APPENDIX 3
advertisement

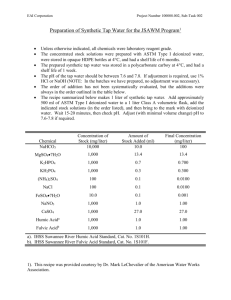
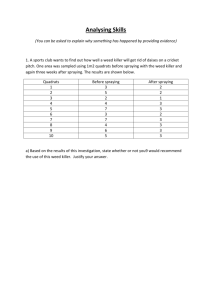
APPENDIX 3 MEDIA AND STAINING SOLUTIONS Yeast Mannitol Broth (YMB) Constituents: Mannitol 10.0 g* K2HPO4 0.5 g MgSO4.7H2O 0.2 g NaCl 0.1 g Yeast Extract 0.5 g Distilled Water 1.0 liter *This amount has been used traditionally, however more recent findings (H. Keyser, unpublished) show that 1 g l-1 is sufficient for most rhizobia. Preparations: - Add mannitol and salts to 1 l distilled water - Dissolve under continuous stirring - Adjust pH to 6.8 with 0.1 N NaOH - Autoclave at 121C for 15 min. Yeast Mannitol Agar (YMA) Constituents: Yeast Mannitol Broth Agar 1 liter 15 g Preparation: - Prepare YMB - Add agar, shake to suspend evenly, autoclave. - After autoclaving, shake flask to ensure even mixing of melted agar with medium. Glucose Peptone Agar Ingredients per liter: Glucose 5 g Peptone 10 g Agar 15 g Preparation: - Dissolve glucose and peptone in 1 liter distilled water - Add 10 ml BCP stock solution* to achieve a BCP concentration of 100μg ml l-1 (Prepare BCP stock solution by dissolving 1 g BCP in 100 ml ethanol) - Add agar and suspend evenly - Autoclave at 121C for 15 minutes Fermentor Broth (Burton, 1967) Constituents per liter: Mannitol 2.0 g Sucrose 10.0 g Tripotassium phosphate (K3PO4) 0.2 g Monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4) 0.4 g Magnesium sulphate (MgSO4.7H2O) 0.2 g Sodium chloride (NaCl) 0.06 g Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) 0.2 Calcium sulphate (CaSO4.H2O) 0.04 g Yeast Extract 0.5 Ammonium phosphate [(NH4)2HPO4] Water g g 0.1 1000 g ml Micronutrient – Stock Solution (Burton) Constituents: Boric Acid (H3BO3) 2.78 g Manganese sulphate (MnSO4.7H2O) 1.54 g Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4.7H2O) 0.21 g Sodium molybdate (Na2MoO4) 4.36 g Ferric chloride (FeCl3.6H2O) 5.00 g Cobalt sulphate (CoSO4.6H2O) 0.004 g Lactic acid (88%) 580 ml Distilled water 420 ml *Addition of 1.0 ml per liter of medium gives: boron 0.5 μg; manganese 0.5 μg; zinc 0.05 μg; molybdenum 1.0 μg; iron 100 μg and cobalt 0.0005 μg per liter (or parts per million). - Dissolve mannitol, sucrose, yeast extract and salts in 1 liter distilled water - Add 1 ml of micronutrient stock solution - Autoclave at 121C for 15 min. Bergersen’s defined medium for preparation of Rhizobium for antiserum production Constituents: K2HPO4 1.0 g KH2PO4 1.0 g MgSO4·7H2O 0.25 g CaCl2·6H2O 0.1 g FeCl3·6H2O 0.01 g Sodium glutamate 1.10 g Mannitol 10.00 g Agar 15.00 g Water 1 liter Dispense known volumes into bottles, autoclave and add 1 ml of Biotin-thiamine solution per liter. a. Dissolve 0.1 g thiamine and 0.025 g biotin in 1 liter distilled water. b. Dispense 2 ml quantities via sterile Seitz or Millipore filter into small bottles (dispense 50 and discard remainder of solution). c. Store in freezer and dispense aseptically into autoclaved medium at 1 ml/liter. DYES INCORPORATED IN MEDIA Bromthymol Blue (BTB) Stock solution: 0.5 g/100 ml ethanol Add 5 ml stock/liter YMA Final concentration of BTB: 25 ppm. Congo Red (CR) Stock solution: 0.25 g/100 ml Add 10 ml stock/liter YMA Final concentration of CR: 25 ppm. Bromcresol Purple (BCP) Stock solution: 1 g/100 ml ethanol Add 10 ml stock per liter peptone glucose agar. Final concentration: 100 ppm. Brilliant Green (BG) Stock solution: 125 mg/100 ml ethanol Add 1 ml stock to 1 liter of YMA before autoclaving Final concentration of BG: 1.25 ppm. YMA with antibiotics Streptomycin (str) Stock solution: 400 mg str/100 ml water (4 mg str/ml) Add 5 ml str stock/500 ml YMA to make plates containing 40 g str/ml. 10 ml str stock/500 ml YMA for plates containing 80 µg str/ml. Spectinomycin (spc) Stock solution: 1.25 g spc/50 ml water (250 mg spc/ml) Add 5 ml spc stock to 500 ml YMA for plates with 250 µg spc/ml. Add 10 ml spc stock to 500 ml YMA for plates with 500 mg spc/ml. Autoclave YMA together with magnetic stirring bar in an Erlenmeyer flask. Add filter sterilized antibiotics after the agar has cooled below 80oC. Mix well and pour after bubbles resulting from mixing have dispersed. Fahraeus C- and N-free Madium* CaCl2 0.1 g MgSO4·7H2O 0.12 g KH2PO4 0.1 g Na2HPO4·2H2O 0.15 g Ferric citrate 0.005 g *Mn, Cu, Zn, B, Mo traces Distilled water 1000 ml PH after autoclaving is 6.5 Sterilize at 121oC for 20 minutes. Seedling Agar (Jensen, 1942)* CaHPO4 1.0 g K2HPO4 0.2 g MgSO2·7H2O 0.2 g NaCl 0.2 g FeCl3 0.1 g Water 1.0 liter Agar Microelementsa a 15.0 g 1.0 ml (Gibson 1963)* From stock containing: 0.5% B; 0.05% Mn; 0.005% Zn; 0.005% Mo; and 0.002% Cu. *Taken from Vincent 1970 Seedling Agar Slants Autoclave seedling agar at 121oC for 15 minutes and dispense equal volumes into tubes (tube size depends on plant species). An appropriate amount of molten agar is dispensed so that after solidifying in inclined tubes, a 5-10 cm long agar face is presented for seedling growth. SOLUTIONS FOR GRAM STAIN (Vincent, 1970) Solution I: Crystal violet solution Crystal violet Ammonium oxalate 10 g 4 g Ethanol 100 ml Water (distilled) 400 ml Solution II: Iodine solution Iodine 1 g Potassium iodide 2 g Ethanol 25 ml Water (distilled) Solution III: 95% Ethanol 100 ml Solution IV: Counterstain 2.5% Safranin in ethanol Water (distilled) 10 ml 100 ml Carbol Fuchsin Stain Basic fuchsin 1 g Ethanol 10 ml 5% phenol solution 100 ml The fuchsin stain should be diluted 5-10 times with distilled water before use. Preparation of Yeast Water Fresh starch-free cakes of yeast are preferred in making yeastwater. Suspend 100 g of yeast in 1,000 ml of water and boil slowly or steam for 3 to 4 hours, replacing the water lost regularly. Allow the cooled suspension to stand until yeast cells have settled (usually 10 to 12 hours) to the bottom. Siphon off the clear, straw-colored liquid; adjust the liquid to pH 6.6 to 6.8 with sodium hydroxide; bottle and autoclave for 30 to 40 minutes at 121C. Following sterilization, the yeast water may be stored at room temperature. Dried yeast may also be used in making yeast-water. One kg of dry yeast is equivalent to about 2.5 kg of wet yeast. g of dry yeast in one liter of water. Suspend 40 Boil, decant, bottle, and sterilize in the same way as described for fresh yeast. One hundred ml of yeast-water should contain about 75 mg of nitrogen. Yeast extract powders prepared by spray-drying aqueous autolyzed yeast preparations are available in many countries. When these are available, about 0.5 g per liter of the dried preparation is used to replace yeast-water. Dry preparations are convenient and usually satisfactory. The media containing yeast may foam excessively when aerated vigorously in fermentor vessels. Foaming can be controlled by adding a small amount of sterile white mineral oil or silicone emulsion. Preparation of Soybean Water Grind 100 g soybean seeds to a course flour and place in 1000 ml of water. regularly. Boil slowly for 2 hours replacing the lost water Allow to cool and centrifuge at 5000 rpm. supernatant, autoclave, and store. ml per liter. Remove the For rhizobia media, use 100 Nitrogen sources can also be prepared from other grain legume seeds in the same way. Table A.1. N-free Nutrient Solution (Broughton and Dillworth, 1970). Stock Solutions Element M Form MW g/l M 1 Ca 1000 CaCl2•2H2O 147.03 294.1 2.0 2 P 500 KH2PO4 136.09 136.1 1.0 3 Fe 10 Fe-citrate 355.04 6.7 0.02 Mg 250 MgSo4•7H2O 246.5 123.3 0.5 K 250 K2SO4 174.06 87.0 0.5 Mn 1 MnSO4•H2O 169.02 0.338 0.002 B 2 H3BO3 61.84 0.247 0.004 Zn .5 ZnSO4•7H2O 287.56 0.288 0.001 Cu .2 CuSO4•5H2O 249.69 0.100 0.0004 Co .1 CoSO4•7H2O 281.12 0.056 0.0002 Mo .1 Na2MoO2•2H2O 241.98 0.048 0.0002 4 For each 10 liters of full strength culture solution, take 5.0 ml each of solutions 1 to 4, then add to 5.0 liters of water, then dilute to 10 liters. pH to 6.6-6.8. Use 1 N NaOH to adjust the For plus N control treatments, KNO3 (0.05%) is added giving an N concentration of 70 ppm.