column until you get to 10 hundredths. Ask students what you should do now that you have 10 hundredths. Model this trade. Encourage students to notice that each place value is 10 times greater than the place to the right. Make connections to what students know about whole numbers. Write a multiplication expression for each place value: Hundredths 0.001 x 10 = 0.01 Tenths 0.01 x 10 = 0.1 Ones 0.1 x 10 = 1 Tens 1 x 10 = 10 Hundreds 10 x 10 = 100 combinations. Model combinations as addition sentences, such as: • If I have 2 tenths, how many more tenths do I need to get to the number 1? (0.2 + 0.8 = 1) • If I have 4 hundredths, how many more do I need to get to the number 0.1? (0.04 + 0.06 = 0.1) Explain that when they use the Decimal Place Value Bars, they may have to trade 10 Bars for another Bar of equal value. Comparing Decimals Encourage students to use the Decimal Place Value Bars to compare decimal numbers and tell which number is greater. Display the number sentence 0.23 _______ 0.35 and model building each decimal number: There are 2 tenths in 0.23 and 3 tenths in 0.35, so I can know that 0.23 is less than 0.35. Ask students to complete the number sentence 0.23 < 0.35. Copy and distribute the Decimal Place Value Bars Reproducible for students to practice comparing numbers, and to keep in their math folders for later use. Display the problem 0.45 − 0.16. Remind students that when they subtract, they are taking numbers away from each other. Model building 0.45 with 4 tenths and 5 hundredths. Emphasize that you are not building 0.16 because this needs to come from the 0.45. Think aloud as you trade the Decimal Place Value Bars, and model the problem on a place value chart. Answers (Comparing Decimals): 1) <, 2) <, 3) >, 4) <, 5) >, 6) <, 7) =, 8) > Recognizing Combinations of 10 in Decimal Numbers Remind students how they used combinations of the number 10 in addition. (If they have 3, they will need 7 more to make 10.) Ask them to identify other combinations of 10. Show students how to apply complements of 10 to decimals with combinations, such as 0.4 + 0.6 = 1, which is the same as 4 tenths plus 6 tenths. Encourage students to think about the number of Decimal Place Value Bars as they consider the Helping Teachers Make A Difference® © 2014 Really Good Stuff® 1-800-366-1920 www.reallygoodstuff.com Made in China #162278 Helping Teachers Make A Difference® Adding and Subtracting Decimal Numbers Explain to students that they can use Decimal Place Value Bars to model addition and subtraction of decimal numbers <1.0. Display the problem 0.34 + 0.27. Model building 0.34 and 0.27. Remind students that when they add, they are putting numbers together. Combine the tenths in one area and the hundredths in another area. Show students how to count to find the total. Tell students that the total is 5 tenths and 11 hundredths. Model physically trading 10 of the hundredths in for 1 tenth, so the answer is 6 tenths and 1 hundredth or 0.61. Display the problem 0.56 − 0.324. Model building 0.56 with 5 tenths and 6 hundredths. In this problem, explain that you need to take away 4 thousandths, but no thousandth are shown in 0.56. Model trading 1 hundredth for 10 thousandths with the Decimal Place Value Bars, and record on a place value chart. Ask students to practice both addition and subtraction problems on their Decimal Place Value Bars Repoducible. Encourage them to consider whether their answers are reasonable by estimating the answer to a problem. Answers (Adding and Subtracting Decimals): 1) 0.72, 2) 0.424, 3) 0.933, 4) 0.816, 5) 0.819, 6) 1.049, 7) 0.03, 8) 0.44, 9) 0.23, 10) 0.074, 11) 0.127, 12) 0.438 © 2014 Really Good Stuff® 1-800-366-1920 www.reallygoodstuff.com Made in China #162278