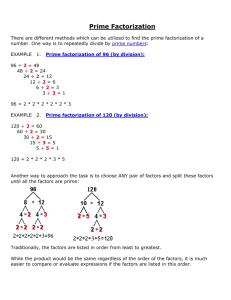
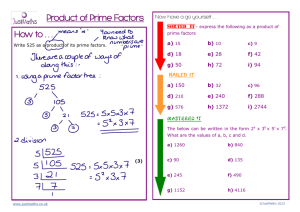
4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization
advertisement

4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization Learn to write prime factorizations of composite numbers. Course 1 4-2 Factors Insert Lesson TitleFactorization Here and Prime Vocabulary factor prime factorization Course 1 4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization Whole numbers that are multiplied to find a product are called factors of that product. A number is divisible by its factors. 2 3=6 Factors Course 1 Product 6 3=2 6 2=3 6 is divisible by 3 and 2. 4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization Helpful Hint When the pairs of factors begin to repeat, then you have found all of the factors of the number you are factoring. Course 1 2-5 Greatest Common Factor T-Chart/ Prime Factorization Method 36 12 1 2 3 Course 2 12 6 1 2 36 18 4 3 4 6 12 9 6 O O 54 1 2 3 6 O 54 27 18 9 4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization You can use factors to write a number in different ways. Factorization of 12 1 • 12 2•6 3•4 3•2•2 Notice that these factors are all prime. The prime factorization of a number is the number written as the product of its prime factors. Course 1 4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization Helpful Hint You can use exponents to write prime factorizations. Remember that an exponent tells you how many times the base is a factor. Course 1 4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization Additional Example 2A: Writing Prime Factorizations Write the prime factorization of each number. A. 24 Method 1: Use a factor tree. Choose any two factors of 24 to begin. Keep finding factors until each branch ends at a prime factor. 24 24 2 • 2 • 6 12 • 6 2 • 3 3 • 2 4 2 • 2 24 = 3 • 2 • 2 • 2 24 = 2 • 2 • 2 • 3 3 The prime factorization of 24 is 2 • 2 • 2 • 3, or 2 • 3 . Course 1 4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization Additional Example 2B: Writing Prime Factorizations Write the prime factorization of each number. B. 42 Method 1: Use a ladder diagram. Choose a prime factor of 42 to begin. Keep dividing by prime factors until the quotient is 1. 3 42 2 14 2 7 7 1 42 = 3 • 2 • 7 42 21 3 7 7 1 42 = 2 • 3 • 7 The prime factorization of 42 is 2 • 3 • 7. Course 1 4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization In Example 2, notice that the prime factors may be written in a different order, but they are still the same factors. Except for changes in the order, there is only one way to write the prime factorization of a number. Course 1 4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization Try This: Example 2A Write the prime factorization of each number. A. 28 Method 1: Use a factor tree. Choose any two factors of 28 to begin. Keep finding factors until each branch ends at a prime factor. 28 28 2 • 14 2 • 7 7 28 = 2 • 2 • 7 • 4 2 • 2 28 = 7 • 2 • 2 The prime factorization of 28 is 2 • 2 • 7, or 22 • 7 . Course 1 4-2 Factors and Prime Factorization Try This: Example 2B Write the prime factorization of each number. B. 36 Method 1: Use a ladder diagram. Choose a prime factor of 36 to begin. Keep dividing by prime factors until the quotient is 1. 3 36 3 12 2 3 12 3 6 2 36 4 2 3 1 36 = 3 • 2 • 2 • 3 2 2 1 36 = 3 • 3 • 2 • 2 The prime factorization of 36 is 3 • 2 • 2 • 3, or 32 • 23. Course 1 4-2 Factors Insert Lesson and Prime TitleFactorization Here Lesson Quiz List all the factors of each number. 1. 22 1, 2, 11, 22 2. 40 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, 40 3. 51 1, 3, 17, 51 Write the prime factorization of each number. 4. 32 25 5. 120 23 Course 1 3 5