Polarization of Light
advertisement
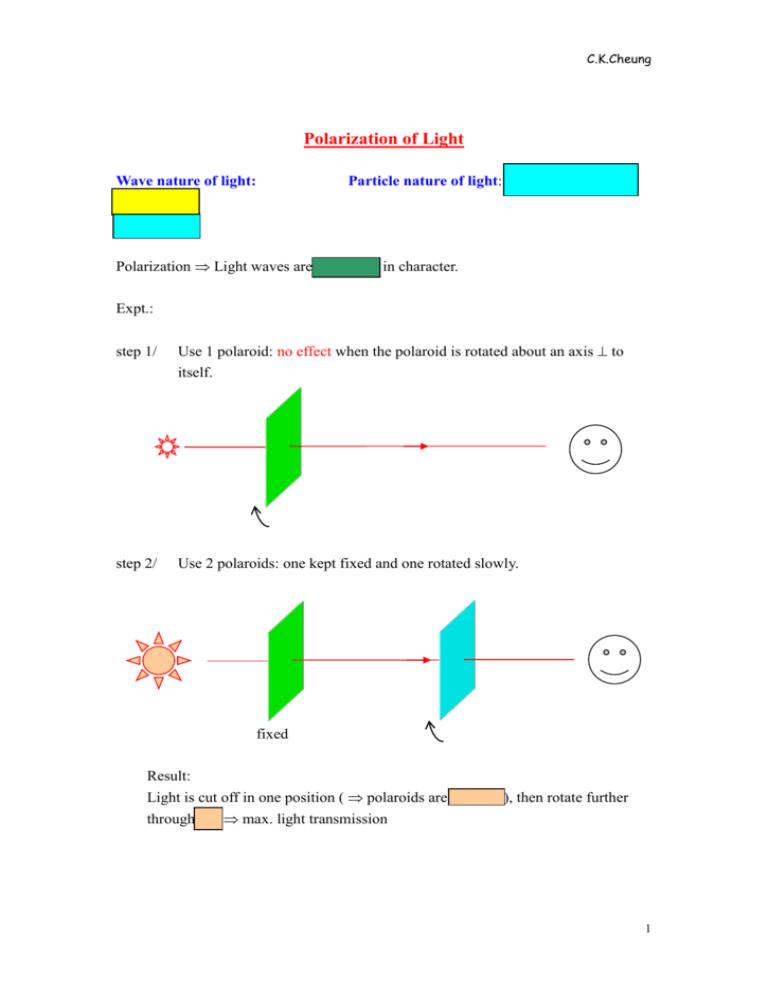
C.K.Cheung Polarization of Light Wave nature of light: Interference diffraction Particle nature of light: Photoelectric Effect Polarization Light waves are transverse in character. Expt.: step 1/ Use 1 polaroid: no effect when the polaroid is rotated about an axis to itself. step 2/ Use 2 polaroids: one kept fixed and one rotated slowly. fixed Result: Light is cut off in one position ( polaroids are crossed ), then rotate further through 900 max. light transmission 1 C.K.Cheung Explanation: unpolarized plane polarized If the right slit is further rotated 900: unpolarized plane polarized plane polarized Note: A longitudinal wave would emerge from both slots whatever their relative position. Hence, longitudinal wave cannot be polarized. E.M. wave: E . B 2 C.K.Cheung Experiment shows that the interaction of light with matter is more often through the E. if light is vertically polarized the plane containing E and the direction of travel, called plane of vibration, is vertical. In general: plane of polarization ~ 109 times s- 1 E resolve into 2 components: unpolarize Partially plane polarize 3 C.K.Cheung Producing polarized light: 1/ By Polaroid polarized light unpolarized incident light polaroid Polaroid transmits light vibration, i.e. E vibration, in one particular plane and absorb those in a mutually plane. 4 C.K.Cheung 2/ By reflection when unpolarized light falls on glass, water and some other materials, the reflected light is, in general, partially plane polarized. But at one particular angle, called the Brewster’s angle, the polarization is completed. plane polarized reflected light unpolarized incident light partially plane polarized refracted ray Formula: tan = n For water: = 530 For glass: = 570 5 C.K.Cheung 3/ By scattering polarized (blue) unpolarized (yellow + red) unpolarized polarized (blue) Equal amounts of polarized light are scattered in all sideways ( ) directions. Note: + max. intensity _ F=qE smaller intensity E=0 6 C.K.Cheung Using Polarized Light 1/ Polaroid disc, suitably oriented, are used in sunglasses and in photograph as ‘filters’ where they are placed in front of the camera lens, thereby enabling details to be seen that would otherwise be hidden by glare a/ no filter: b/ with filter: 7 C.K.Cheung Blue sky! EARTH Scattering Effect 1 4 blue sky Question: Why the sky is orange in colour at evening? 8 C.K.Cheung 2/ To measure the concentration of optically active liquids ( e.g. sugar solution ) by means of a polarimeter. solution concentration Measure the concentration in terms of the emergent intensity through the polaroid. 3/ Stress analysis: When certain substances (e.g. glass, perspex, polythene etc. ) under stress, they become doubly refracting. E (not obey Snell’s law) O (obey Snell’s law) Polaroid plastic sheet F polaroid F If viewed in white light ( unpolarized ) between 2 crossed polaroids, coloured fringes are seen round the regions of stress. The effect is called photoelasticity. 9 C.K.Cheung Classification of radio waves long wave f/Hz 30 k– 300 k /m 103-104 Communication: medium wave short wave 300 k –3 M 100 - 500 U.H.F. microwave 3 M – 30M 30M – 300M 300M – 3000M > 3000 M 10 - 100 too steep an angle gradual refraction n f < 30 M Hz V.H.F. 1-10 10 cm – 1 < 10 cm f > 30 M Hz Ionosphere (80km-500km) until completely attenuated transmitting aerial bounces back 10 C.K.Cheung f: 30 k Hz ~ 30 M Hz ( below V.H.F.) Long range communication ( ~ 106 m ) between countries. f > fc ( critical frequency ) = 30 M Hz ( above V.H.F. ) No refraction, emitted waves go skywards. Usually, fc depends on temp., pressure etc., fc varies with time of day, sessions etc.. communication depends on environment ( disadvantage ). Hence: 1/ for short range broadcasting, use: a/ V.H.F. ( : 1m – 10m) Local F.M. b/ U.H.F. ( : 10CM – 1m) TV ( carry picture and sound ) Range: ~ 105 m (if no obstacles) small, < 10 m little diffraction from buildings, antenna must points to station, especially for TV. 2/ For long range, use: microwave, which can penetrate through the ionosphere, they are used in radars and in communications between satellites and ground stations. Advantage of satellite communications: 1/ 2/ more dependable ( not affected by environment) they contain amplifiers to boost the microwave signal used. 11 C.K.Cheung Antenna 4 Oscillator 4 4 4 reflector 4 Directors Tuning circuit Note: 1/ Long waves usually show polarization because they are produced artificially by generating currents in certain direction. 2/ Short waves emitted by individual atoms have a random mixture of planes of polarization. 12 C.K.Cheung 13