QUESTION 1. Which is an example of a physical change A. boiling B
advertisement

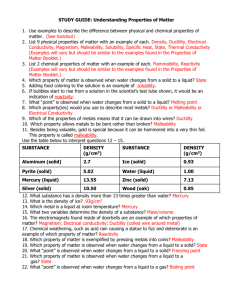
Monday, October 20 QUESTION VOCABULARY 1. Which is an example of a physical change A. boiling B. burning C. rotting D. rusting density * boiling point * state of matter * melting point * shape freezing point * solubility specific heat magnetism electrical conductivity thermal conductivity malleability ductility reactivity flammability combustion oxidation electrolysis 2. Which of the following best describes why ice floats in a glass of water? A. the charged ends of water molecules attract polar molecules B. ice is less dense than liquid water C. ice is more dense than liquid water D. ice melts at 0˚ C already have Words squared should be defined on property sheet NOTES Return papers to be put in 3 ring notebook or portfolio Physical change – a change that affects one or more physical properties but does not form a new substance. Check grade sheet for first 9 week grade. Chemical change – when one or more substances change into a new one with new properties. HW : comparing cubes/ life cycle of an ice cube. solubility – ability of a substance to dissolve in another substance specific heat – amount of energy needed to change the temperatre of 1Kg by 1 degree Celsius magnetism - the property of some materials to attract iron or something that has iron in it. thermal conductivity – rate at which a substance transfers heat electrical conductivity – the ability to allow charges ( electricity) to move through a material malleability – ability of a substance to be rolled or pounded into thin sheets ductility – ability of a substance to be pulled into a wire reactivity – ability of 2 or more substances to combine and form new substances flammability – ability of a substance to burn combustion – rapid combination fo fuel with oxygen and heat to produce heat, light and new substances oxidation – the ability to react with oxygen to form rust electrolysis – use of electricity to break a compound into elements or simpler compounds