Lesson 1.2 Writing Rational Numbers as Decimals
advertisement

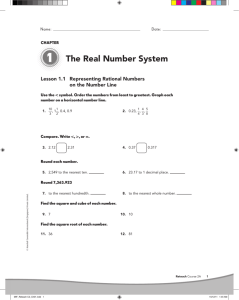
Name: Date: Lesson 1.2 Writing Rational Numbers as Decimals Use long division to write rational numbers as terminating decimals. Example 5 8 0.625 8) 5.000 48 20 16 40 40 0 So, b) 2 Add zeros after the decimal point. The remainder is 0. You could also write 1 2 as the mixed 4 9 and then number 4 5 5 0.625. 8 1 4 0.25 4 ) 1.00 8 20 20 0 1 So, 2 5 2.25. 4 1. 3 25 Divide 5 by 8. ) 25 3.00 divide: 9 4 4. Divide 1 by 4. Add zeros after the decimal point. The remainder is 0. 2. 17 16 ) 16 17.000 © Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. a) 8 Chapter 1 Lesson 1.2 MIF_Reteach C2_Ch01.indd 8 15/12/11 1:46 AM Name: Date: Using long division, write each rational number as a terminating decimal. 3. 2 1 4. 8 5. 3 16 6. 9 20 18 8 Use long division to write rational numbers as repeating decimals. Example 7 9 Stop dividing when you see the digits repeat themselves. 0.7 7 7 9 7.000 63 70 63 70 63 7 7 So, 5 0.777... 9 © Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. ) 7. 6 11 11 6.0000 ) 8. 17 15 15 17.000 ) Reteach Course 2A 9 MIF_Reteach C2_Ch01.indd 9 15/12/11 1:46 AM Name: Date: Using long division, write each rational number as a repeating decimal. Use bar notation to indicate the repeating digits. Example 5 11 0.4545 11) 5.0000 44 60 55 50 44 60 55 5 5 So, 5 0.4545... 5 0.45 11 9. 2 9 The digits 5 and 4 form a repetitive group. 10. 30 22 Using long division, write each rational number as a repeating decimal with 3 decimal places. Identify the pattern of repeating digits using bar notation. 11. 13 6 12. 34 33 © Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. 10 Chapter 1 Lesson 1.2 MIF_Reteach C2_Ch01.indd 10 15/12/11 1:46 AM Name: Date: Using a calculator, write each rational number as a repeating decimal. Use bar notation to indicate the repeating digits. 13. 18 14. 5 15. 17 16. 11 18 36 29 27 Compare the positive rational numbers using the symbols or . Use a number line to help you. Example 9 and 10 8 9 © Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. 9 5 1.125 8 Write each rational number as a decimal. 10 5 1.111... 5 1.1 9 Compare the decimals, 1.125 and 1.1. 10 9 9 8 1.110 1.115 1.120 1.125 1.130 1.1 1.125 lies to the right of 1.1. So, 1.125 9 8 1.1. 10 9 Reteach Course 2A 11 MIF_Reteach C2_Ch01.indd 11 15/12/11 1:46 AM Name: Date: Complete. 25 17. 22 and 8 7 Write each rational number as a decimal. 22 5 7 25 5 8 Compare the decimals, Complete the number line and compare the numbers. and lies to the right of So, . . . Compare the positive rational numbers using the symbols or . Use a number line to help you. 18. 3 and 5 19. 10 and 9 9 20. 13 and 8 21. 17 and 1 11 6 8 11 8 10 9 © Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. 4 12 Chapter 1 Lesson 1.2 MIF_Reteach C2_Ch01.indd 12 15/12/11 1:46 AM Name: Date: Compare the negative rational numbers using the symbols or . Use a number line to help you. Example 1 and 1 4 5 Method 1 Write each rational number as a decimal. 1 2 5 20.25 4 1 2 5 20.2 5 |20.25 |5 0.25 |20.2 | 5 0.2 4 5 1 1 0.3 © Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. 0.2 0.25 Compare using a number line. Use the absolute value of 0.25 and 0.2 to help you graph the decimals on a number line. 0.25 units 0.2 units 0.1 0 From the number line, you see that 20.25 lies farther to the left of 0 than 20.2. So, 20.2 20.25 ? 1 1 2 5 4 2 Method 2 Write an inequality using the absolute value of the two numbers. |20.25 | |20.2 | The two numbers are negative, so the number with the greater absolute value is farther to the left of 0. It is the lesser number. 20.2 20.25. 2 You can compare using place value. 1 1 2 5 4 Reteach Course 2A 13 MIF_Reteach C2_Ch01.indd 13 15/12/11 5:35 PM Name: Date: Complete. 22. 22 7 and 22 8 9 8 Method 1 Write each rational number as a decimal. Then find the absolute value of each decimal to help you graph the decimals on a number line. 22 7 5 8 units units | |5 8 22 5 9 | From the number line, you see that of 0 than 0 5 |5 . Method 2 Write an inequality using the absolute values of the two numbers. | || | The number with the greater absolute value is left of 0. Hence it is the So, and it is farther to the number. Compare the negative rational numbers using the symbols or . Use a number line to help you. 23. 2 3 4 and 2 4 5 24. 2 1 22 and 23 10 7 © Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. So, lies farther to the left 14 Chapter 1 Lesson 1.2 MIF_Reteach C2_Ch01.indd 14 15/12/11 1:46 AM Lesson 1.2 9.0.2 10.1.36 0.12 1. 25 3.00 25 11. 2.166 12.1.030 ) 13. 1.63 14.0.27 15. 0.472 16.1.074 50 50 17. 0 2. 3 5 0.12 25 1.0625 16 17.0000 ) 22 7 25 5 3.142857... Compare the decimals, 3.142857… and 3.125. 8 5 3.125 25 8 16 22 7 100 96 40 32 80 80 3.120 17 5 1.0625 16 3.140 3.150 3.142857... 3.142857… lies to the right of 3.125. So, 3.142857… 3.125 0 3.130 22 18. 7 25 8 5 6 3 4 3.2.1254.0.45 5.0.18756.2.25 0.5454 11 6.0000 55 ) 0.7 19. 50 44 60 55 50 44 6 8. 6 11 ) 4 5 6 9 10 10 11 10 11 0.910 9 10 20. 1.10 13 11 1.15 8 21. 5 17 15 1.20 9 1 1.870 50 45 13 11 9 8 20 15 50 45 0.9 0.900 5 0.5454... 1.133 15 17.000 15 3 0.8 1 1.880 7 8 8 9 1 1 7 8 8 9 1.890 © Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. 7. 5 1.133... 156 Answers MIF_Reteach C2_Ch01-05_Ans.indd 156 15/12/11 5:17 AM 22. Method 1 7. 5; 6 7 22 5 22.875 8 5.7 32 22.875 5 2.875 22 5 2 2.888... 5 2 2.8 8 9 22.8 5 2.8 2 8 522.828427125... 2 8 lies between the tenths 22.8 and 22.9. The value of 2 8 with two decimal places is 22.83. Which tenth is 2 8 closer to? 22.8. 7 2 8 8 2 9 2.8 units 2.875 units 3 2 0 1 2.8 2.875 2.9 From the number line, you see that 22.8 lies farther to the left of 0 than 22.875. 9. 22; 23 So, 22.875 22.8 7 8 8 9 22 22 So, 22.875 22.8 7 8 8 9 4 22 1 4 5 7 10 9 , 2 , 22.31, 11 7 8 , 3.001 Find an approximate value of 14 by using a The value of 14 with two decimal places is 3.74. Which tenth is 14 closer to? 3.7 calculator: 14 5 3.741657387... 3.7 4.7 7.0 6.9 48 7.2 7.3 53 10.8 117 3.8 14 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Use a calculator to represent each number in decimal form with 3 decimal places. 0.831 0.832, 2 8 22.828, 1 p 1.571, 0.143, 2 7 22.646 Ordering the numbers from least to greatest using the symbol , 1 p 2 8 2 7 0.831 14 lies between the tenths 3.7 and 3.8. 4. 2; 3 5.8 34 Lesson 1.4 14 between? 2.4 6. 4; 5 5.9 14. 210.817 3. Which two whole numbers is 3 and 4 2.8 5. 2; 3 4.5 21 10.9 1 2. 2 19 , 2 23 , 13, 4.6 Lesson 1.3 2.6 7 13.7.280 3 4 , 5, 12. 27; 28 23. 2 2 24. 2 23 1. 2.7 11. 25; 26 The number with the greater absolute value is 22.8 and it is farther to the left of 0. Hence it is the lesser number. 22 22 2.8 8 10. 24; 25 Method 2 22.875 22.8 © Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited. 5.6 8. Which two integers is 2 8 between? 22 and 23 Find an approximate value of 2 8 by using a calculator: 7 2.9 8 2.5 6 23 7 2 8 3 2 1 7 7 2 1 0 0.831 1 π 2 2 4.8 Reteach Course 2A 157 MIF_Reteach C2_Ch01-05_Ans.indd 157 15/12/11 5:18 AM