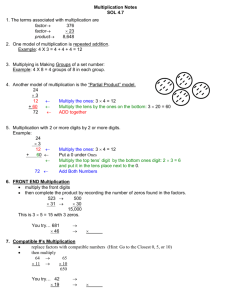
Partial-Products Multiplication
advertisement

Partial-Products Multiplication Partial-Product Multiplication is an alternative method for solving multi-digit multiplication problems. This is a strategy that is based on the distributive (grouping) property of multiplication. Information from the Algorithms Handbook of the Everyday Math Program Lining up the problem One of the key components of this strategy is making sure your partial products are lined up properly. Example from the Algorithms Handbook of the Everyday Math Program Created by: Chris Cheatham and Maria Farmer WB 2010 Solving the Problem First you start with the bottom Factor and multiply that factor with the largest digit from the top factor. In this example that is the hundreds place. Then you multiply the same bottom factor with the next biggest digit from the top factor. In this example that is the tens place. Next you multiply the same bottom factor with the number in the ones place. Example from the Algorithms Handbook of the Everyday Math Program Created by: Chris Cheatham and Maria Farmer WB 2010 Solving the problem After you have multiplied each factor you need to add up all of the partial products to get your final product. Example from the Algorithms Handbook of the Everyday Math Program Created by: Chris Cheatham and Maria Farmer WB 2010 Two by Two Multiplication You still start by multiplying the bottom factor to the top factor. Since the bottom factor has two digits you need to start with the highest digit from the bottom factor and multiply it to the highest digit from the top factor. In this example you will multiply the tens place from the bottom factor to the tens place of the top factor. Then you will multiply the tens place from the bottom factor to the ones place of the top factor. Example from the Algorithms Handbook of the Everyday Math Program Created by: Chris Cheatham and Maria Farmer WB 2010 Two by Two Multiplication Next you move to the next biggest digit in the bottom factor and multiply that by both digits from the top factor. The tens place goes first and then the ones. Example from the Algorithms Handbook of the Everyday Math Program Two by Two Multiplication After you have multiplied each factor you need to add up all of the partial products to get your final product. Example from the Algorithms Handbook of the Everyday Math Program Created by: Chris Cheatham and Maria Farmer WB 2010