Unit 10 - Hillsborough County Schools
advertisement

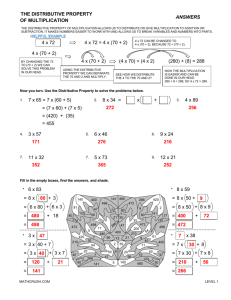
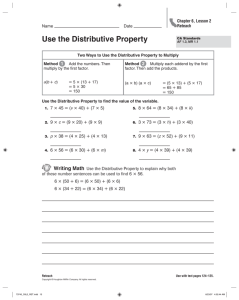
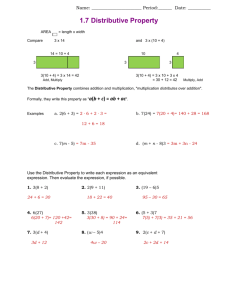
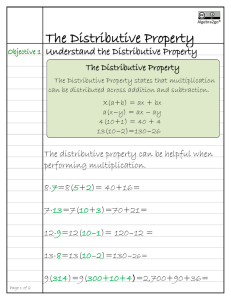
Hillsborough County Public Schools Elementary Mathematics Parent Connection Grade 4 – Unit 10: Strategies and Properties of Multi-Digit Multiplication In this unit your child will work to build an understanding of strategies based on place-value and the properties of multiplication to multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply 2 two-digit whole numbers. Students will illustrate and explain their calculations using equations, arrays and the area model. Modeling and applying the distributive property to multiply multi-digit whole numbers: o The distributive property of multiplication allows students to break apart factors into addends to create simpler multiplication problems. Strategies rooted in the distributive property are referred to as “break apart” and “partial products”. o In 3rd grade, your child built understanding of the distributive property and applied it to build basic fact fluency. For example, to find the product of 9 and 7: 9x7 9x5 The 7 could be broken apart into the addends of 2 and 5. Each addend is then multiplied by 9 to find the partial products. In this case, the 9x5=45 and 9x2=18. The sum of these partial products, 45+18, results in the final product of 56. This application of the distributive property can be recorded using the equation 9x7=(9x5)+(9x2). 9x2 th o In 4 grade, students will use explore and apply their understanding of the distributive property to multiply multidigit numbers. o Each strategy below shows an application of the distributive property for finding the product of 35 x 12. In the examples, the factors are broken apart by place value into their expanded form; 35 is broken apart into 30 + 5 and 12 is broken apart into 10 + 2. Area Model (“the box method”) Written Method for Partial Products Distributive Property (35 x 12) = (30x10)+(30x2)+(5x10)+(5x2)= When representing the distributive property with larger numbers, it is more efficient to use an area model than to draw out an array. 300 + 60 + 50 + 10= 420 o As shown in the examples above, the distributive property allows students to take large problems and break them apart into easier problems where they can apply their knowledge of basic facts and multiplying by multiples of ten. o Your child may begin to make connections to the traditional algorithm (the way we learned to multiply multidigit numbers) towards the end of this unit; however, fluency with this algorithm is not an expectation until 5th grade. Check out the “Parent Quick Smarts” video by scanning the QR code or clicking on the link below! http://youtu.be/yfdsj1yztNk?list=UUB5Abf61qsuS1aN8_6uZkng Other Helpful Links: Tutorials and Videos on the Area Model and Partial Products: o https://grade4commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcpss.org/fil e/view/4.NBT.5_PartialProductsTutorial.ppt/440849702/ 4.NBT.5_PartialProductsTutorial.ppt o https://m.youtube.com/watch?v=2xmsEtyOB10 Online and Printable Games to Practice Strategies: o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/multiplication-race-1x3digit.pdf o http://downloads.bbc.co.uk/skillswise/maths/ma12pape /game/ma12pape-game-writtenmultiplication/multiplication.swf Sample tasks your child should be able to work through by the end of the unit: Look at Cici’s work for solving 3 x 9,423. The bell on a clock tower rings every 15 minutes. If the bell has rung 24 times, how many minutes have passed? A. B. C. D. 220 minutes 342 minutes 360 minutes 380 minutes Explain what Cici did wrong. Angel thinks A is correct. How did she get that answer? What is the correct answer for 3 x 9,423? Purposeful Practice you and your child may work on at home together: Together with your child, think of things that can be counted in one minute, such as the number of sit-ups or jumping jacks. Have one person do the activity and count the number of reps while the other person times the activity for one minute. Have your child use the number of times the activity was completed in one minute to figure out the number of times that activity could be completed in 15 minutes, or an hour or a day. Have your child use an area model or partial products to multiply and find the answer. Together with your child, find out the number of words your child reads from a book in 3 minutes. Have your child use this number to find out the number of words they would read in 30 minutes. Then, challenge your child to figure out the number of words they would read if they read for 30 minutes each day for an entire week. Have your child justify their thinking with an area model, numbers and words. (This can be adjusted to the number of pages instead of words, or the time can be changed to best support your child.)