Unit: Data Analysis
advertisement

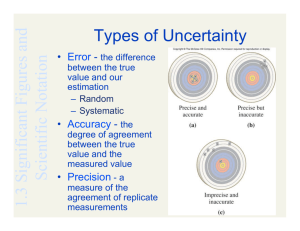
Chemistry Chapter 1& 2 Objectives Unit: Data Analysis ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Terminology Be able to define each of the following terms and to give examples of each where appropriate. mass dimensional analysis (factor-label method) weight conversion factor (unit equality) safety ratio Système Internationale d’Unités (SI) counted quantity metric unit prefixes measured quantity base unit measuring instrument derived unit uncertainty mass reliability length precision time accuracy volume percent error density significant figures (digits) temperature independent variable Celsius dependent variable Kelvin interpolate Fahrenheit extrapolate absolute zero slope scientific notation ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Important Equations/Mathematical Models. Know (memorize) each of the following equations and be able to use each of them to solve problems. Know what quantity is represented by each symbol/variable indicated. Be able to manipulate each equation for a specific variable. Use your knowledge of algebra to do this. Make sure that appropriate units are included for each number involved, in the supportive work and in each answer. d= M V % Error = Note: The %Error equation will be given to you. You will need to know how to use it. Experimental Value − Accepted Value ×100% Accepted Value --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Concepts/Skills. Be able to do each of the following: • • • • • • • • • • • • Know and demonstrate safe lab procedures. Discuss the benefits of the metric system. Describe the current standard for the meter, kilogram, and second. (MKS units) Give examples of derived units and their component base units. Know the meaning, numerical value, and symbol for each of the metric prefixes from giga (G) through nano (n). Use dimensional analysis (factor-label method) to solve conversion problems. Convert metric quantities from one unit to another using dimensional analysis. Do this for any prefix from giga (G) through nano (n). Solve problems involving the density concept. Describe how the Celsius and Kelvin temperature scales are related to the freezing and boiling points of water. Also describe how they are related to each other. Discuss what happens to a particle system that approaches absolute zero and why 0oC is not absolute. Distinguish between a counted quantity and a measured quantity. Concepts/Skills Continued • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Discuss the benefits of using a measuring instrument. Identify and use basic measuring instruments and tools used in chemistry. Discuss the benefits of using scientific notation in communicating quantities. Convert numbers in standard form to scientific notation and visa versa. Add/subtract and multiply/divide quantities in scientific notation. Manipulate numbers in standard form and scientific notation with your calculator. Identify factors that contribute to uncertainty in an investigation. Discuss how reliability of measurements is assessed by determination of precision and/or accuracy. Tell how the measuring instrument affects the number of significant figures/digits in a measured quantity. Describe which figures/digits are significant for measured quantities. Know the rules for recognizing significant figures in measured quantities. Determine the number of significant figures/digits in a given measured quantity. Describe what the number of significant figures/digits in a given measured quantity indicates about the precision of the measuring instrument and measuring process. Correctly round off answers to addition/subtraction problems and multiplication/division problems involving measured quantities. Distinguish between different types of graphs. Construct graphs with proper format. Interpret, analyze, and predict data using graphs. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Sample Problems. Be able to solve each of the following problems and other similar problems. Always show all of your work in organized fashion and include appropriate units throughout your work. Always show the equation (if there is one) in proper form before you substitute the given quantities. Clearly indicate your answer. If you need help with any of these problems, see your teacher for help. The answer to each problem shown below is in parentheses. 1. Convert 2.730 g to cg. (273.0 cg) 2. Convert 47500.0 dL to kL. (4.75000 kL) 3. Convert 87.5 g/cL to cg/mL. (875 cg/mL) 4. Determine the density of a solid that has a mass of 14.70 g and that displaces a volume of water of 20.1 mL in a graduated cylinder. (0.731 g/mL) 5. The density of a substance is 5.50 g/mL. A 78.0 g sample of this substance is obtained. Determine the volume of this sample. (14.2 mL) 6. (5.31 × 10-2 cm) × (2.46 × 105 cm) (1.31 × 104 cm2) 7. (9.33 × 104 mm) ÷ (3.0 × 102 mm) (3.1 × 105) 8. Write in scientific notation: 538,704 s (5.38704 × 105 s) 9. Write in scientific notation: 0.08025 g (8.025 × 10-2 g) 10. Determine the number of significant figures in each of the given measurements: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. 29.233 m (5) 0.00290 L (3) 42000 kg (2) 4.20 × 104 kg (3) 7.0060 oC (5) 93000.2 dL (6) 120.0 cm (4) 11. In a chemistry investigation the density of gold is experimentally determined to be 17.5 g/cm3. The accepted value for gold’s density is 19.3 g/cm3. Determine the percent error in this determination of density. (9.33%)