Factored Item Similarity Models - Department of Computer Science
advertisement

Recommendation with Implicit Feedbacks:
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
Weike Pan
College of Computer Science and Software Engineering
Shenzhen University
1502030001: Semantic Web (Spring 2015)
Focus on Intelligent Recommendation Technology
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
1 / 18
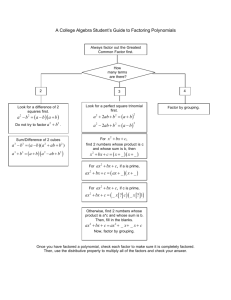
Outline
1
Introduction
2
Method
3
Experiments
4
Conclusion
5
References
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
2 / 18
Introduction
Recommendation with Implicit Feedbacks
We may represent users’ implicit feedbacks in a matrix form:
If we can estimate the missing values (denoted as “?”) in the
matrix or rank the items directly, we can make recommendations
for each user.
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
3 / 18
Introduction
Notations (1/2)
Table: Some notations.
n
m
u ∈ {1, 2, . . . , n}
i, i ′ ∈ {1, 2, . . . , m}
rui
P
A, |A| = ρ|P|
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
user number
item number
user ID
item ID
observed rating of user u on item i
the whole set of observed (user, item) pairs
a sampled set of unobserved (user, item) pairs
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
4 / 18
Introduction
Notations (2/2)
Table: Some notations.
bu ∈ R
bi ∈ R
d ∈R
Vi· , Wj· ∈ R1×d
V, W ∈ Rm×d
r̂ui
T
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
user bias
item bias
number of latent dimensions
item-specific latent feature vector
item-specific latent feature matrix
predicted rating of user u on item i
iteration number in the algorithm
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
5 / 18
Method
Factored Item Similarity Model (FISM)
FISM with different loss functions,
FISMrmse
FISMauc
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
6 / 18
Method
Prediction Rule
The predicted rating of user u on item i,
−i T
r̂ui = bu + bi + Ūu·
Vi·
(1)
where,
−i
Ūu·
=
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
1
|Iu \{i}|α
X
Wi ′ · , 0 ≤ α ≤ 1
i ′ ∈Iu \{i}
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
7 / 18
Method
Objective Function
The objective function of FISMrmse ,
X
min
Θ
fui
(2)
(u,i)∈P∪A
where Θ = {Vi· , Wi ′ · , bu , bi }, i, i ′ = 1, . . . , m, u = 1, . . . , n, and
fui =
1
αv
αw
(rui − r̂ui )2 +
||Vi· ||2F +
2
2
2
X
||Wi ′ · ||2F +
i ′ ∈Iu \{i}
βu 2 βv 2
b + bi
2 u
2
Notes:
P is the whole set of observed (user, item) pairs
A is a sampled set of unobserved (user, item) pairs
According to the loss function, we can see that FISMrmse is a
pointwise method
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
8 / 18
Method
Gradients
For each (u, i) ∈ P ∪ A, we have the gradients,
∇bu =
∇bi
=
∇Vi· =
∇Wi ′ · =
∂fui
= −eui + βu bu
∂bu
∂fui
= −eui + βv bi
∂bi
∂fui
−i
= −eui Ūu·
+ αv Vi·
∂Vi·
1
∂fui
= −eui
V + αw Wi ′ · , i ′ ∈ Iu \{i}
∂Wi ′ ·
|Iu \{i}|α i·
where eui = rui − r̂ui . Note that rui = 1 if (u, i) ∈ P, and rui = 0 if
(u, i) ∈ A.
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
9 / 18
Method
Update Rules
For each (u, i) ∈ P ∪ A, we have the update rules,
bu = bu − γ∇bu
bi
= bi − γ∇bi
Vi· = Vi· − γ∇Vi·
Wi ′ · = Wi ′ · − γ∇Wi ′ · , i ′ ∈ Iu \{i}
where eui = rui − r̂ui . Note that rui = 1 if (u, i) ∈ P, and rui = 0 if
(u, i) ∈ A.
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
10 / 18
Method
Algorithm
Initialize the model parameters Θ
for t = 1, . . . , T do
3:
Randomly pick up a set A with |A| = ρ|P|
4:
for each (u, i) ∈ P ∪ A in aP
random order do
−i
1
= |Iu \{i}|
5:
Calculate Ūu·
α
i ′ ∈Iu \{i} Wi ′ ·
1:
2:
6:
7:
8:
9:
10:
−i T
Vi·
Calculate r̂ui = bu + bi + Ūu·
Calculate eui = rui − r̂ui
Update the bu , bi , Vi· and Wi ′ · , i ′ ∈ Iu \{i}
end for
end for
Figure: The SGD algorithm for FISMrmse .
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
11 / 18
Experiments
Data Set
We use the files u1.base and u1.test of MovieLens100K1 as our
training data and test data, respectively.
user number: n = 943; item number: m = 1682.
u1.base (training data): 80000 rating records, and the density (or
sparsity) is 80000/943/1682 = 5.04%.
u1.test (test data): 20000 rating records.
Pre-processing (for simulation): we only keep the (user, item)
pairs with ratings 4 or 5 in u1.base and u1.test as preferred (user,
item) pairs, and remove all other records. Finally, we obtain
u1.base.OCCF and u1.test.OCCF.
1
http://grouplens.org/datasets/
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
12 / 18
Experiments
Evaluation Metrics
Pre@5: The precision of user u is defined as,
k
1X
δ(i(ℓ) ∈ Iute ),
Preu @k =
k
ℓ=1
where δ(x)
δ(x) = 0 otherwise. Then, we have
P= 1 if x is true and
te
Pre@k = u∈U te Preu @k/|U |.
Rec@5: The recall of user u is defined as,
1 X
δ(i(ℓ) ∈ Iute ),
|Iute | ℓ=1
k
Recu @k =
which means how many preferred items
P are recommended in the
top-k list. Then, we have Rec@k = u∈U te Recu @k/|U te |.
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
13 / 18
Experiments
Initialization of Model Parameters
We use the statistics of training data to initialize the model parameters,
bu =
m
X
=
n
X
yui /m − µ
i=1
bi
yui /n − µ
u=1
Vik
= (r − 0.5) × 0.01, k = 1, . . . , d
= (r − 0.5) × 0.01, k = 1, . . . , d
P
P
where r (0 ≤ r < 1) is a random variable, and µ = nu=1 m
i=1 yui /n/m.
Wi ′ k
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
14 / 18
Experiments
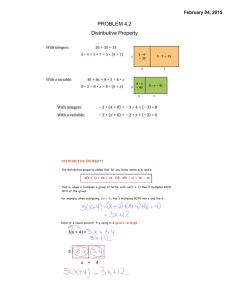
Parameter Configurations
We fix α = 0.5 and γ = 0.01, and search the best values of the
following parameters,
αv = αw = βu = βv ∈ {0.001, 0.01, 0.1}
T ∈ {100, 500, 1000}
Finally, we use α = 0.5, γ = 0.01, ρ = 3, d = 20,
αv = αw = βu = βv = 0.001 and T = 100, which performs best in our
experiments.
It takes about 75 seconds for training.
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
15 / 18
Experiments
Results
Table: Prediction performance of PopRank and FISMrmse on MovieLens100K
(u1.base.OCCF, u1.test.OCCF).
Pre@5
Rec@5
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
PopRank
0.2338
0.0571
FISMrmse
0.3846
0.1270
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
16 / 18
Conclusion
Conclusion
Learning factored (item, item) similarities is helpful.
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
17 / 18
Conclusion
Homework
Implement FISMrmse and conduct empirical studies on
u2.base.OCCF, u2.test.OCCF of MovieLens100K with similar
pre-processing
Read the KDD 2013 paper [Kabbur et al., 2013], and study the
algorithm of FISMauc
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
18 / 18
References
Kabbur, S., Ning, X., and Karypis, G. (2013).
Fism: Factored item similarity models for top-n recommender systems.
In Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD ’13,
pages 659–667, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
W.K. Pan (CSSE, SZU)
Factored Item Similarity Models (FISMrmse )
1502030001 (Spring 2015)
18 / 18