Properties of Matter: Solids & Chemical Reactions
advertisement

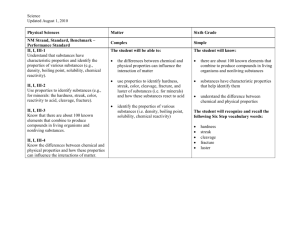
Chapter 12 - Properties of Matter 12.1 – Properties of Solids pp. 270-275 & 17.1 Chemical Reactions pp. 384-387 PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS • Different kinds of matter have different characteristics. • Characteristics that you can observe directly are called physical properties. • Substances can be identified by their physical properties. Physical Properties Can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the matter Include: • Color ∙odor ∙mass • Volume ∙density ∙solubility • Malleability ∙ductility • State of matter • Thermal conductivity malleability The ability to be pounded into thin sheets Example: Aluminum can be rolled or pounded into sheets to make foil ductility • The ability to be drawn into a thin wire • Example: copper can be drawn into a thin wire Density • Formula used to calculate density • D=m V Where D = density (measured in g/cm3) m = mass (measured in g) And V= volume (measured in cm3) DENSITY OF A SOLID • Depends on two things: –The mass of the object –How tightly packed together the atoms are. TWO TYPES OF SOLID • Crystalline solid particles are arranged in a repeating pattern of rows. Ex.: diamond, ice, iron, salts, minerals, metals • Amorphous solid Particles are not in any particular order Examples include: oobleck, rubber, wax, glass • Tensile strength A measure of how much stress from pulling a material can withstand before breaking. Brittle materials have low tensile strength. • Hardness measure's a solid’s resistance to scratching. Ex.: MOH’S scale of hardness. • Elasticity • This describes a solid's ability to be stretched and return to its original shape. • Brittleness- the tendency of a solid to crack or break before stretching very much. Glass is a brittle material. Physical Changes • A change that affects one or more physical properties of a substance • Physical changes can be undone • Examples: freezing water for ice cubes • Cutting your hair • Bending a paper clip Chemical Properties • describe a substance based on its ability to change into a NEW substance with DIFFERENT properties Include: 1. flammability (the ability to burn) 2. Reactivity to oxygen 3. Reactivity with water 4. Reactivity with acids Chemical Change • Example: baking a cake + + = • A chemical change occurs when one or more substances are changed into COMPLETELY DIFFERENT substances with DIFFERENT PROPERTIES Clues to Chemical Changes • • • • • Change in color Fizzing Foaming Heat Production of sound, light or odor Chemical Changes • Cannot be undone by ordinary physical means • Some chemical changes may be undone by other chemical means – Example: Water formed in the space shuttle’s rockets could be split back into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity