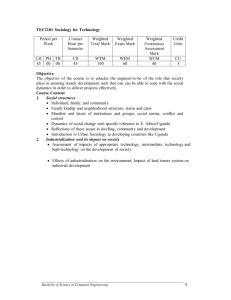
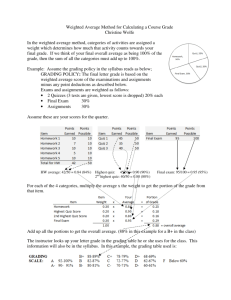
Weighted Mean
advertisement

Weighted Mean Audio Welcome to our video tutorial on the Weighted Mean. Video This video’s title, “The Weighted Mean,” is shown. Weighted Mean Page 1 of 8 Edward Volchok, PhD Weighted Mean Audio The Weighted Mean is similar to the Arithmetic Mean. But, unlike the Arithmetic Mean, which gives each random variable equal weight, the Weighted Mean is used in cases where the data have unequal weights. The basic formula for the Weight Mean is the sum of the product of the weights, or w, and the random variables, or X over the sum of the weights. The Weighted Mean is used to calculate the “average” when data are unequally weighted. A student’s Grade Point Average is calculated using a Weighted Mean as 2, 3, and 4 credits courses have different weights in the calculation. And, in business the Weighted Mean is used frequently whenever the Mean for unequally weighted data is needed. Video Video shows the formula for the Weighted Mean Weighted Mean Page 2 of 8 Edward Volchok, PhD Weighted Mean Audio Microsoft Excel does not have a built-in function for calculating the Weighted Mean. In this video, you will learn how easy it is to calculate the Weighted Mean using Excel. Video Video displays the words, “Microsoft Excel does not have a Weighted Mean function.” Weighted Mean Page 3 of 8 Edward Volchok, PhD Weighted Mean Audio In our scenario, we have four brands, each with a different retail price and different unit sales, and we want to calculate the Average Retail Price per Unit Sold. The Arithmetic Mean of the four retail prices, $47.99, is not the correct Average Retail Price per Unit Sold. This is true because each of the four brands has different weights based on their different units sales. Video The video shows an Excel worksheet in which the Arithmetic Mean being calculated is based on each of the four brands’ retail price. Weighted Mean Page 4 of 8 Edward Volchok, PhD Weighted Mean Audio To calculate the Average Retail Price per Unit Sold, we must take into account the different Unit Sales for each brand. To do this, we use the Weighted Mean formula. In the context of this problem, the formula for the Average Retail Price per Unit Sold is Total Dollar Sales (ΣwX) over Total Unit Sales (Σw). Dollars Sales are calculated by multiplying a brand’s Units Sales, or w, by its Retail Price, or X. Video Video displays the calculation of the Dollar Sales for each of the four brands. Weighted Mean Page 5 of 8 Edward Volchok, PhD Weighted Mean Audio Total Dollars Sales, $5,858.69, is the sum of each of the four brands’ Dollar Sales. And, Total Units Sales, 131, is the sum of each of the four brands’ Unit Sales. Video The video now displays Total Dollar Sales, $5,858.69, along with the Total Unit Sales, 131. Weighted Mean Page 6 of 8 Edward Volchok, PhD Weighted Mean Audio We now have all the information to complete the formula. Total Dollar Sales, $5,858.69, over Total Units Sales of 131, equals an Average Retail Price per Unit Sold of $44.72. That is the correct answer. The Arithmetic Mean of the four retail prices, $47.99, is the wrong answer because it fails to take into account each brand’s different weights or different Unit Sales. Video The video displays the calculation of the Weighted Mean or Average Price per Unit Sold. Weighted Mean Page 7 of 8 Edward Volchok, PhD Weighted Mean Audio This has been our video on the Weighted Mean. Video The video displays “The End.” * Weighted Mean * Page 8 of 8 * Edward Volchok, PhD