Properties of Addition & Subtraction
advertisement

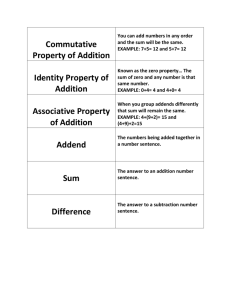
Grade Level: Third Grade Content Area: Math Quarter: First Unit: Properties of Addition/Subtraction Priority Standards: 3.2 The student will recognize and use the inverse relationships between addition/subtraction and multiplication/division to complete basic fact sentences. The student will use these relationships to solve problems. 3.20A Investigate the identity and the commutative properties for addition 3.20a Investigate the identity property for addition and determine that when the number zero is added to another number or another number is added to the number zero, that number remains unchanged. Examples of the identity property for addition are 0 + 2 = 2; 5 + 0 = 5. Vocabulary: Commutative property of addition Mathematical relationships Identity property of addition Equal sign Equivalent Nonequivalent Order Student Friendly Learning Targets: (I can…) 3.2 I can use the inverse relationship between addition/subtraction to complete basic fact sentences. This means I can use an addition/subtraction basic fact sentence to make a related basic fact sentence. 3.20A I can investigate the identity property for addition. This means that I can find facts about the identity property for addition. 3.20A I can investigate the commutative property for addition. This means that I can find facts about the commutative property for addition. Assessments: 3.2 3.20A Written Response 3.20a I can investigate the identity property for addition. This means that I can find facts about the identity property for addition and find out that when the number zero is added by another number that number won't change. 3.2 I can recognize the inverse relationship between addition/subtraction to complete basic fact sentences. This means I can turn around an addition/subtraction basic fact sentence to make a related basic fact sentence. 3.2.b I can write three related basic fact sentences when give one basic fact sentence for addition/subtraction. This means I can write three more basic fact sentences related to the one given. 3.20B I can identify examples of identity and commutative properites for addition. This means I can name examples of identity and commutative properites for addition. 3.20a Written Response 3.20.a I can determine what happens when the number zero is added to another number. This means I can find out what happens when the number zero is added to another number. 3.20.c I can recognize the commutative property for addition is an order property. This means I will know the commutative property for addition is an order property. 3.20.d I can recognize the commutative properties for addition and multiplication. This means I will know the commutative properties for addition and multiplication when I see them. 3.20.e I can write number sentences to represent equivalent mathematical relationships. This means I can write number sentences to serve as an example for equal mathematical relationships. 3.20.f I can identify properties for addition. This means I can recognize the properties for addition. 3.20f I can identify the commutative properties for addition. This means I can name the commutative properties for addition. Supporting Standards (Cluster Standards): 3.2 Recognize and use the inverse relationships between addition/subtraction and multiplication/division to complete basic fact sentences. use these relationships to solve problems. 3.2a Use the inverse relationships between addition/subtraction and multiplication/division to solve related basic fact sentences. For example, 5 + 3 = 8 and 8 – 3 = __; 4 3 = 12 and 12 ÷ 4 = __. 3.2b Write three related basic fact sentences when given one basic fact sentence for addition/subtraction and for multiplication/division. For example, given 3 2 = 6, solve the related facts __ 3 = 6, 6 ÷ 3 = __, and 6 ÷ __ = 3. 3.20B identify examples of the identity and commutative properties for addition. 3.20c Recognize that the commutative property for addition is an order property. Changing the order of the addends does not change the sum (5 + 4 = 9 and 4 + 5 = 9). 3.20e Write number sentences to represent equivalent mathematical relationships (e.g., 4 x 3 = 14 ­ 2). 3.20f Identify examples of the identity and commutative properties for addition. Resources: Manipulatives *Base 10 Blocks *Numberlines Dinah Zikes Foldable: *Vocabulary Book (Vocabulary Words) *Layer Book book (Addition properties) *One Fold (Headings: Equation­Inverse Operation) *Flip Chart (pg. 7 Notebook Foldables: Inverse Operations) Print Resources * VDOE Enhanced Scope and Sequence (ESS) 3.2 Inverse Relationships 3.20 Property Communte 3.20 My Identity is in My Pocket *VDOE ­ Math Word Wall Vocabulary *VDOE ­ Modules *If I know…...Then I know…….. EnVision Math SOL 3.2 3­1 pp. 66­67 8­1 pp. 184­185 SOL 3.20 2­1 pp. 32­33 5­2 pp. 110­113 5­9 pp. 130­131 Math Out of The Box: 3.1 SOL 3.2 Ordering and Arranging Module A Lessons 1­6 Lesson 8 Lessons 15­24 SOL 3.20 Ordering and Arranging Module A Lessons 25­28 Plotting and Growing Lessns 6­12 Corresponding Literature: ___________________________________________ Technology Resources: iReady Brain Pop Smart Exchange National Library of Virtual Manipulatives (nlvm.usu.edu/en) **Number Line Bounce ** Base 10 Blocks