3A USES AND ABUSES OF PERCENTAGES
advertisement

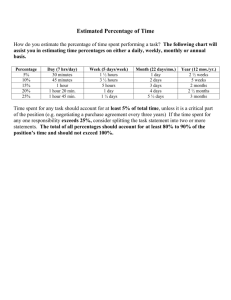
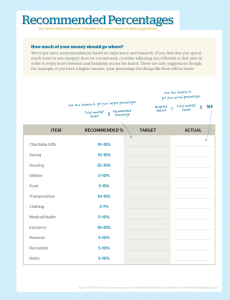
3A USES AND ABUSES OF PERCENTAGES Part 1: Three ways of using percentages i) Using percentages as fractions Example 64 % of 1069 people =64 % × 1069 people =684 people Example You have $ 8 and your friend has $ 4. Then your friend's money is 50 % of yours. Your money is 200 % of your friend's. ii) Using percentages to describe changes Example: The population increases from 100000 to 150000. There are two ways to describe the change: 1. Absolute change = 150000-100000=50000 50000 2. Relative change = 100000 × 100% = 50% Denition The absolute change describes the actual increase or decrease from a reference value/ old value to a new value. Absolute change = new value - reference value The relative change descrives the size of the change compared to the reference value. absolute change Relavite change = . reference value Example You now have 2 TV and you used to have 1 more. What is the absolute and relative changes of the number of TV? iii) Using percentages for comparisons Example: John scores 60 pts in a game and Mary scores 50 pts. Two ways to compare Mary's score to John's score. (Absolute) Mary scores 10 pts more than John. (Relative) Mary scores 20% more than John. Denition Compare A to B (A is the compared value and B is the reference value) 1 2 3A USES AND ABSUSES OF PERCENTAGES absolute dierence = compared value -reference value . Relative dierence = absolute dierence × 100%. reference value Example Compare Mary's score to John's. Caution: Be aware of the change of the reference value. e.g. A is 20 % more than B. Then B is not 20 % less than A. (See the above examples) 3A USES AND ABSUSES OF PERCENTAGES 3 Part 2: Of versus more than Example Consider the population in City A (200 people) and the population in City B (600 people). 1. Using of: The popolution in A is 33.3 % of that in B. The populaton in B is 600 % of that in A. 2. Using more than: A has 66.7 % more population than B. B has 200 % less popluation than B. We have the following formulae: If the compared value is P % more than the reference value, it is (100 + P )% of the reference value. If the compared value is P % less than the reference value, it is (100 − P )% of the reference value. Part 3: Solving percentage problems Basic strategy is to identify the compared value and reference value in the question. Example If the retail price is 25 % more than the wholesale price and the wholesale price is $ 10, what is the retail price. Example A shirt is 25 % o. If you nally pay $ 12.5 (neglecting tax), what is the labelled price?