1 Order, Order! Key words: decimal number, decimal fraction, less
advertisement
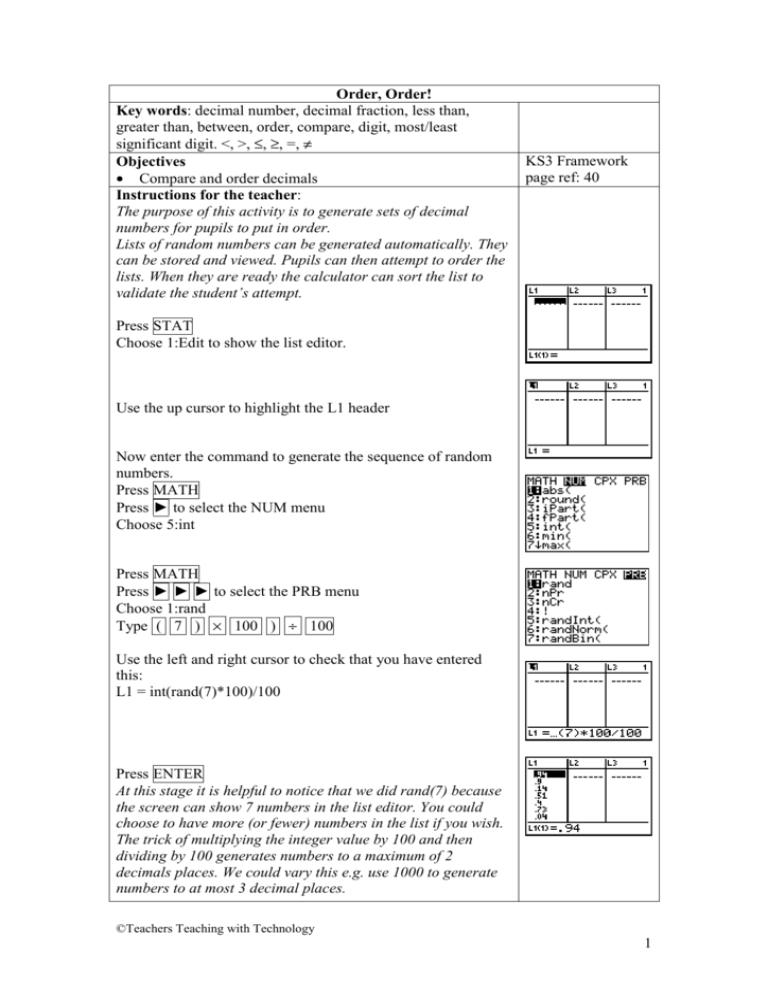
Order, Order! Key words: decimal number, decimal fraction, less than, greater than, between, order, compare, digit, most/least significant digit. <, >, ≤, ≥, =, ≠ Objectives • Compare and order decimals Instructions for the teacher: The purpose of this activity is to generate sets of decimal numbers for pupils to put in order. Lists of random numbers can be generated automatically. They can be stored and viewed. Pupils can then attempt to order the lists. When they are ready the calculator can sort the list to validate the student’s attempt. KS3 Framework page ref: 40 Press STAT Choose 1:Edit to show the list editor. Use the up cursor to highlight the L1 header Now enter the command to generate the sequence of random numbers. Press MATH Press ► to select the NUM menu Choose 5:int Press MATH Press ► ► ► to select the PRB menu Choose 1:rand Type ( 7 ) × 100 ) ÷ 100 Use the left and right cursor to check that you have entered this: L1 = int(rand(7)*100)/100 Press ENTER At this stage it is helpful to notice that we did rand(7) because the screen can show 7 numbers in the list editor. You could choose to have more (or fewer) numbers in the list if you wish. The trick of multiplying the integer value by 100 and then dividing by 100 generates numbers to a maximum of 2 decimals places. We could vary this e.g. use 1000 to generate numbers to at most 3 decimal places. ©Teachers Teaching with Technology 1 Pupils can now work on their list. When they are ready the calculator can order the list for you. Press 2nd STAT to show the LIST menu Press ► to select the OPS menu Choose 1:SortA meaning sort in ascending order Press 2nd 1 to sort list L1 Press ENTER Press STAT Choose 1:Edit to display the sorted list. Once you feel confident with the procedure, it is possible to vary the sequence in lots of different ways. Notably you can change the range of the sequence by using a scaling factor: e.g. L1 = int(rand(7)*500)/100 This generates a sequence between 0 and 5 to at most 2 decimal places. e.g. L1 = int((1+rand(7))*500)/100 This generates a sequence between 1 and 6 to at most 2 decimal places. The random number generator needs a seed to start the sequence it generates. To make sure that different sequences are generated you can change the seed. To do this, enter any number into rand. (For example: change the seed to 0.5) Press 2nd MODE (for QUIT) to get the main screen Press 0.5 Press STO→ Press MATH Press ► ► ► to select the PRB menu Choose 1 (rand) Press ENTER Answers to student activity sheet. 1. 0.04, 0.14, 0.4, 0.51, 0.73, 0.8, 0.94 2. 0.02, 0.2, 0.3, 0.61, 0.83, 0.97, 0.98 3. 0.42, 0.99, 1.56, 3.16, 3.48, 4.92, 4.98 ©Teachers Teaching with Technology 2 Order, order! First: Reset your TI 83-Plus • Press 2nd + to get MEM • Choose 7 (Reset…) • Choose 1 (All Ram…) • Choose 2 (Reset) This activity will give you a list of decimals. Your job is to put them in order. You can use your calculator to check if you have got it right. The first three questions will help you practice without the calculator. 1. Look at the list of decimals in the list L1. Write them in order of size, smallest first. 2. Now write this list in order of size: 3. Now write this list in order of size: ©Teachers Teaching with Technology 3 4. Now you can make lists of your own. Press STAT Choose 1:Edit to show the list editor Press ▲ Use the up cursor to highlight the L1 Press MATH Press ► to select the NUM menu Choose 5:int Press MATH Press ► ► ► to select the PRB menu Choose 1:rand Type ( 7 ) × 100 ) ÷ 100 Press ENTER Write down the list in order of size, smallest first. 5. Now sort the list on the calculator Press 2nd STAT to show the LIST menu Press ► to select the OPS menu Choose 1:SortA Press 2nd 1 to sort list L1 Press ENTER Press STAT Choose 1:Edit to display the sorted list Check that your answers are the same. 6. Now repeat steps 4 and 5 at least 4 times. You will keep getting different lists because the calculator uses a random number generator to make the lists. Challenge 7. Repeat steps 4 and 5 again, but change this line: Type ( 7 ) × 100 ) ÷ 100 , to: (a) (b) (c) (d) Type Type Type Type ( ( ( ( 7 7 7 7 ) ) ) ) × × × × 300 500 1000 2000 ) ÷ 100 ) ÷ 100 ) ÷ 1000 ) ÷ 1000 ©Teachers Teaching with Technology 4