AP Statistics - Orange County School of the Arts
advertisement

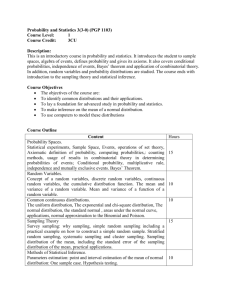
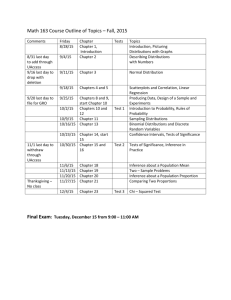
ORANGE COUNTY HIGH SCHOOL OF THE ARTS AP Statistics Course Outline There is no summer assignment for AP Statistics. Please read this information to prepare you for the expectations of the course. Course PURPOSE/Goals The purpose of this course is to introduce students to the major concepts and tools for collecting, analyzing, and drawing conclusions from data. Students are exposed to four broad conceptual themes: 1. Exploring Data: Describing patterns and departures from patterns (SIA CH.2 & 3) 2. Sampling and Experimentation: Planning and conducting a study (SIA Ch. 4) 3. Anticipating Patterns: Exploring random phenomena using probability & simulation (SIA Ch. 5, 6) 4. Statistical Inference: Estimating population parameters and testing hypotheses (SIA Ch. 7-11) It is the expectation of the instructor that you plan to take the A.P. test in the spring. COURSE Materials Primary Textbook (in class daily): Supplemental Textbooks (optional): Moore, David S., and George McCabe. Introduction to the Practice of Statistics. W.H. Freeman & Company; 5th ed. (February 2005). (IPS) Bluman, Allan G. Elementary Statistics: A Brief Version. McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math; 3 ed. (January 1, 2006) (ESBV) Gonick, Larry, and Woollcott Smith. A Cartoonist Guide to Statistics. Harper Resource (1993) (TOON) Graphing Calculator (in class daily): TI-83, TI-84, TI-85, or TI-86 (TI) Software: Access to Microsoft Excel (home as well as in the computer lab) (IMMRC) Course OUTLINE In the following course outline you will find the key topics, questions to be completed from the text, project assignments, supplementary information, and assessments that are organized by units of study. The ordering here is intended to define the scope of the course but not necessarily the sequence. The percentages in parentheses for each content area indicate the coverage for that content area of the exam. UNIT 1 – Exploring the Data: Describing patterns and departures from patterns (20%-30%) Exploratory analysis of data makes use of graphical and numerical techniques to study patterns and departures from patterns. Emphasis should be placed on interpreting information from graphical and numerical displays and summaries. Constructing and interpreting graphical displays of distributions or univariate data (dotplot, stemplot, histogram, cumulative frequency plot) Center and Spread Clusters and Gaps Outliers and other unusual features Shape Summarizing distributions of univariate data Measuring center: mean, median’ Measuring spread: range, interquartile range, standard deviation Measuring positions: quartiles, percentiles, standardized scores (z-scores) Using boxplots The effect of changing units on summary measures Comparing distributions of univariate date (dotplot, back-to-back stemplot, parallel boxplot) Comparing center and spread: within group, between group variation Comparing clusters and gaps Comparing outliers and other unusual features Comparing shapes Exploring bivariate data Analyzing in scatterplots Correlation and linearity Least-squares regression line Page 1 of 4 ORANGE COUNTY HIGH SCHOOL OF THE ARTS AP Statistics Course Outline Residual plots, outliers and influential points Transformations to achieve linearity: logarithmic and power transformations Exploring categorical data Frequency tables and bar charts Marginal and joint frequencies for two-way tables Conditional relative frequencies and accusations Comparing distributions using bar charts UNIT 2 – Sampling and Experimentation: Planning and conducting a study (10%-15%) Data must me collected according to a well-developed plan if valid information on a conjecture is to be obtained. This plan includes classifying the question and deciding upon a method of data collection and analysis Overview of methods of data collection Census Sample survey Experiment Observational study Planning and conducting surveys Characteristics of a well-designed and well-conducted survey Populations, samples, and random selection Sources of bias in sampling and surveys Sampling methods, including simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, and cluster sampling Planning and Conducting Experiments Characteristics of well-designed and well conducted experiments Treatments, control groups, experimental units, random assignments, and replication Sources of bias and confounding, including placebo effect and blinding Completely randomized design Randomized block design, including matched pairs Generalizability of results and types of conclusions that can be drawn from observational studies, experiments, and surveys Page 2 of 4 ORANGE COUNTY HIGH SCHOOL OF THE ARTS AP Statistics Course Outline UNIT 3 – Anticipating Patterns: Exploring random phenomena using probability and simulation (20%-30%) Probability is the tool used for anticipating what the distribution of data should look like under a given model. Probability Interpreting probability, including long-run relative frequency interpretation “Law of Large Numbers” concept Addition rule, multiplication rule, conditional probability, and independence Discrete random variables and their probability distributions (binomial & geometric) Simulation of random and probability distributions Mean (expected value) and standard deviation of a random variable, and linear transformation of a random variable Combining Independent Random Variables Notion of Independence vs. dependence Mean and standard deviation for sums and differences of independent random variables Normal Distribution Properties of the normal distribution Using tables of the normal distribution The normal distribution as a model for measurements Sampling Distributions Sampling distributions of a proportion Sampling distribution of a sample mean Central limit theorem Sampling distribution of a difference between two sample proportions Sampling distribution of a difference between two independent sample means Simulation of sampling distributions t-distribution chi-square distribution UNIT 4 – Statistical Inference: Estimating population parameters and testing hypotheses (30%-40%) Statistical inference guides the selection of appropriate models. Estimation (point estimators and confidence intervals) Estimating population parameters and margins of error Properties of point estimators, including unbiasedness and variability Logic of confidence intervals, meaning of confidence level and intervals, and properties of confidence intervals Large sample confidence interval for a proportion Large sample confidence interval for a difference between two proportions Confidence interval for a mean Confidence interval for a difference between two means (unpaired and paired) Confidence interval for the slope of a least-squares regression line Tests of significance Logic of significance testing, null and alternate hypotheses; p-values; one and two-sided tests; concepts of Type I and Type II errors; concept of power Large sample test for a proportion Large sample test for a difference between two proportions Test for a mean Test for a difference between two means (unpaired and paired) Chi-square test for goodness of fit, homogeneity of proportions, and independence (one and two-way tables) Test for the slope of a least-squares regression line Page 3 of 4 ORANGE COUNTY HIGH SCHOOL OF THE ARTS AP Statistics Course Outline Course – Curriculum Map SEPTEMBER Unit of Study/ Concept/Topic OCTOBER Unit of Study/ Concept/Topic NOVEMBER Unit of Study/ Concept/Topic DECEMBER Unit of Study/ Concept/Topic JANUARY Unit of Study/ Concept/Topic Chapter 2 – Data Distributions Chapter 4 – Experimentation Chapter 5 – Probability Continued Chapter 6 – Probability Distributions Chapter 7 – Sampling Distributions AP Standards: 3.0,4.0 AP Standards: 1.0, 2.0, 9.0 AP Standards: 7.0, 8.0, 11.0, 15.0, 16.0 AP Standards: 7.0, 8.0, 11.0, 15.0, 17.0 FEBRUARY Unit of Study/ Concept/Topic MARCH Unit of Study/ Concept/Topic APRIL Unit of Study/ Concept/Topic MAY Unit of Study/ Concept/Topic JUNE Unit of Study/ Concept/Topic Chapter 8 – Inference for proportions Chapter 9 – Inference for distributions Chapter 11 – Inference for Regresison Final Case Study Project – Upon completion of Video 26 UNIT 1 TEST Chapter 3 – Data Relationships Chapter 5 – Probability AP Standards: 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 10.0, 12.0,13.0, 14.0 STAR TESTING Chapter 10 – Chi2 Distributions UNIT 2 TEST UNIT 3 TEST AP Test AP Standards: 7.0, 8.0, 11.0, 15.0, 16.0, 17.0 AP Standards: 7.0, 8.0, 11.0, 12.0,13.0 AP Standards: 14.0, 15.0, 16.0, 17.0 Page 4 of 4 AP Standards: 14.0, 15.0, 16.0, 17.0, 19.0 FINAL Benchmark Assessment (Ch 1-9, 10, 12) AP Standards: 14.0, 15.0, 16.0, 17.0, 19.0