Math Grade 4 Unit 1 Whole Numbers, Place Value, and Rounding in
advertisement

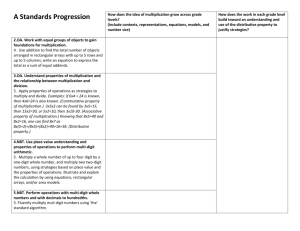
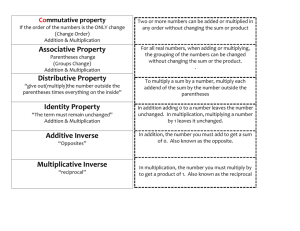
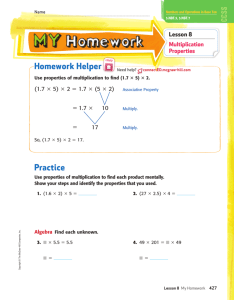
Math Grade 4 Unit 1 Whole Numbers, Place Value, and Rounding in Computation “I Can” Help My Student I can … understand that multiplication fact problems can be seen as comparisons of groups (e.g., 24 = 4 x 6 can be thought of as 4 groups of 6 or 6 groups of 4). 4.OA.1 multiply or divide to solve word problems by using drawings or writing equations and solving for a missing number. 4.OA.2 recognize that in multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. 4.NBT.1 read and write larger whole numbers using numerals, words and in expanded form. 4.NBT.2 multiply two two-digit numbers. 4.NBT.5 find whole-number quotients and remainders with up to four-digit dividends and onedigit divisors. 4.NBT.6 Key Words to Know Algorithm - a step-by-step procedure for calculations Distributive Property - an algebra property which is used to multiply a single term and two or more terms inside a set of parentheses. Digits – Any one of the ten symbols 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9 used to write numbers. Dividend – The number that is to be divided in a division problem. Divisor – The number that divides the dividend. Division (repeated subtraction) – The number of times a number is subtracted from another before no further rational subtraction can take place. Factors- A number that is multiplied by another number to find a product. Multiplicand- a number that is multiplied by another number multiplier. The number 2 is the multiplicand in the statement 2 × 4 = 8. (the number of row) Multiplier –one of the factors in a multiplication equation. In the 9s equation, each of the numbers that multiplies 9 is the multiplier. (the number of columns) Multiples –a number that is the product of a given number and any whole number. Partition division (fair-sharing/chunking) –division as the amount of shares to each group. Product –the answer to a multiplication problem 3 x 4=12, 12 is the product. Properties – http://www.purplemath.com/modules/numbprop.htm Parent Guide What your student should know & do at home Important Understandings and Concepts What should my student already know before I begin….. Your child should be able to : Solve multi-step word problems using four operations Fluently multiply and divide within 100 using strategies Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number Multiply two two-digit numbers Divide up to four digit dividends by one digit divisors Use number talks to reinforce properties of operations and mental computation Learning at a Glance In this unit students will generalize place value to 1,000,000 and understand relative size of numbers in each place. They will use models for multiplication (equal-sized groups, arrays and area model), place value, and properties of operations, in particular the distributive property, as they develop accurate methods to multiply multi-digit whole numbers. They will select and accurately apply appropriate methods to estimate and mentally calculate products. In addition, students will use deep understanding of the relationship between multiplication and division to divide with up to four-digit dividends and onedigit divisors to find whole number quotients with remainders and determine the meaning of the remainder within context of the problem. They will select and accurately apply appropriate methods to estimate and mentally calculate quotients. Finally, students will solve multi-step word problems utilizing the four operations and represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. 20 5 20 400 100 500 80 20 100 480 120 600 4 Math Grade 4 Unit 1 Whole Numbers, Place Value, and Rounding in Computation Sample Your class is collecting bottled water for a service project. The goal is to collect 300 bottles of water. On the first day, Max brings in 3 packs with 6 bottles in each container. Sarah wheels in 6 packs with 7 bottles in each container. About how many bottles of water still need to be collected? Parent Guide What your student should know & do at home Interactive Learning Lessons The following are great interactive Math videos. Your student can watch the videos alone or with you. Have your student take notes while watching. Allow them to watch as many times as needed. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vpOmC248psQ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zWeCr97A_QI http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lrUiFpi7MvI Task Robert and his family traveled from Atlanta, Georgia to Washington D.C. to visit the Martin Luther King Monument. They traveled a total of 648 miles. It took them a total of 9 hours to get to Washington, D.C. If they traveled the same route back to Georgia, about how many miles would they drive? Explain your answer. Recommended Children’s Literature The use of children’s literature is equally important as problems and deserves some attention. Use these books to integrate and enhance both language literacy and mathematical literacy for an interdisciplinary connection during story time. These books can be checked out at your local Atlanta-Fulton Public Library System www.afplweb.com Amanda Bean's Amazing Dream: A Mathematical Story by Cindy Neuschwander Interactive Learning Games Playing games is a wonderful way to practice skills at home in a fun environment. http://www.sedl.org/scimath/compass/v03n02/3.html http://www.mathwire.com/strategies/is.html) http://www.abcya.com/comparing_number_values.htm Stack-n-Pack books contain several math games covering math concepts from Kindergarten through High School. Stack-n-Pack card games may be checked out from your school (contact your school’s Parent Liaison) or purchased online: Stack-n-Pack Mathematics Card Games for K-HS . Stack-n-Pack Grades 3 - 5 • Place Value Identification game