U13 L-4 Real Number Charts
advertisement

Unit 13 L-3 Math 8
Aim: To classify real numbers as rational or irrational and understand that every
number has a decimal expansion (8.NS.1)
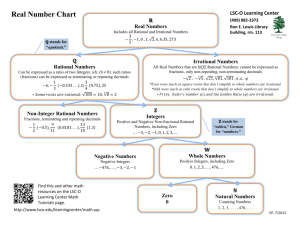
Real
Numbers
Rational
Numbers
Integers,
whole
numbers,
natural
numbers
Ratios,
terminating
and repeating
decimals
Irrational
Numbers
Examples:
-5, 2/3, 4 1/4,
-1/6, 0, 11,
7.288,
9.6666...,
0.512512.... Nonterminating,
nonrepeating
decimals
π,
0.121221222...,
square root of
3, square root
of 8
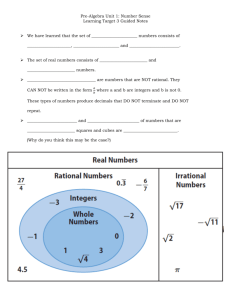
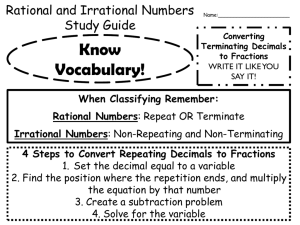
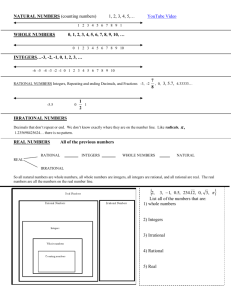
Classifying Sets of Numbers
Natural Numbers, or Counting Numbers
{1, 2, 3, 4, ….}
Whole Numbers – the set of Natural numbers plus zero:
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ….}
Integers – consists of Whole Numbers and their Opposites: {…-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 …}
!
Rational Numbers – a number you can write as the ratio of two integers in the form ! ,
where b ≠ 0. Rational numbers can be represented as either repeating or terminating
decimals. This set includes the integers, whole numbers, and natural numbers as well as
fractions, terminating decimals, and repeating decimals.
Irrational Numbers – numbers that are not rational and cannot be written as a ratio.
Irrational numbers include non-terminating, non-repeating decimals like π, 2.141141114…,
3, or 5.
2014-2015